TEACHING SUGGESTIONS - Baltimore County Public Schools
advertisement

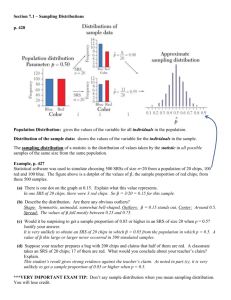
Baltimore County Public Schools Department of Curriculum and Instruction Concept Unit Title Theme Statement/ Enduring Understandings Essential Question(s) Suggested Timeframe Staff Teaching Responsibility Develop a research proposal General Notes: Teacher Note: This entire course will provide many of the lesson materials through the BCPS independent research website. Students will need access to this website on a daily basis. See this website at: http://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/researchcourse/steps.html. Objective: Standards Alignment Formative Assessment Digital Content, Tools, and Resources Before Direct Instruction Inquiry is a framework for learning. Research is a process. How does a researcher generate and use sample groups? Two periods, 45 minutes each. Media Specialist/ Teacher The teacher should keep in mind that this lesson includes suggestions for meeting the stated objectives. The teacher should adjust the lesson based on the needs of his or her students; however, all objectives should be covered. Students will examine the sampling process in order to generate samples which are representative of a larger population. AASL Standards for the 21st Century Learner: 1.1.1 Follow an inquiry- based process in seeking knowledge in curricular subjects, and make the real- world connection for using this process in own life. 1.1.6 Read, view, and listen for information presented in any format (e.g., textual, visual, media, digital) in order to make inferences and gather meaning. AASL Standards for the 21st Century Learner: Standard 2.0 - Learners use skills, resources, and tools to draw conclusions, make informed decisions, apply knowledge to new situations, and create new knowledge. (2.0) 2.1.1 Continue an inquiry-based research process by applying critical-thinking skills (analysis, synthesis, evaluation, organization) to information and knowledge in order to construct new understandings, draw conclusions, and create new knowledge. 2.1.3 Use strategies to draw conclusions from information and apply knowledge to curricular areas, real-world situations, and further investigations. 2.3.1 Connect understanding to the real world. Students will examine the attached research abstract and explain in a paragraph, which sampling method would be most appropriate to use with that research project. http://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/researchcourse/develop_data_sampling.html#sampling_tools. Unit #, Lesson # Lesson: Sampling Review materials at: http://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/researchcourse/develop_data_sampling.html#sampling_tools. Review all other digital content identified above. Need two sets of matching chips. Number the chips from 1 to N, where N is the class size. Decide on the mix of colors. (see stratified sample below). Choose a sample size, n. Materials: o Student computers o Student surveys o Candy o Chips identified above 1 Summer 2010 Baltimore County Public Schools Suggested Activity Sequence: Department of Curriculum and Instruction Drill – Direct students to the website below and direct them to read the introduction. After reading, students will explain the reasons that sampling is used in research: http://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/researchcourse/develop_data_sampling.html#sampling_tools. Classroom Activity – Conduct a number of exercises used to represent different sampling methods. A. Volunteer sample: Ask for a few volunteers to answer a survey. After answering the survey, reward the volunteers (ie with candy). The class becomes involved and students hope to be selected. B. Random Sample: From your bag of matching chips, select n. Since each chip is numbered, you can announce color and number (or, you can use a calculator to generate the random numbers). Have the students in the random sample answer the same survey and give them the reward. C. 1 in K Systematic Sample: Have students line up in numerical order in front of the room. Choose k. From the first k students, chose 1 at random. (can use your matching chips if sort them out ahead of time or can use calculator random number function). Have that student step forward. Then have every kth student step forward. The selected students will answer the survey and be given a reward. D. Stratified Sample: Have students group according to the color of the poker chip. (the like characteristic is chip color). As poker chips come in three colors, you will have three strata. Randomly sample from each strata, using the matching chips. (As students are moving into groups, you can sort your chips.) If you vary the size of the strata, you may draw different size samples proportionately from each. Or, you may draw an equal sample from each strata and find a weighted average. Once again, those sampled answer the survey and are given a reward. E. Cluster Sample: Have students group according to the color of the poker chip. Each group is a mini-population. Randomly select one color. Give the survey and reward to each student in that color group. F. Multistage: Cluster followed by random sample. Follow-up Activities 1. How many times were the individual students selected to answer the survey? (As they took a piece of candy each time selected, they know.) Discuss the fact that some are chosen frequently, others never. This happens in the world as well (i.e. jury duty) 2. Look at survey results for each type of sample. As a minimum, a frequency table can be created for the categorical variable. (I divide the class into groups and give each group one set of completed surveys. The results are summarized on the board.) The results will differ from one sample to the other. Discuss the fact that statistics vary. As the groups are working, I find the results for the entire population (the parameter). Compare the parameter with the statistics. Reinforce that statistics vary and the parameter is fixed. 3. Stress the difference between stratified sampling and cluster sampling. This seems to be the most difficult distinction for the student to make. Formative Assessment: Students will examine the attached research abstract and explain in a paragraph, which sampling method would be most appropriate to use with that research project. Kathleen Carino Eastern Technical High School Room - Library – Reference Poster Session 7:45 – 8:15 p.m. Research Question: How does stress relate to academic performance? Statement of purpose: The purpose of this research is to study the correlation between stress in high school students and their academic performance. How does stress caused by factors such as pressure to do well in tests, finish college applications, and the like affect a student's performance in school? Can stress actually be good for you? How much stress is too much Unit #, Lesson # 1 Summer 2010 Baltimore County Public Schools Department of Curriculum and Instruction stress? Background: My desire to research this project stemmed from my interest in neurology so I picked a research topic that would cover neurological topics such as how stress affects the brain and as a consequence how this affects a person's learning ability as demonstrated by their academic performance. Classes such as Anatomy and Physiology and AP Psychology have provided me some background on the physiology of the brain and how stress affects it. My participation in the Brain Bee has also increased my interest in doing further research on the topic. Significance: The topic is worth considering because the information gathered could be used to assess and possibly re-evaluate how much stress is imposed on high school students. By understanding how stress affects academic performance, school administrations can be encouraged to provide ways in alleviating the stress the student’s experience, especially for seniors. The information can also be used to promote a certain amount of stress in students if it proves that some stress can be beneficial for students. Differentiation Suggestions Unit #, Lesson # Components Content Process Product Curriculum Resources Brief Description 1 Summer 2010