iCell in app text
advertisement

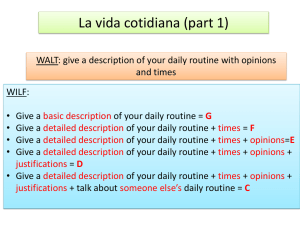
iCell in app text Cell Membrane The cell (or plasma) membrane monitors and selectively controls entry into and out of the cell. The cytoplasm is the fluid that fills the bacteria. Membrana Celular La membrana celular (o plasmática) monitorea substancias y controla selectivamente sus entradas y salidas en la célula. El citoplasma es el fluido que llena a las bacterias. Nucleoid The nucleoid is the region of the bacteria that contains the DNA. Nucleoide El nucleoide es la región de la bacteria que contiene el ADN. Ribosome Ribosomes are the protein-making machinery of the cell. Ribosoma Los ribosomas son las maquinas que construyen proteínas en la célula. Flagellum Flagella are whip-like tails that help bacteria move. Flagelo Los flagelos son colas en forma de látigo que ayudan a las bacterias a moverse. Plasmid Plasmids are a small extra piece of circular DNA that may be found inside some Bacteria. Plásmido Los plásmidos son pequeñas piezas circulares de ADN que se encuentran dentro de las bacterias. Cell Membrane The cell (or plasma) membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell. It is made of a large network of lipids and proteins that regulates the transport of materials into and out of the cell, allows the cell to be recognized, and has sites for cellular communications. The cytoplasm, also called cytosol, is the fluid that fills the bacteria. The various parts of the bacteria are suspended in the cytoplasm. Membrana Celular La membrana celular (o plasmática) es una barrera permeable pero selectiva que rodea a la célula. Esta hecha de una gran red de lípidos y proteínas los cuales regulan el transporte de sustancias tanto hacia fuera como hacia adentro de las células, permitiendo a la célula ser reconocida y tener sitios para la comunicación celular. Nucleoid The nucleoid is the region of the bacteria that contains the DNA. Unlike the nucleus of plant and animal cells, the nucleoid is not enclosed by a membrane. Nucleoide El nucleoide es la región de la bacteria que contiene el ADN. A diferencia del núcleo de las células de plantas y animales, el nucléolo no esta rodeado por una membrana. Ribosome Ribosomes are the protein making machinery of the cell. In bacteria, all ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm. Ribosoma Los ribosomas son las maquinas que construyen proteínas en la célula. En bacterias, todos los ribosomas flotan libremente en el citoplasma celular. Flagellum Flagella are whip-like tails that allow bacteria to move quickly through liquid surroundings. Flagelo Los flagelos son colas en forma de látigo que ayudan a las bacterias a moverse rápidamente atreves del liquido que las rodea. Plasmid Plasmids are small circular pieces of DNA that may be found inside some bacteria. The plasmid is separate from the bacterial chromosome, which contains the majority of the bacteria's DNA. They confer different functions on the bacteria, including the ability to cause disease or gain resistance against antibiotics. Plásmido Los plásmidos son pequeñas piezas circulares de ADN que se encuentran dentro de las bacterias. Los plásmidos están separados del cromosoma bacteriano, el cual contiene la mayoría del ADN de las bacterias. Ellos confieren diferentes funciones a las bacterias, incluyendo la habilidad de causar enfermedades o resistir antibióticos. Cell membrane The cell membrane is a semi-permeable double phospholipid bilayer, which contains proteins and lipids that aid the cell in transportation, attachment, recognition, fluidity, and reception. This double layer is made up of phospholipids, each of which contains two fatty acid hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails that are attached to a glycerol hydrophilic (waterloving) head. The cytoplasm, also called cytosol, is the fluid inside the bacteria. Enzymes dissolved in the cytoplasm carry out reactions to convert one molecule to another. Membrana Celular La membrana celular es una doble bicapa de fosfolípidos semipermeable, la cual contiene proteínas y lípidos que ayudan en el transporte, unión, reconocimiento, fluidez y recepción. Esta bicapa esta hecha de fosfolípidos los cuales están constituidos por dos colas hidrofobicas (no se mezclan con agua) hechas de ácidos grasos que están unidas a una cabeza hidrofilica (se mezcla con agua) hecha de glicerol. El citoplasma, también llamado citosol, es el fluido localizado dentro de las bacterias. Enzimas disueltas en el citoplasma llevan acabo las reacciones que convierten una molécula en otra. Nucleoid The nucleoid is a space in the bacteria that contains the cell's genetic material. Unlike the nucleus of plant and animal cells, the nucleoid is not surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer. In addition, the genome of most bacteria are circular double stranded pieces of DNA that are smaller than the genomes of plant and animal cells and are not tightly wound around proteins to reduce the overall size. Nucleoide El nucleoide es un espacio en la bacteria el cual contiene el material genético de la célula. A diferencia del núcleo de las células de plantas y animales, el nucleoide no esta rodeado por una bicapa de fosfolípidos. Además, los genomas de la gran mayoría de bacterias son piezas circulares de ADN de doble cadena más pequeñas que los genomas de las células de plantas y animales y los cuales no están enredados con proteínas para reducir su tamaño. Ribosome Ribosomes direct the production of polypeptides, using the instructions contained in the RNA transcript. Bacteria contain free floating ribosomes that are composed of both small and large subunits composed of ribosomal RNA fragments and several proteins. Ribosoma Los Ribosomas dirigen la producción de polipéptidos usando las instrucciones contenidas en el ARN mensajero. Flagella Flagella are one of the ways bacteria are able to move through a liquid environment. They are long whip-like filaments that are connected to hook-like structures at the surface of the bacterial cell membrane. The motor, powered by a flow of hydrogen ions across the cell membrane, is located on the inner cell membrane. Flagella allow bacteria to move as quickly as 60 cell lengths per second. Flagelo Los flagelos son uno de los mecanismos que las células usan para moverse através de un ambiente líquido. Ellos son largos filamentos en forma de látigo que están conectados a la superficie de la membrana celular de la bacteria por medio de unas estructuras en forma d gancho. El motor, cuya energía se produce por medio del transporte de iones de hidrogeno através de la membrana, esta localizado en la parte interna de la membrana celular. Los flagelos permiten a la bacteria moverse tan rápido como 60 longitudes celulares por segundo. Plasmid Plasmids are small extra chromosomal circular DNA molecules that may be found inside some bacteria. Plasmids are capable of replicating within the bacteria. Some types of plasmids can be transferred to other bacteria. Plasmids may confer different functions on the bacteria, including the ability to turn the bacteria into a pathogen (that causes disease) or may lead to antibiotic resistance. Plasmids may also be used as biotechnology tools to introduce foreign genes into the bacteria. This process of genetic engineering could produce, for example, large quantities of protein from the inserted gene. Plásmido Los plásmidos son pequeñas piezas circulares de ADN que pueden ser encontradas dentro de las bacterias. Los plásmidos son capaces de replicarse dentro de la bacteria. Algunos tipos de plásmidos pueden transferirse de una bacteria a otra. Plásmidos pueden conferir diferentes funciones en la bacteria, incluyendo la habilidad de transformar bacteria nopatógenas en patógenas (que causan enfermedades) o de generar resistencia a antibióticos. Plásmidos pueden usarse como herramientas biotecnológicas para introducir genes de otras fuentes celulares en las bacterias. Este proceso de ingeniería genética pude producir, por ejemplo, grandes cantidades de proteínas generadas por el gene incorporado en el plásmido. Cell Membrane The cell (or plasma) membrane monitors and selectively controls entry into and out of the cell. The cytoplasm is the fluid that fills the cell. Membrana Celular La membrana celular (o plasmática) regula el transporte de sustancias tanto hacia fuera como hacia adentro de las células. El citoplasma es el fluido que llena las células. Cell Wall The cell wall is a thick, rigid layer that surrounds the plant cell. Pared Celular La pared celular es una gruesa y rígida capa que rodea las células de las plantas. Vacuole The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled space inside the plant cell. Vacuola Las Vacuolas son grandes espacios llenos de fluido que se encuentran dentro de las células de plantas. Golgi Body The Golgi body or Golgi apparatus aids in the modification, packaging, and distribution of proteins that are made in the cell. Cuerpos de Golgi Los cuerpos de Golgi, o aparato de Golgi, ayuda en la modificación, empaquetamiento, y distribución de proteínas que son hechas en las células. Mitochondrion The mitochondrion is known as the power house of the cell and produces energy to fuel the cell's activities. Mitocondrias Las mitocondrias son conocidas como la central de poder de las células y producen energía que alimenta las actividades celulares. Endoplasmic Reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum aids in the transport of proteins made by ribosomes (the small structures on the surface). Retículo endoplásmico El retículo endoplásmico ayuda en el transporte de proteínas hechas por los ribosomas (las pequeñas estructuras en la superficie). Ribosome Ribosomes are the protein making machinery of the cell. Ribosomas Los ribosomas son la maquinaria de las células que hacen las proteínas. Nucleus The nucleus holds the genetic information (DNA) for the cell. Núcleo El núcleo contiene la información genética (ADN) para la célula. Chloroplast The chloroplast is the food producer for the plant cell. It converts the energy of the sun into sugar. Cloroplasto El cloroplasto es el productor de comida para la célula de plantas. Convierte la energía de el sol en azucares. Nucleolus The nucleolus is part of the nucleus that makes the parts needed to build a ribosome. Nucléolo El nucléolo es parte de el núcleo que hace las partes necesarias para construir ribosomas. Cell Membrane The cell (or plasma) membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell. It is made of a large network of lipids and proteins that regulates the transport of materials into and out of the cell, allows the cell to be recognized, and has sites for cellular communications. The cytoplasm, also called cytosol, is the fluid that fills the cell. The various organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm. Membrana Celular La membrana celular (o plasmática) es una barrera permeable pero selectiva que rodea a la célula. Esta hecha de una gran red de lípidos y proteínas los cuales regulan el transporte de sustancias tanto hacia fuera como hacia adentro de las células, permitiendo a la célula ser reconocida y tener sitios para la comunicación celular. El citoplasma, también llamado citosol, es el fluido que llena las células. Los diferentes organelos celulares están suspendidos en el citoplasma. Cell Wall The cell wall is a thick, rigid membrane made of a complex molecule called cellulose. The wall surrounds the plant cell and provides support and structure. Pared Celular La pared celular es una gruesa y rígida capa hecha de una compleja molécula llamada celulosa. La pared rodea las células de las plantas y proporciona soporte y estructura. Vacuole The vacuole is a large fluid-filled space within the cell that takes up much of the plant cell's volume. The vacuole helps the cell maintain its shape and may also be used to store nutrients, waste products or even the pigments that provide flower color. Vacuola Las vacuolas son grandes espacios llenos de fluido en las células las cuales usan gran parte del volumen celular de las plantas. Golgi Body The Golgi body or Golgi apparatus is a stack of membrane-bound disks. It aids in the modification, packaging, and secretion of proteins made in the cell. The golgi body acts as a sophisticated check for protein products before they are shipped to their final destinations. Cuerpos de Golgi Los cuerpos de Golgi, o aparato de Golgi, es una pila de discos unidos por membrana. Ayuda en la modificación, empaquetamiento, y secreción de proteínas que son hechas en las células. Los cuerpos de Golgi actúan como un sofisticado punto de revisión para productos proteicos antes de que estos sean enviados a sus destinos finales. Mitochondrion The mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound organelle that is primarily responsible for metabolizing sugar molecules to provide usable ATP, which is the main energy source for the majority of cellular functions. Mitocondrias Las mitocondrias son organelos de doble membrana que son primariamente responsables de metabolizar azucares para producir ATP usable, el cual es la mayor fuente de energía para la mayoría de las funciones celulares. Endoplasmic Reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum is a large membranous organelle that serves a variety of functions. Most importantly, it is a site for ribosomes (the small structures on the surface) to bind and translate RNA into proteins and aids in the transport of those proteins onto final processing and distribution. Retículo endoplásmico El retículo endoplásmico ayuda en el transporte de proteínas hechas por los ribosomas (las pequeñas estructuras en la superficie). Ribosome Ribosomes are the protein making machinery of the cell. In plant and animal cells, ribosomes are found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the outer surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. Nucleus The nucleus is a double membrane-bound organelle that acts as the central storage area for genomic DNA. The DNA shown inside the nucleus has been tightly would around proteins to condense its overall size. Chloroplast The chloroplast is an organelle that contains chlorophyll, a green-colored molecule that uses energy from sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide into sugar and oxygen. This process is called photosynthesis. Nucleolus The nucleolus is a dense bundle of DNA and RNA within the nucleus that is responsible for building the various protein and RNA components of ribosomes. The assembled ribosomes move out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm or to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Membrane The cell membrane is a semi-permeable double phospholipid bilayer, which contains proteins and lipids that aid the cell in transportation, attachment, recognition, fluidity, and reception. This double layer is made up of phospholipids, each of which contains two fatty acid hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails that are attached to a glycerol hydrophilic (waterloving) head. The cytoplasm, also called cytosol, is the fluid inside a cell. Cell organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm. Enzymes dissolved in the cytoplasm carry out reactions to convert one molecule to another. Cell Wall The cell wall is a rigid structure that helps the plant cell maintain its shape. Cell walls provide mechanical strength to the plant, allowing it to grow tall without collapsing. The main ingredient of the cell wall is a polysaccharide (complex sugar) called cellulose. The cellulose assembles into chains known as microfibrils that give the cell wall its strength. A variety of proteins and lipids (such as wax) are also present. Vacuole The vacuole is a membrane-bound sac that takes up most of the space inside the cell. Vacuoles provide structural support and carry out a number of functions including storage of salts, minerals, waste or nutrients. Under optimal conditions, the vacuole is filled with water and exerts significant pressure against the cell wall. This helps maintain the structural integrity of the plant. In flowers, vacuoles may store the pigments that provide color to the petals. Golgi Body Each Golgi body or Golgi apparatus is composed of a stack of membrane bound discs that modify, sort and package various large molecules produced within the cell. Macromolecules synthesized by the endoplasmic reticulum arrive enclosed in membrane vesicles. These fuse with the Golgi and move through the membrane stack for modification and packaging. At the end of the Golgi, new vesicles bud off to transport the macromolecules around the cell. Mitochondrion The mitochondrion is a double membrane organelle where cellular respiration takes place. Molecules such as glucose and oxygen are modified into useable energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Unlike other organelles, the mitochondrion contains its own circular DNA and replicates independently from the rest of the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membranous structure that serves as the primary site of protein translation for eukaryotes. The ER connects to the nuclear membrane and contains smooth and rough sections. The rough ER is usually in the shape of flattened sacs and is studded with ribosomes; it manufactures and packages secreted proteins, many lysosomal enzymes and membrane-embedded proteins. The smooth ER is typically a network of tubules; where lipid (phospholipids and steroids) synthesis and carbohydrate metabolism takes place. Ribosome Ribosomes direct the production of polypeptides, using the genetic code contained in RNA. In plant and animal cells, ribosomes are found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the outer surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Free ribosomes synthesize proteins for immediate use in the cytoplasm. Polypeptides assembled at the rough endoplasmic reticulum are either inserted directly into cell membranes or transported to the Golgi Body or elsewhere in the cell. Nucleus The nucleus is where the DNA is stored and replicated and where mRNA is transcribed. It is surrounded by the nuclear envelope, which is a double membrane structure with pores that control intake and export. The DNA in the nucleus shown here is tightly coiled around a number of proteins known as histones to reduce its overall length. The nucleus also contains the nucleolus, where the ribosomes are assembled before being exported to the cytoplasm. Chloroplast The chloroplast is the double membrane organelle where photosynthesis occurs. Within the inner space are stacks of thylakoids, sub-organelles that contain light absorbing pigments such as chlorophyll and carotenoids. These pigments use sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugar and oxygen. The radiant energy from the sun is transferred to the bond energy that holds together the atoms of the glucose molecule. The chloroplast also contains one or more strands of circular DNA and a small number of ribosomes. While the chloroplast is capable of translating and transcribing a small number of proteins, most chloroplast proteins are encoded by genes found in the nuclear DNA. Nucleolus The nucleolus is a densely packed area of the nucleus containing both DNA and RNA. This region is responsible for making both the RNA and protein subunits of a ribosome. After assembly, the ribosomes leave the nucleus and move to either the cytoplasm or to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Because the DNA that codes for these ribosomal components is spread across the genome, the nucleolus is assembled from multiple chromosomes interacting together. Centriole Centrioles are only found in animal cells. They help chromosomes move during cell division. Lysosome Lysosomes act as the digestive system inside a cell, breaking down unneeded substances in the cell. Peroxisome Peroxisomes are small structures surrounded by a membrane that contain enzymes used by the cell to produce energy. Lysosome Lysosomes act as the digestive system inside a cell. They help break down old or unneeded parts of the cell, and substances that have been brought into the cell from the outside. Peroxisome Peroxisomes are small structures surrounded by a membrane. They contain many different types of enzymes used by the cell to produce energy. Centriole Centrioles are protein structures found only in animal cells. The help form spindle fibers, which guide chromosome movement during mitosis and meiosis. Lysosome Lysosomes are specialized membrane-bound organelles containing enzymes that can break down all four types of macromolecules: proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids. Peroxisome Peroxisomes contain at least 50 different enzymes involved in the breakdown of harmful chemicals in the cell, such as hydrogen peroxide. In addition, peroxisomes work with the mitochondria to produce energy. In seeds, this energy specifically helps the seed to sprout (germinate). Centriole Centrioles are found only in animal cells and are made of bundles of thin tubes called microtubules. There are two centrioles in each cell. During mitosis and meiosis, centrioles segregate to opposite sides of the cell and form spindle fibers - long microtubule strands that guide chromosome movement. Lysosome Lysosomes contain about 50 different acid hydrolases, enzymes that break down all four types of macromolecules: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. The enzymes function at very acidic pH (about 5). This pH is specifically maintained in the lysozyme - if the enzymes were accidentally released into the cytoplasm (pH approximately 7.2), they would become inactive, protecting the cell from widespread breakdown. Peroxisome Peroxisomes are a small membrane-bound organelle containing over 50 different enzymes, some of which break down substrates such as amino acids and fatty acids through oxidative reactions. In animal cells, peroxisomes are also involved in generating lipids. In plants, peroxisomes have additional functions such as converting fatty acids to carbohydrates (used during seed germination) and photorespiration in leaves.