Health and fitness - Curriculum Support
advertisement

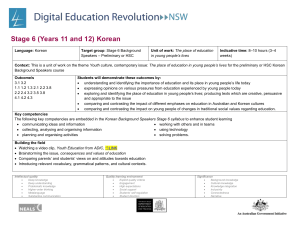
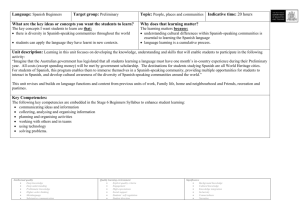
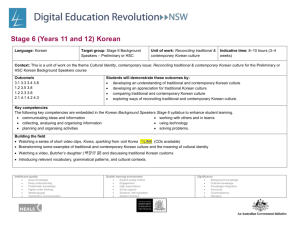
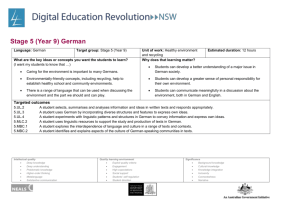
Stage 5 (Year 10) Korean Language: Korean Target group: Stage 5 (Year 10) What are the key ideas or concepts you want the students to learn? The key concepts I want students to learn are that: physical activity and a healthy diet are vital components of healthy lifestyles. There is a range of language structures and associated behaviours that can be used when communicating in Korean about health and fitness. different cultures have different perceptions about health and body image. Topic: Health and fitness Indicative time: 5 weeks (10 hours) Why does that learning matter? The learning matters because: students will develop the language required to participate in meaningful discussions about health and fitness in Korean being able to compare and contrast health and fitness between Australia and Korea will enable students to gain an understanding of different cultural perceptions. Unit description: In this unit, students learn to describe healthy activities, lifestyles and how they maintain their state of health. At the end of this unit, students will be able to: talk about the sports they play and those they don’t as well as their favourite sports discuss their state of health and their body parts discuss healthy activities and design a healthy eating plan talk about and discuss their illnesses with doctors. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Building the field: Brainstorm stimulus questions such as, ‘How do we stay healthy?’ Suggested responses: healthy food, exercise, regular medical check, dressing appropriately to suit the weather, having enough sleep. Korean traditional sports for staying healthy Use flashcards to introduce the parts of the body in Korean. Class discussion about what we do in Australia to keep fit and healthy. Ranking exercise to rank strategies for a healthy lifestyle elicited in the class brainstorm in order of importance Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Outcomes: Students learn about: Students learn to: 5.UL.1 A student selects, summarises and analyses information and ideas in spoken texts and responds appropriately ways in which texts are formatted for particular purposes and effects explore the way text content is developed and how ideas and information are sequenced, e.g. heading, paragraphing, introductory sentences, topic shifts the manipulation of structure, format and choice of vocabulary to achieve specific purposes 5.UL.4 A student experiments with linguistic patterns and structures in Korean to convey information and to express own ideas select and manipulate particular structures to achieve specific communication goals, e.g. omit particles when speaking, use appropriate tense for recounting, emotive languages for effect, 별로, 참, 아주, 정말, 그 얘기(는) 정말 재미 있었어요. the use of technology to express ideas and create own text access websites to transfer and manipulate data to produce a specific text, e.g. multimedia presentation 5.MBC.1 A student explores the interdependence of language and culture in a range of texts and contexts ways to analyse and explain features of language in use, and their relationship to the system analyse aspects of language in order to identify and explain structures and patterns in text the value of developing respect for and appreciation of other cultures discuss and compare the values and beliefs of diverse cultures analyse the use of words or expressions with particular cultural significance in Korean texts, e.g. 소 잃고 외양간 고치기, 누워서 떡 먹기, 천리 길도 한 걸음부터 5.UL.2 A student selects, summarises and analyses information and ideas in written texts and responds appropriately 5.UL.3 A student uses Korean by incorporating diverse structures and features to express own ideas 5.MBC.2 A student identifies and explains aspects of the culture of Korean-speaking communities in texts 5.MLC.1 A student demonstrates understanding of the nature of languages as systems by describing and comparing linguistic features across languages idioms, colloquialisms, register and formality in language use 5.MLC.2 A student uses linguistic resources to support the study and production of texts in Korean Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Suggested teaching, learning and assessment activities: Note: teaching and learning activities marked with an asterisk (*) could be used as formal assessment tasks. Structures in italic script could be used for advanced level. LR: Listening and Responding, RR: Reading and Responding, W: Writing, S: Speaking Evidence of learning and ongoing feedback for students throughout unit of work Class discussion and teacher feedback on student contributions Student use of appropriate vocabulary and structures 1. Discussing the importance of sports and healthy lifestyles. Student ability to sequence ideas 2. Expressing likes and dislikes about different sports. Student use of culturally appropriate behaviour 3. Describing healthy activities. 4. Designing a healthy diet plan for someone who suffers from obesity or diabetes, etc. Teacher observation of level of participation in class discussion and oral feedback 5. Presenting information about one’s favourite sport in Korean to the class (others may take notes as a listening exercise). 6. 7. Ongoing feedback through: teacher observation oral/written feedback construct a conversation between a doctor and a patient (RR/S) * student self-evaluation Listening exercise: dialogue enquiring about and expressing one’s health peer evaluation. Parts of the body: students read and label a picture of the human body and then 어디가 아파요? (편찮으세요?) 몸이 아파요? 머리가 아파요? dialogue related to healthy food/diet 야채, 과일, 생선, 고기 8. Students answer comprehension questions: Reading texts on meals, benefits of healthy food (RR)* Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Listening activities: teacher observation and oral feedback on purpose and content. Speaking activities: teacher provides oral feedback on correct pronunciation Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative 9. Reading/Writing: students read and fill in a medical questionnaire (RR/W) * and vocabulary and ability to maintain an interaction. 10. Discussion: students read an advertisement on smoking, discuss its content and analyse the structure and language used. (RR/S) Discussion activities: teacher observation and oral feedback on how well students participate and recognise and use the vocabulary. 11. Research: students research a particular disease or illness and present their findings in Korean to the class Reading activities: teacher gives oral/written feedback on identifying general or specific information, purpose and content. 12. Speaking: students pair up and ask questions about what they have for each meal and write down their answers. An extended activity would be a piece of descriptive narrative writing based on their interview activity (RR/S/W) Written activities: teacher observation and written feedback on purpose and content; peer evaluation. 13. Discussion: topic would be ‘Fast food, excessive dieting, 패스트 푸드, 무리한 식이요법, 보양식, 거식증 – Treasure hunt at computer lab (RR/S/W) ICT activities: use of Korean language websites to consolidate and reinforce new structures and to provide additional listening and speaking activities that allow for independent student progression. 14. Survey: Students move around the room, asking five students whether they exercise or not and what their favourite sport and how many times each week they play it. Then students report the result of survey to the class. (LR/S) 15. Role play: students construct a dialogue between a patient and a doctor; consulting a doctor and discussing the illness, asking for medicine and treatment, giving advice and expressing hope. (S) Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Resources: Key structures and vocabulary: Arirang Book 2, unit 5 Pictures related to ‘Stop smoking’ Teacher worksheets modified from various sources such as support documents related to heath and illness and eating and drinking. Korean vocabulary: 건강, 몸, 몸에 좋아요, 운동, 약을 드세요, 의사에게 가세요, 물을 많이 드세요, 약 드세요, 푹 쉬세요, 목이 말라요, 피곤해요, 며칠 전부터 ….머리, 어깨, 팔, 다리, 손, 손목, 허리, 발, 발목, 등, 무릎, 눈, 코, 입, 귀, 목이(가) 아파요, 잠 자요, 늦게(일찍)자요, 따뜻한 옷(선선한 옷)을 입으세요, 감기, 기침, 열, 태권도, 걷기, 맨손체조, 에어로빅, 수영, Survey forms 필라테, 요가, 조깅, 테니스, 야채, 과일, (양, 소, 닭, 돼지)고기, 생선 Computer/access to the internet Audio tape/CDs Websites: Grammatical aspects: Descriptive verbs, e.g. 아파요, 가려워요, 열이 나요, 아프다, 가렵다, 따갑다, 쑤시다, 저리다. o http://lei.snu.ac.kr/site/click-korean/I_KOR_14/intro.html o http://lei.snu.ac.kr/site/click-korean/I_KOR_18/intro.html Interrogative pronouns, e.g. 어디가/어떻게/언제부터 아파요? o www.langintro.com/kintro/body.htm Request forms: -을/를 하세요, 운동을 하세요. o www.arts.monash.edu.au/korean/klec/pictorial-exercise-level1/index.php o hompi.sogang.ac.kr/korean/kkl101/lesson09/index.html o hompi.sogang.ac.kr/korean/kkl100/lesson04/index.html Imperative verbs: - (으) 세요. 숨을 크게 쉬세요, 입을 크게 벌리세요. Text types: advertisement, description, personal letter, explanation, dialogue Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative (spoken texts) Evaluation and variation: (Considerations: Time allocated for unit; variety of teaching strategies used; opportunities for teacher feedback and student reflection; suitability of resources; suitability of ICT/laptop activities; literacy/numeracy links) Teacher name: _________________________ Signature: _________________________ Date: Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative ________________________