4- Content Outline Vitals Chapter 4 Outline Part 2 Blood Pressure
advertisement

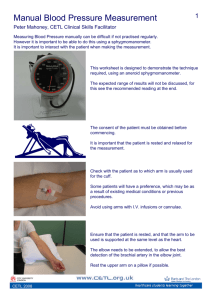
Vitals Chapter 4 Outline Part 2 Blood Pressure Mechanism of Blood Pressure 1. Blood pressure: 2. Systole: a. 3. Systolic pressure: a. 4. Diastole: 5. Diastolic pressure: a. b. Interpretation of Blood Pressure 1. Blood pressure: abbreviated _________ 2. Measurement expressed as a _____________ a. Numerator: __________ _______________ b. Denominator: __________________ ______________ 3. Measured in ______________ of ______________(mm Hg) 4. New guidelines from National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute a. Normal BP: __________ than _______ mm Hg b. Prehypertension Sustained _____________: _______ to _______ ______ Hg or Sustained __________: ________ to ________ mm Hg 5. BP should be taken ___ ____________ office visit a. Several readings taken on different occasions Provide a good index of baseline BP b. Rise or fall of 20 to 30 mm Hg in baseline BP is significant Even if still in normal range 6. ______________________: high blood pressure a. Hypertension stage 1 Sustained _____________: ________ to ________mm Hg or Sustained _________________: _____ to _________ mm Hg b. Hypertension stage 2 Copyright © 2012, 2008, 2004, 2000, 1995, 1990, 1984, 1979 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Content Outline Sustained systolic: _________ mm Hg or higher or Sustained diastolic: _______ mm Hg or higher c. Caused by ___________ _______________ on ___________ _________ d. Most common condition that causes an abnormal BP reading 7. ________________: low blood pressure a. Reduced pressure on _____________ _____________ b. BP reading less than ___________mm Hg 8. Pulse pressure: difference between systolic and diastolic pressures a. Determined by subtracting smaller number from larger number Example: If BP is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse pressure is 40 (110 minus 70) b. Normal range: 30 to 50 Factors Affecting Blood Pressure 1. ________: as age increases, BP gradually increases 2. __________: after puberty, women have a lower BP than men of the same age a. After menopause: BP is higher in women 3. ______________ ______________: BP is lower in the morning and higher in the afternoon a. During sleep a.. As metabolism and activity increase during the day Blood pressure rises 4______________ _____________: increase BP (anger, fear, excitement) a. Calm patient before taking BP 5. ________________: temporarily increases BP a. If a patient has been involved in physical activity Allow patient to rest 20 to 30 minutes before taking BP 6. __________ ________________: BP varies based on position a. Diastolic pressure in sitting position: higher than in lying position b. Make a notation if position is other than sitting L: lying St: standing 7. _______________: may increase or decrease BP (depending on type of medication) a. Important to record prescription and OTC medications in patient’s chart 8. Also increases BP a. Recent meal b. Caffeine c. Smoking d. Bladder distention e. Pain Assessment of Manual Blood Pressure 1. Equipment needed a. _________________________________ b. ________________________________ Copyright © 2012, 2008, 2004, 2000, 1995, 1990, 1984, 1979 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 4-2 Content Outline 4-3 2. __________________: instrument for amplifying and hearing sounds produced by the body 3. Stethoscope chest piece a. Types ______________: large flat disc - Most useful for hearing high-pitched sounds (1) (2) ________: bowl-shaped appearance - Most useful for hearing low-pitched sounds (1) __________ _______________ (2) _______________ _____________ ________________ Sphygmomanometers 1. ____________________: instrument for measuring ___________ BP 2. Consists of a. _____________: scale for registering the pressure of air in the bladder b. ___________ ______________ ______________ surrounded by a covering (cuff) c. Pressure bulb with a control valve: to inflate and deflate inner bladder Cuff Sizes 1. Variety of sizes a. Measured in centimeters (cm) 2. Size of cuff: refers to inner bladder rather than outer covering 3. Inner bladder of cuff should a. __________ _______% of arm circumference (but not more than 100%) b. Be wide enough to cover two-thirds of the distance from _________ to _____________ space Cuff must fit properly to ensure an accurate reading 4. _________ _________ often used for adult with thin arms 5. _________ _________ used for average-sized adult arm 6. _________ _________ used for thigh or adults with large arms 7. If cuff is ________ __________: reading is falsely _________ 8. If cuff is ________ __________: reading is falsely _________ 9. Center of inflatable bag should be directly over the brachial artery a. To allow complete compression of the brachial artery 10. Velcro is used to secure the cuff 11. Obese patients with an arm circumference of more than 50 cm (20 inches) a. May not be possible to fit adult thigh cuff around arm b. Blood pressure can be measured using forearm and radial artery Korotkoff Sounds 1. Used to determine systolic and diastolic BP readings a. When bladder of the cuff is inflated Copyright © 2012, 2008, 2004, 2000, 1995, 1990, 1984, 1979 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Content Outline 4-4 b. As cuff is ________________ Sounds become ______________ Guidelines to Prevent Errors in Blood Pressure Measurement 1. Before BP measurement, instruct patient _________ to a. Consume __________________ b. Use _____________ c. ________________ For _______________ minutes before BP 2. Patient should be comfortably seated in a quiet room a. For at least 5 minutes before BP measurement _____________ and ______________: can cause spasm of the brachial artery 3. Always use ________________ __________ ___________ 4. ___________ take _________ over __________________ 5. _____________ patient properly a. Seated in chair Legs _________________ - Crossed legs: increases ______________ pressure Back ________________ - Back not supported (e.g.: sitting on examination table): increases ______________ pressure b. Position arm at _____________ ___________ 6. Avoid extraneous sounds from cuff: interfere with accurate measurement a. Position cuff 1 to 2 inches above bend in elbow b. Prevents stethoscope from touching cuff 7. Compress brachial artery completely a. Center bladder of cuff directly over artery to be compressed Most cuffs: labeled with arrows indicating center of bladder for right and left arms b. Centering allows for complete compression of the brachial artery 8. Apply equal pressure over the brachial artery a. Apply cuff so that it fits smoothly and snugly around the patient’s arm Prevents bulging or slipping Permits application of equal pressure over brachial artery b. Loose-fitting cuff: falsely high reading 9. Instruct patient to relax and ___________ _________ during the procedure 10. Release pressure at a _________________ steady rate 11. Avoid ___________ congestion a. If you need to take the BP in the same arm again Wait ____ to _________ minutes - Allows blood trapped in veins (venous congestion) to be released b. Venous congestion can result in: Falsely high systolic reading and a falsely low diastolic reading Copyright © 2012, 2008, 2004, 2000, 1995, 1990, 1984, 1979 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.