Sample Curriculum Map - Utah Business Education
advertisement
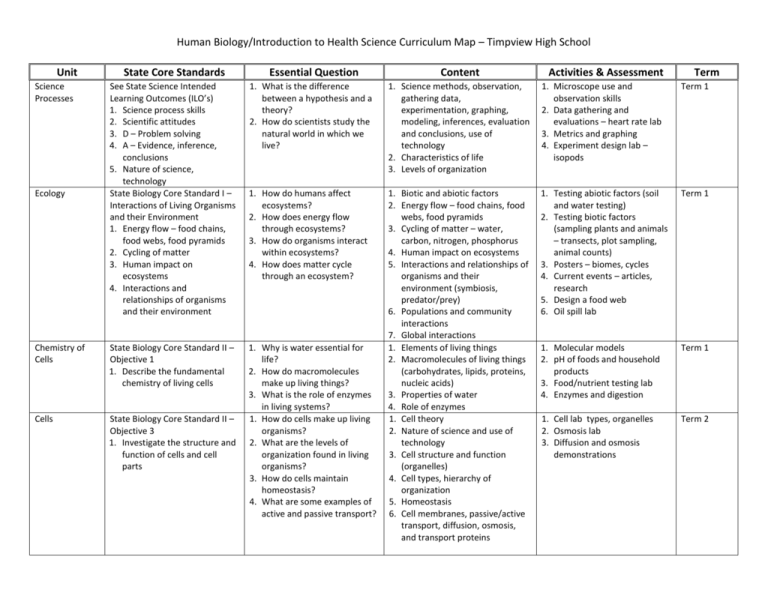
Human Biology/Introduction to Health Science Curriculum Map – Timpview High School Unit Science Processes Ecology State Core Standards See State Science Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO’s) 1. Science process skills 2. Scientific attitudes 3. D – Problem solving 4. A – Evidence, inference, conclusions 5. Nature of science, technology State Biology Core Standard I – Interactions of Living Organisms and their Environment 1. Energy flow – food chains, food webs, food pyramids 2. Cycling of matter 3. Human impact on ecosystems 4. Interactions and relationships of organisms and their environment Chemistry of Cells State Biology Core Standard II – Objective 1 1. Describe the fundamental chemistry of living cells Cells State Biology Core Standard II – Objective 3 1. Investigate the structure and function of cells and cell parts Essential Question Content Activities & Assessment Term 1. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? 2. How do scientists study the natural world in which we live? 1. Science methods, observation, gathering data, experimentation, graphing, modeling, inferences, evaluation and conclusions, use of technology 2. Characteristics of life 3. Levels of organization 1. Microscope use and observation skills 2. Data gathering and evaluations – heart rate lab 3. Metrics and graphing 4. Experiment design lab – isopods Term 1 1. How do humans affect ecosystems? 2. How does energy flow through ecosystems? 3. How do organisms interact within ecosystems? 4. How does matter cycle through an ecosystem? 1. Biotic and abiotic factors 2. Energy flow – food chains, food webs, food pyramids 3. Cycling of matter – water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus 4. Human impact on ecosystems 5. Interactions and relationships of organisms and their environment (symbiosis, predator/prey) 6. Populations and community interactions 7. Global interactions 1. Elements of living things 2. Macromolecules of living things (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) 3. Properties of water 4. Role of enzymes 1. Cell theory 2. Nature of science and use of technology 3. Cell structure and function (organelles) 4. Cell types, hierarchy of organization 5. Homeostasis 6. Cell membranes, passive/active transport, diffusion, osmosis, and transport proteins 1. Testing abiotic factors (soil and water testing) 2. Testing biotic factors (sampling plants and animals – transects, plot sampling, animal counts) 3. Posters – biomes, cycles 4. Current events – articles, research 5. Design a food web 6. Oil spill lab Term 1 1. Molecular models 2. pH of foods and household products 3. Food/nutrient testing lab 4. Enzymes and digestion Term 1 1. Cell lab types, organelles 2. Osmosis lab 3. Diffusion and osmosis demonstrations Term 2 1. Why is water essential for life? 2. How do macromolecules make up living things? 3. What is the role of enzymes in living systems? 1. How do cells make up living organisms? 2. What are the levels of organization found in living organisms? 3. How do cells maintain homeostasis? 4. What are some examples of active and passive transport? Energy in Living Systems State Biology Core Standard II – Objective 2 1. Investigate the structure and function of cells and cell parts 1. How do organisms obtain energy? 2. How is energy transferred in living organisms? 1. Photosynthesis, leaf adaptations 2. Respiration – aerobic/anaerobic 3. ATP production and use Genetics – Structure and Function of DNA State Biology Core Standard IV – Objective 3 1. Explain how the structure and replication of DNA are essential to heredity and protein synthesis 1. How does the structure of DNA affect protein synthesis? 2. What is the role of mutation in genetic diversity? 3. What are some modern applications of DNA technology? Reproduction State Biology Core Standard IV – Objective 1 1. Compare sexual and asexual reproduction 1. How do cells pass on genetic information to daughter cells? 2. What are advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction? Genetics State Biology Core Standard IV – Objective 2 1. Predict and interpret patterns of inheritance in organisms 1. How are character traits inherited? Evolution and Classification State Biology Core Standard V – Objective 1-3 1. Natural selection and biodiversity 2. Evidences for evolution 3. Classification hierarchy 1. What are the evidences that support the theory of evolution? 2. What is the role of natural selection in evolution? 3. How are organisms classified? 1. Structure of DNA 2. History of the Discovery of DNA and the cumulative nature of science 3. DNA replication 4. Protein synthesis 5. DNA and heredity 6. Mutations and gene expression 7. Genetic technologies – gene splicing, transgenic foods and other products, forensics & DNA 1. Cell cycle and cell division 2. Mitosis – phases, plants, and animals, 3. Advantages of asexual and sexual reproduction 4. Meiosis and its role in genetic variation 5. Chromosome anomalies 1. Mendel’s Law of Segregation and Independent Assortment 2. Inheritance of traits – dominant/ recessive traits, incomplete dominance, co-dominance, sexlinked traits 1. Definition of evolution, theories, nature of science 2. Evidences for evolution – fossil record, homologous and vestigial structures, molecular evidence (DNA and proteins) 3. Natural selection and modern theories 4. Classification hierarchy 5. Scientific naming 6. Kingdoms and diversity of organisms 1. Plant pigments and chromatography lab 2. Leaf structure and stomata lab 3. Photosynthesis / respiration (CO2) lab 1. DNA model building 2. Research projects of genetic technologies 3. DNA fingerprinting Term 2 1. Mitosis lab – phases and structures 2. Mitosis and phase counts and relative time 3. Plant cuttings 4. Karyotype lab Term 2 1. Corn genetics lab 2. Genetics problems Term 3 1. Natural selection lab 2. What can we learn from fossils lab 3. Scientific names and level research lab using field guides and other resources 4. How to use a classification key Term 3 Term 3 Structure and Function State Biology Core Standard V – Objective 1-2 1. Describe the structure and function of organs and organ systems in plants and animals 1. How do systems within organisms interact to maintain homeostasis? 2. How does the structure of a tissue or organ relate to its function? 1. Plant anatomy and functions – roots, stems, leaves, flowers 2. Animal organs and systems – digestive, respiration, circulation, protection and support, nervous 3. Comparisons between animal and plant phyla 1. Root and stem microscope labs 2. Flower dissection 3. Frog dissection 4. Exercise labs 5. Virtual labs Term 4