Present Participle
advertisement
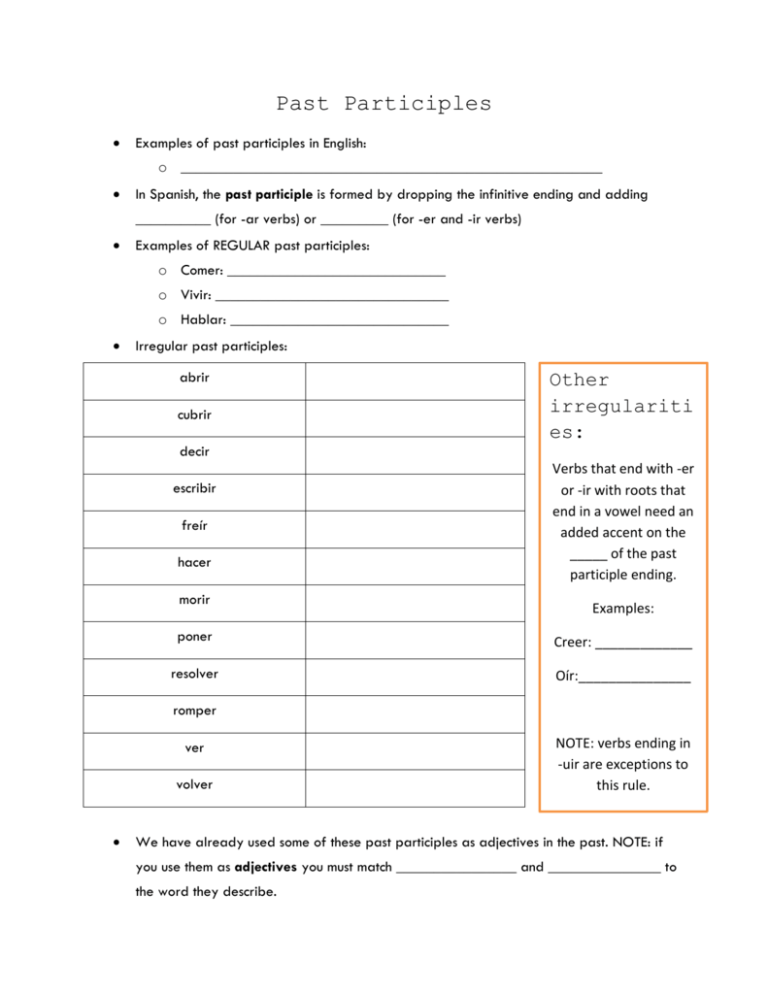
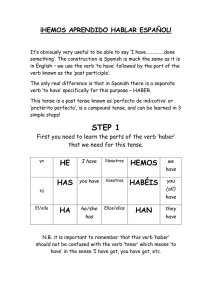
Past Participles Examples of past participles in English: o ________________________________________________________ In Spanish, the past participle is formed by dropping the infinitive ending and adding __________ (for -ar verbs) or _________ (for -er and -ir verbs) Examples of REGULAR past participles: o Comer: _____________________________ o Vivir: _______________________________ o Hablar: _____________________________ Irregular past participles: abrir cubrir Other irregulariti es: decir escribir freír hacer morir Verbs that end with -er or -ir with roots that end in a vowel need an added accent on the _____ of the past participle ending. Examples: poner Creer: _____________ resolver Oír:_______________ romper ver volver NOTE: verbs ending in -uir are exceptions to this rule. We have already used some of these past participles as adjectives in the past. NOTE: if you use them as adjectives you must match ________________ and _______________ to the word they describe. The perfect tenses: The perfect tenses are formed by using the verb “has” or “have” with the past participle. The verb used for “has” or “have” in this tense is the verb ____________ English Examples: I have eaten. They have studied. We had jumped. They will have written Present perfect: [Present tense conjugation of haber] + [past participle] NOTE: Since you are using the past participle as part of the verb rather than as an adjective you don’t need to match _____________________ -- the past participle doesn’t change. Haber (present tense) Examples: o I have studied. Yo he estudiado._____________________________________ o They have eaten. Ellos han comido.___________________________________ o We have paid. __________________________________________________ o You (s. inf.) have lived. ____________________________________________ o You all haven’t eaten. _____________________________________________ NOTE: When working with a direct object, indirect object, or reflexive pronoun used with the verb the pronoun goes ______________________ the first verb (haber, the auxiliary verb). Examples: o I have brushed my teeth. ___________________________________________ o He has bathed. __________________________________________________ o We have left. ____________________________________________________