important topics
advertisement

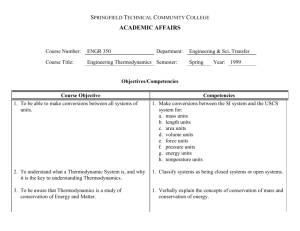
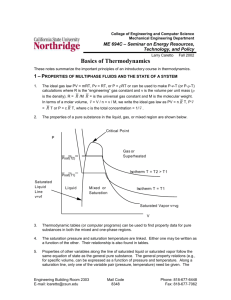
THERMODYNAMICS IMPORTANT TOPICS (Section-A) UNIT-1-BASIC CONCEPT OF THERMODYNAMICS Macroscopic and Microscopic Approaches, Thermodynamic Systems, Surrounding and Boundary, Thermodynamic Property – Intensive and Extensive, Thermodynamic Equilibrium, NUMERICALS ON WORK & HEAT TRANSFER State, Path, Process and Cycle, (ASSIGNMENT No-1) Quasi-static process Reversible and Irreversible Processes, Working Substance. Concept of Thermodynamic Work and Heat, Equality of Temperature Zeroth Law of Thermodynamic and its utility (Section-A) UNIT-2-FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Energy and its Forms 1st law of Thermodynamics NUMERICALS ON FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Internal Energy and Enthalpy (ASSIGNMENT No:-2&3) PMMFK Steady flow energy equation 1st Law Applied to Non flow process Steady Flow Process Throttling Process Free Expansion Process (Section-B) UNIT-3-SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Limitations of First Law NUMERICALS ON HEAT ENGINE, HEAT PUMP & Thermal Reservoir REFREGERATOR (C.O.P.) Heat Source and Heat Sink (ASSIGNMENT No:-4) Heat Engine, Refrigerator and Heat Pump, Kelvin- Planck and Clausius Statements and their Equivalence PMMSK. Carnot Cycle, Carnot Heat Engine and Carnot Heat Pump Carnot Theorem and its Corollaries Thermodynamic Temperature Scale. (Section-B) UNIT-3-Entropy Clausius Inequality Entropy Entropy-A property of system (Point function) Entropy generation (Why isentropic process is not necessarily an adiabatic process ) Causes of irreversibility T.dS Equations NUMERICALS ON ENTROPY (ASSIGNMENT No:-5) Entropy Change in Different Processes, Principle of Entropy Increase, Application of entropy principle Heat transfer through a finite temperature difference Mixing of two fluid Maximum work obtainable from two finite bodies at temperature T 1 & T2 Maximum work obtainable from a finite body & a T.E.R Introduction to Third Law of Thermodynamics. (Section-B) UNIT-4-Availability and Irreversibility High and Low Grade Energy Availability and Unavailable Energy Dead state of a system A.E. & U.E. when heat is with draw at constant temperature (Thermal Reservoir) A.E. & U.E. when heat is with draw from a finite body. Loss of Available Energy Due to Heat Transfer Through a Finite Temperature Difference Prepared by:-Sumit Sharama Mech. Engineering. Deptt. THERMODYNAMICS IMPORTANT TOPICS Heat transfer from a body at temperature T 1 to T2 (T1>T2>T0) Availability of a Non-Flow or Closed System Availability of a Steady Flow System Helmholtz and Gibb’s Functions, Effectiveness and Irreversibility, Second law efficiencies of processes & cycles. (Section-C) Unit-5-PURE SUBSTANCE Pure Substance Vaporization, Evaporation and Boiling Phase and Phase Transformation at constant pressure or Formation of steam by the help of T-V, P-V & (T-S) Diagrams Use of Enthalpy – Entropy (H-S) Diagrams (Mollier diagram) Types of steam Properties of Steam Solid – Liquid – Vapour Equilibrium (P-T Plots ) Throttling and Measurement of Dryness Fraction of Steam. (Section-C) Unit-6-IDEAL AND REAL GAS Concept of an Ideal Gas Basic Gas Laws Characteristic Gas Equation, Avogadro’s law and Universal Gas Constant, Vander Waal’s Equation of state Reduced Co-ordinates (parameters) Compressibility factor Mixture of Gases, Mass, Mole and Volume Fraction, Gibson Dalton’s law, Gas Constant Specific Heats Derivation for entropy change for ideal gas Proof that for ideal gas internal energy depends on temperature only. Proof that for ideal gas enthalpy depends on temperature only. Proof that for ideal specific heat depends on temperature only. PVy=C for reversible adiabatic process. (Section-D) Unit-7-thermodynamics Relations Maxwell Relations Clapeyron Equation Relations for changes in Enthalpy Relations for changes in Internal Energy Relations for changes in Entropy, Specific Heat Capacity Relations,(Mayer’s relations) Joule Thomson coefficient & inversion curve Carnot Cycle Otto Cycle Diesel Cycle Dual Cycle Stirling Cycle Ericson cycle Brayton cycle NUMERICALS ON A.E. & U.E. ASSIGNMENT No:-6 NUMERICALS ON PURE SUBSTANCE ASSIGNMENT No:-7 (Section-D) Unit-8-Gas Power Cycles NUMERICALS ON GAS POWER CYCLES (ASSIGNMENT No-8) Prepared by:-Sumit Sharama Mech. Engineering. Deptt.