Atmosphere Part 2 Notes Understanding Air Pressure Air Pressure
advertisement
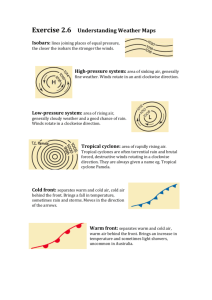
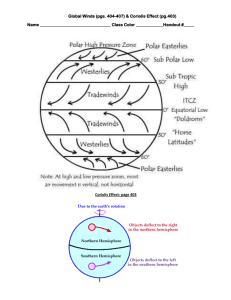
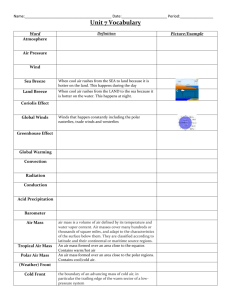
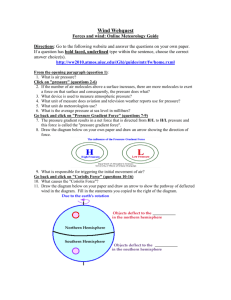
Atmosphere Part 2 Notes A. Understanding Air Pressure a. Air Pressure - is _______ in all directions: down, up , sideways i. Sea level pressure = 1 kilogram per square inch b. Measuring Air Pressure i. ___________ - used to tell the air pressure around you (in millibars) ii. Increases in ___________ = mercury rises iii. Decreases in __________ = mercury lowers c. Wind i. A result of __________ difference in air _________ ii. Flows from ______ to _______ pressure iii. Solar radiation = ultimate source for ______ d. Control Wind i. Three factors 1. _________________ 2. Coriolis Effect 3. Friction e. Pressure Differences i. Pressure ___________ - read from the isobars ii. __________ isobars = _______ winds iii. __________ isobars = _______ winds f. Coriolis Effect i. A _________ angle to the direction of air flow ii. Effects _________ and wind speed iii. Strong wind = strong ________ iv. Strong at _________, weak at the ________ g. Friction i. Slows down air movement which changes direction ii. Above layer = _________ to isobars (_________ friction) iii. Jet Streams - fast moving “______” of air B. Pressure Centers and Winds a. High Pressure vs. Low Pressure i. Anticyclones 1. _________ increases from _____ to ______ 2. Winds blow __________ and ________ 3. Net flow = __________ ii. Cyclones 1. ___________ decrease from ______ to ______ 2. Winds blow ________ and ________ 3. Net flow = _________ b. Weather and Air Pressure i. Rising Air = ________ formation and ________ ii. Sinking Air = _________ skies iii. Have to have _________ and __________ c. Weather Forecasting i. Low pressure system = ______________ d. Global Winds i. Atmosphere = air conditioner ii. Warm air goes _________ high latitudes iii. Cool air goes ________ the equator e. Non - Rotating Earth Model i. Where hot air goes to the _______ when it reaches the troposphere f. Rotating Earth Model i. 4 pockets 1. Trade Winds, Westerlies, Polar Easterlies, Polar Front g. Influence of Continents i. Southern Hemisphere - __________ pressure system ii. __________ + _________ = ___________ pressure system h. Monsoons i. Seasonal changes in the ______________ ______________ ii. Lots of rain!!! C. Regional Wind Systems a. General Info i. _____________ in the middle latitudes in _________ and does not fit the _______ system described for the tropics b. Local Winds i. Caused by either __________ effects or by ____________ in surface composition 1. Land and Water c. Valley and Mountain Breezes i. Valley Breeze - heat during the day = ________ air rises ii. Mountain Breeze - cools at night = air moving into the _______ d. Measuring Wind i. Two basic measurements 1. ____________ and __________ ii. Labeled by the ________ they flow 1. Ex. North wind - _____________ towards the _______ 2. Measured by a ______________ iii. Wind direction - __________ wind = blows from the same direction ________ 1. Ex. Westerlies (US) iv. Wind Speed - measured by an _________ e. El Nino i. Warm _________ that becomes usually strong and ______ cold offshore water with warm water - Every ____ years f. La Nina i. When _________ temperatures in the eastern Pacific are colder than ________ 1. Distinctive set of _________ patterns