Name: OBJ 2.1.1 & 2.1.3 EEn 2.1.1: Rock Cycle Which of the
advertisement
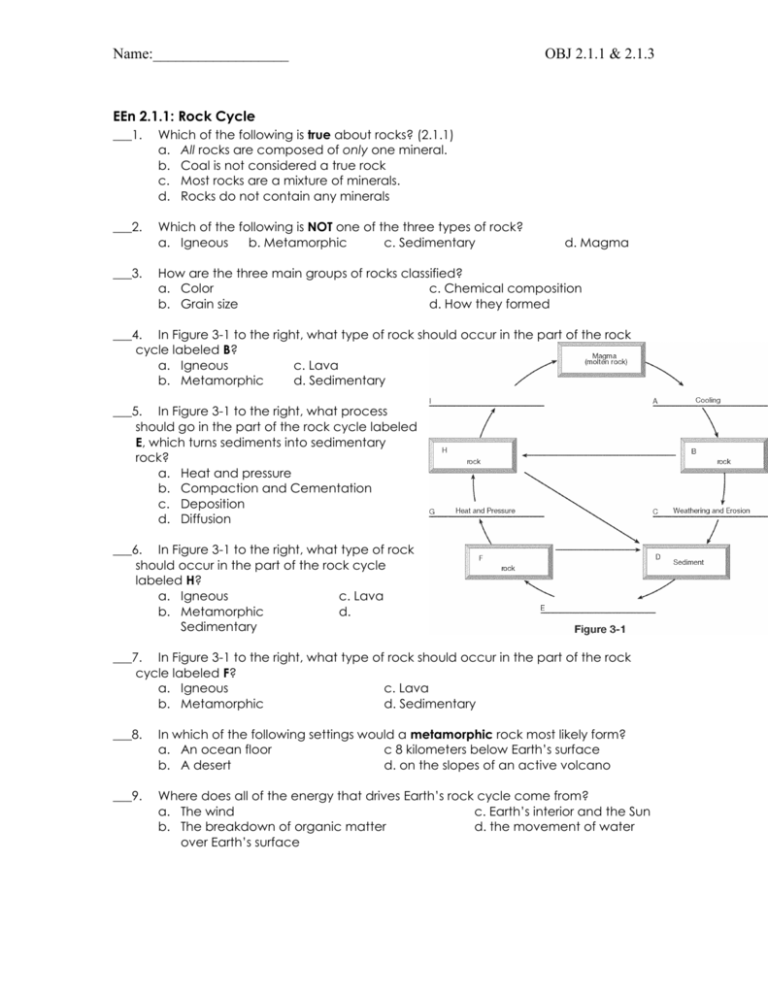
Name:__________________ OBJ 2.1.1 & 2.1.3 EEn 2.1.1: Rock Cycle ___1. Which of the following is true about rocks? (2.1.1) a. All rocks are composed of only one mineral. b. Coal is not considered a true rock c. Most rocks are a mixture of minerals. d. Rocks do not contain any minerals ___2. Which of the following is NOT one of the three types of rock? a. Igneous b. Metamorphic c. Sedimentary ___3. d. Magma How are the three main groups of rocks classified? a. Color c. Chemical composition b. Grain size d. How they formed ___4. In Figure 3-1 to the right, what type of rock should occur in the part of the rock cycle labeled B? a. Igneous c. Lava b. Metamorphic d. Sedimentary ___5. In Figure 3-1 to the right, what process should go in the part of the rock cycle labeled E, which turns sediments into sedimentary rock? a. Heat and pressure b. Compaction and Cementation c. Deposition d. Diffusion ___6. In Figure 3-1 to the right, what type of rock should occur in the part of the rock cycle labeled H? a. Igneous c. Lava b. Metamorphic d. Sedimentary ___7. In Figure 3-1 to the right, what type of rock should occur in the part of the rock cycle labeled F? a. Igneous c. Lava b. Metamorphic d. Sedimentary ___8. In which of the following settings would a metamorphic rock most likely form? a. An ocean floor c 8 kilometers below Earth’s surface b. A desert d. on the slopes of an active volcano ___9. Where does all of the energy that drives Earth’s rock cycle come from? a. The wind c. Earth’s interior and the Sun b. The breakdown of organic matter d. the movement of water over Earth’s surface Name:__________________ OBJ 2.1.1 & 2.1.3 ___10. How does a metamorphic rock form? a. From high heat and pressure c. From the cementation of sediments b. From weathering and erosion d. From the cooling of magma ___11. How does a sedimentary rock form? a. From high heat and pressure b. From compaction and cementation of sediments c. From weathering and erosion d. From the cooling of magma ___12. How does an extrusive igneous rock form? a. The cementation of sediments b. The cooling of lava above Earth’s surface c. Extreme heat & pressure d. the cooling of magma below Earth’s surface ___13. Which of the following is NOT considered to be a rock? a. Coal b. Pumice c. Sandstone d. Lava ___14. Granite is one of the main three types of rocks. To form, it experienced high temperatures and high pressure deep within the Earth. Which of the three main types of rocks is granite? a. Sedimentary b. Sediments c. Metamorphic d. Igneous ___15. Moesha and her family went on vacation to Hawaii and went sight seeing. As they visited a local volcano, Moesha noticed a number of strange rocks that were relatively close to the volcano. Moesha thought it was strange that there were rocks next to a volcano. Given your knowledge of rocks, what type of rock would you suggest it was? a. metamorphic because they form from the cooling of lava b. igneous rocks because they form from the cooling of lava c. sedimentary rocks because they form from the cooling of lava d. No rocks could exist next to a volcano ___16. In the crayon demo, when showing how sediments can transform into a sedimentary rock, we put our science notebooks atop the sediments. What process was being represented? a. Weathering b. Compaction c. Erosion d. Deposition Name:__________________ OBJ 2.1.1 & 2.1.3 ___17. In the crayon demo, when showing how sediments can transform into a sedimentary rock, we shaved the crayon representing the igneous rock being broken down into smaller pieces. What process was being represented? a. Weathering b. Compaction c. Erosion d. Deposition Use the diagram below to answer question 18. ___18. Which type of rock is formed as a result of these three stages? a. Metamorphic b. Igneous c. Sedimentary d. Lava EEn2.1.3: Weathering and Erosion___________________________________________ Weathering ___19. A tree growing on a cliff is slowly growing its roots into the rocks and causing it to crack. What types of mechanical weathering is occurring? a. Frost wedging b. Unloading c. Biological activity d. Erosion ___20. Xavier found a rock one summer when he was on a camping trip. He brought the rock home and left it outside. A few months later, Xavier noticed the rock had changed color. Which of the following is the best explanation of what happened? a. The water in the rock evaporated, changing the color of the rock. b. The rock underwent the process of chemical weathering, which caused the color change. c. The rock underwent the process of mechanical weathering, which caused the color change. d. Precipitation has fallen on the rock and washed off the outside layer. ___21. Which of the following is an example of mechanical weathering? a. Acid rain b. Frost wedging c. Rusting of metal d. Groundwater infiltrating into an unconfined aquifer Name:__________________ OBJ 2.1.1 & 2.1.3 ___22. Which of the following is an example of chemical weathering? a. Acid rain b. Frost wedging c. Erosion of a river bank d. Animals creating holes in rocks to make a home ___23. What effect does temperature have on chemical weathering? a. High temperature increases the speed of chemical weathering b. High temperature decrease the speed of chemical weathering c. High temperature does not affect the speed of chemical weathering. d. The effect of temperature on weathering is unknown. ___24. The process that occurs when physical forces break rock into smaller pieces without changing the rock’s chemical composition is called ____. a. Differential weathering b. Mechanical weathering c. Chemical weathering d. Erosion ___25. Which of the following weathering processes involves the constant freezing and thawing of water? a. Frost wedging b. Spheroidial weathering c. Exfoliation d. Unloading ___26. Which of the following is NOT associated with mechanical weathering? a. Frost wedging b. Reactions with oxygen c. Biological activity d. Unloading ___27. Which of the following is the result of chemical weathering? a. A rock that has lost its outer layers b. A rock that has been broken into tiny pieces c. A rock that have been split into two d. A rock that had been changed into one or more new compounds ___28. Chemical weathering would be most effective in which climate? a. Most effective in a hot, dry climate b. Most effective in a cold, dry climate c. Most effective in a hot, humid climate d. Equally effective in any climate Erosion: ___29. Transported sediments are usually deposited at locations in which a. the freeing and thawing of water occurs b. the chemical breakdown of rocks occurs c. a decrease in the speed of the agent of erosion occurs d. an increase in the physical weathering of rocks occurs Name:__________________ OBJ 2.1.1 & 2.1.3 ___30. How does weathering differ from erosion? a. Erosion breaks down rocks into sediments and weathering transports sediments to new locations b. Weathering breaks down rocks into sediments and erosion transports sediments to new locations c. Erosion deposits sediments in new locations and weathering builds new landforms d. Weathering and erosion are the same thing. ___31. What is deposition? a. Rocks are broken down into sediments b. Sediments are transported from place to place c. Sediments are dropped off in a new location, building up and creating new landforms over time. d. Sediments are compacted and cemented together ___32. In what way would a sediment particle most likely change while it is being transported by the stream? a. It will become more dense b. It will decrease in size c. It will become more angular d. Its hardness will increase ___33. The process by which wind, water, ice or gravity picks up sediments and moves them to a new location is called: a. Erosion b. Compaction c. Velocity d. Deposition ___34. What is the primary agent of erosion on earth? a. Wind b. Running Water c. Weathering d. Ice