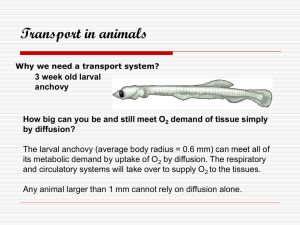
Lesson 6A - Circulatory Systems
advertisement

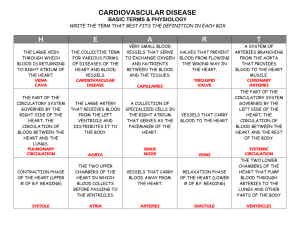
Veterinary Medical Applications Lesson Title: Circulatory System TEKS Addressed in Lesson: 130.6. (c)(6)(a) 130.6. (c)(13) all Lesson Objectives: Explain the anatomy and functions of the circulatory system List the parts of the circulatory system and discuss the function of each Compare and contrast open and closed circulatory systems Compare vertebrates’ circulatory systems by order of evolution Key Terms/Vocabulary Abdomen - The area of the body between the bottom of the ribs and the top of the thighs. Alveoli - Air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. Aorta - The largest artery in the body and the initial vessel to supply blood from the heart. Aortic valve - The valve that regulates blood flow from the heart into the aorta. Arrhythmia (or dysrhythmia) - An abnormal heartbeat. Arterioles - Small, muscular branches of arteries. When they contract, they raise resistance to blood flow, and blood pressure in the arteries increases. Artery - A vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood to the body. Arteritis - Inflammation of the arteries. Atrium (right and left) - The two upper or holding chambers of the heart (together referred to as atria). Atrium - Either one of the heart's two upper chambers. Blood clot - A jelly-like mass of blood tissue formed by clotting factors in the blood. Clots stop the flow of blood from an injury. Clots can also form inside an artery when the artery's walls are damaged by atherosclerotic buildup, possibly causing a heart attack or stroke. Blood pressure - The force or pressure exerted by the heart in pumping blood; the pressure of blood in the arteries. Bradycardia - Abnormally slow heartbeat. Capillaries - Microscopically small blood vessels between arteries and veins that distribute oxygen-rich blood to the body's tissues. Cardiac - Pertaining to the heart. Cardiac arrest - The stopping of the heartbeat, usually because of interference with the electrical signal (often associated with coronary heart disease). Cardiac cachexia - A term for the muscle and weight loss caused by severe heart disease. It is often Cardiology - The study of the heart and its function in health and disease. Cardiomegaly - An enlarged heart. It is usually a sign of another underlying problem, such as high blood pressure, heart valve problems, or cardiomyopathy. Cardiovascular (CV) - Pertaining to the heart and blood vessels that make up the circulatory system. Congenital - Refers to conditions existing at birth Dyspnea - Shortness of breath. Heart attack - Death of, or damage to, part of the heart muscle caused by a lack of oxygen-rich blood to the heart. Heart murmur -An abnormal heart sound caused by turbulent blood flow. The sound may indicate that blood is flowing through a damaged or overworked heart valve, that there may be a hole in one of the heart's walls, or that there is a narrowing in one of the heart's vessels. Heredity - The genetic transmission of a particular quality or trait from parent to child. Inferior vena cava - The large vein returning blood from the legs and abdomen to the heart. Jugular veins - The veins that carry blood back from the head to the heart.. Lipid - A fatty substance that is insoluble (cannot be dissolved) in the blood. Mitral valve - The structure that controls blood flow between the heart's left atrium (upper chamber) and left ventricle (lower chamber). Murmur - Noises superimposed on normal heart sounds. They are caused by congenital defects or damaged heart valves that do not close properly and allow blood to leak back into the chamber from which it has come. Palpitation - An uncomfortable feeling within the chest caused by an irregular heartbeat. Pericardium - The outer fibrous sac that surrounds the heart. Plaque - A deposit of fatty (and other) substances in the inner lining of the artery wall; it is characteristic of atherosclerosis. Platelets - One of the three types of cells found in blood; they aid in the clotting of the blood. Pulmonary - Referring to the lungs and respiratory system. Pulmonary vein - The blood vessel that carries newly oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left atrium of the heart. Septum - The muscular wall dividing a chamber on the left side of the heart from the chamber on the right. Shock - A condition in which body function is impaired because the volume of fluid circulating through the body is insufficient to maintain normal metabolism. This may be caused by blood loss or by a disturbance in the function of the circulatory system. Shunt - A connector that allows blood to flow between two locations. Sinus (SA) node - The "natural" pacemaker of the heart. The node is a group of specialized cells in the top of the right atrium which produces the electrical impulses that travel down to eventually reach the ventricular muscle, causing the heart to contract. Sternum - The breastbone. Superior vena cava - The large vein that returns blood from the head and arms to the heart. Tachycardia - Accelerated beating of the heart. Paroxysmal tachycardia is a particular form of rapid heart action, occurring in seizures that may last from a few seconds to several days. Tachypnea - Rapid breathing. Tricuspid valve - The structure that controls blood flow from the heart's upper right chamber (the right atrium) into the lower right chamber (the right ventricle). Vein - Any one of a series of blood vessels of the vascular system that carries blood from various parts of the body back to the heart, returning oxygen-poor blood to the heart. Ventricle (right and left) - One of the two lower chambers of the heart. Interest Approach/Anticipatory Set Introduce the sound ‘lubba dubba’ (the sound the heart makes) for large animals the ‘lubba dubba’ sound is low and slow because the blood takes a while to circulate. For small animals, it’s a high pitched, quick sound because it doesn’t take as long for the blood to circulate. Teaching Plan and Strategy Presentation of New Material Teacher Presentation: - Animation of blood flow Pulmonary and systemic circulation loops and what happens during both The structures of circulatory system and their functions The flow of blood through both pulmonary and systemic cycles Draw figures of vertebrates’ circulatory system Discuss conditions/diseases of the circulatory system and have students find causation and treatment for all. Activity/Application/Student Engagement/Laboratory Independent Activity: (30 min) Make a poster about open and closed circulatory system and evolution of vertebrates’ circulatory systems Group Activity: (10 min) Have students work in groups of 2-3 to create a mnemonic device to assist in the memorization of the order of blood flow Lab Activity: (50 min) Dissection of lamb heart-provide students with a lab sheet to include the internal and external structures and steps for dissection. Worksheet: (20 min) http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/health_fitness/gln_health_fitness_zone/pdf/heart_rate _monitor_activities/the_heart/the_heart_activity_3.pdf Evaluation/Summary Teacher led discussion. Student written evaluation Student Lab activities Circulatory Quiz 1. The thin wall that divides the left and right sides of the heart is called the____________________. 2. __________________ are responsible for preventing backflow. 3. Un-oxygenated blood appears __________________ in color, while oxygenated blood appears ______________________. 4. The superior vena cava delivers blood to the _____________________________ and the inferior vena cava delivers blood to the _________________________. 5. The largest artery in the body is the ______________________. 6. The two circulation circuits are the ______________________ and the ________________________. 7. How do the functions of the above circuits differ? 8. Smallest blood vessels are the ___________________________. 9. List 4 of the 7 functions of the circulatory system. 10. The heart is located in the ______________________ cavity. 11. The _________________ sac supports the heart and provides lubrication. 12. The bicuspid valve is also called the ________________ valve. 13. The group of cells called the ______________ ___________________ control the beat of the heart by sending out electrical signals. 14. Blood is divided into two parts the cellular portion and the liquid portion known as _____________________________. 15. Label the following heart: 16. Explain the difference between an open and closed circulatory system, give one example of an animal with open and one animal with a closed circulatory system. Match the following to the appropriate term: 17. vessels that carry blood away from the heart 18. vessels that carry blood toward the heart 19. tiny blood vessels with walls that are only one cell thick 20. thick wall that divides the heart into two sides 21. upper chambers of the heart that receive blood 22. lower chambers of the heart that pump blood out of the heart 23. valve between right atrium and right ventricle 24. valve between the left atrium and left ventricle 25. valves found between the ventricles and blood vessels 26. membrane around the heart 27. tiny blood vessels that transport blood between veins and arteries a. semilunar b. tricuspid c. capillaries d. veins e. septum f. pericardium g. arteries h. capillaries i. mitral j. atria k. ventricle References/Additional Materials/Extended Learning Opportunities/Enrichment http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/health_fitness/gln_health_fitness_zone/pdf/heart_rate _monitor_activities/the_heart/the_heart_activity_3.pdf Merk Veterinary Manual Introduction to Veterinary Medicine, Thompson College and Career Readiness Standards: Science VI. A-VI. G