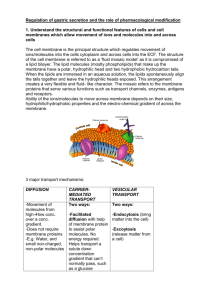
GERD
advertisement
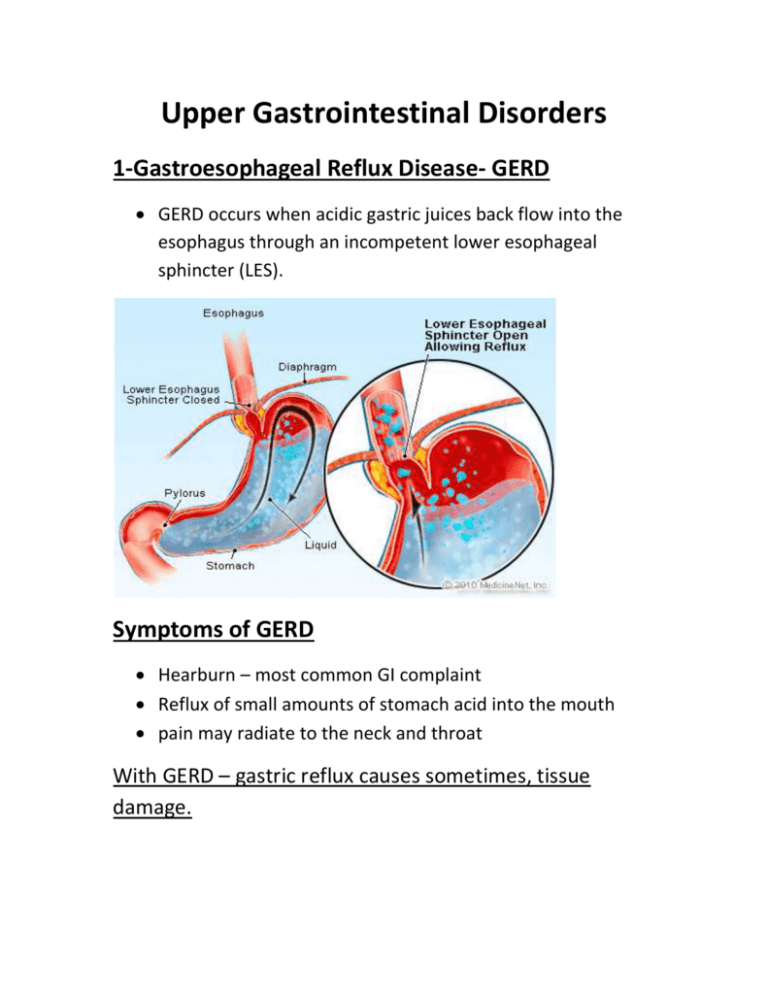
Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders 1-Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease- GERD GERD occurs when acidic gastric juices back flow into the esophagus through an incompetent lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Symptoms of GERD Hearburn – most common GI complaint Reflux of small amounts of stomach acid into the mouth pain may radiate to the neck and throat With GERD – gastric reflux causes sometimes, tissue damage. Causes of GERD Weakening or inappropriate relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter Associated with pregnancy due to the elevation of progesterone which esophageal sphincter Associated with hiatal hernia (a condition in which the upper portion of the stomach protrudes above the diaphragm ) Consequences of GERD Reflux esophagitis (inflammation in the esophagus related to the reflux of acidic stomach contents). Esophageal ulcers Scarring of ulcerated tissue increased risk of cancer Treatment of GERD - lifestyle modifications Avoid large meals to avoid increased gastric pressure Limit foods that weaken chocolate- high fat foodspeppermint) Avoid smoking and alcohol lower esophageal sphincter pressure or increase gastric acid secretion ( caffeine- garlic- onion-chocolate- high fat foods – peppermint) During times of esophagitis, avoid items that may irritate the esophagus such as carbonated beverages, citrus fruits and juices, spicy foods, tomato products, and any other individual intolerances. People who avoid citrus juices and tomato products because of their acidity should be encouraged to eat other sources of vitamin C. Avoid eating bedtime snacks or lying down immediately after meals Remain upright for 45 to 60 minutes after eating Consume meals 2-3 hours before bedtime Prop pillows under the head and upper torso during sleeping Avoid wearing tight clothing that increases pressure in the stomach Lose weight if needed because weight loss decreases intraabdominal pressure Avoid use of non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) Treatment of GERD • Drugs that suppresses acid secretion by inhibiting receptors on acid-producing cells.-Antacids-Surgery 2-Hiatal Hernia 1. Part of stomach protrudes through diaphragm into thoracic cavity 2. Prevents food from moving normally along digestive tract 3. Heartburn and food regurgitation into mouth can occur Medical nutrition therapy of Hiatal Hernia 4. 5. 6. 7. Small, frequent meals of well-balanced diet Avoid irritants to esophagus Avoid foods that relax lower esophageal sphincter Weight loss recommended if necessary 8. Avoid lying down two to three hours after eating Conditions Affecting the Stomach 3- Dyspepsia Symptoms dyspepsia Indigestion in the upper abdominal area Symptoms may include : • • • • • Stomach pain Heartburn Fullness Nausea Bloating Causes of dyspepsia • Medical conditions : peptic ulcers, GERD, motility disorders, malabsorptive disorders,gallbladder disease, abdominal tumors, diabetes mellitus, renal disease, thyroid disease, heart failure • Medications • Dietary supplements Potential food intolerances • Overeating • Specific foods – spicy • Coffee including decaffeinated • High-fat foods • Advised to consume small meals, well-cooked foods - not overly seasoned, in a relaxed atmosphere If the problem is organic in origin, treatment of the underlying cause will be the normal procedure. Bloating and stomach gas • • • • Chewing gum Smoking Rapid eating, drinking carbonated beverages Omitting these practices generally helps to correct the problem. Peptic Ulcer Erosion of the mucosal layer of the stomach (gastric ulcer) or duodenum (duodenal ulcer) caused by an excess secretion of, or decreased mucosal resis tance to, hydrochloric acid. Primary cause • Helicobacter pylori infection is the primary factor of the disease and was found in 60% of Gastric ulcers patients and in 80% of Duodenal ulcers patients • Another major factors is the use of certain drugs like aspirin which can damage mucosal tissue • Emotional stress Other causes for peptic ulcer • genetic predisposition • abnormally high secretion of hydrochloric acid by the stomach Effects of emotional stress: Has effects on physiological processes • Rapid stomach emptying which increase the acid load in the duodenum) • Hormonal changes that impair wound healing • Increased acid and pepsin secretions Has behavioral changes • Use of alcohol • Tobacco use • NSAID use Signs and symptoms of Peptic Ulcer • Peptic ulcer symptoms vary. Ulcer pain may be experienced as a : Hunger pain Burning pain in stomach region Sometimes aggravated by food causes loss of appetite and weight loss Complications of Peptic Ulcer 1-GI bleeding(black stool- vomit that resembles coffee ground) 2-Perforations of the stomach or duodenum leading directly into the peritoneal cavity 3-Gastric outlet obstruction due to inflammation Drug therapy for Peptic Ulcer 1. Drugs that suppresses acid secretion by inhibiting receptors on acid-producing cells 2. Antacids 3. Coating agents 4. Antibiotics to eradicate H.pylori Dietary considerations for peptic ulcer Individualized to personal tolerances Avoid foods that increase acid secretion or irritate the GI lining – alcohol, coffee, caffeine, spicy foods, carbonated beverages, chocolate. Avoid large meals that cause stomach distension Avoid lying down two to three hours after eating No smoking ( it delay the healing) Good chewing of food. Sufficient low-fat protein should be provided but not in excess because of its ability to stimulate gastric acid secretion. It is recommended that clients receive no less than 0.8 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, if there has been blood loss, protein may be increased to 1 or 1.5 grams per kilogram of body weight Although fat inhibits gastric secretions, because of the danger of atherosclerosis, the amount of fat in the diet should not be excessive. Carbohydrates have little effect on gastric acid secretion. Vitamin and mineral supplements, especially iron if there has been hemorrhage, may be prescribed.