Cells and Heredity
advertisement

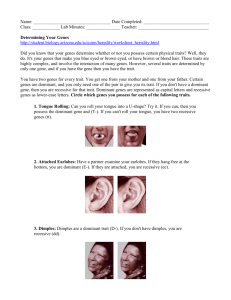
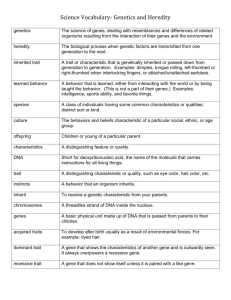
Cells and Heredity: Name ________________________ Period _______________________ What are the functions for: Cell Membrane - It controls and allows gases and nutrients to enter and leave the cell. Cytoplasm – jellylike substances that holds the organelles Nucleus – it controls the activities of the cell Mitochondria – extracts energy from food, respiration occurs Vacuole – storage compartment of cell Ribosomes – synthesizes/makes proteins Cell Wall – rigid support on the outside of plant cell Chloroplast – organelle where the plant makes it food (photosynthesis) Prokaryotic – No nucleus organism ( chromosomes are throughout the cell) Eukaryotic - Nucleus in the organism (chromesomes are contained in the nucleus What are the "things" that go into the equation for: Photosynthesis 6C02 + 6 H20 + light energy_ ------> C6H1206 + 6O2 0rganelle where it takes place Chloroplast in Animal Cell /Plant Cell or Both Respiration C6H1206 + 6O2 ---> _6C02 + 6 H20 + energy 0rganelle where respiration takes place _____Mitochondria Animal Cell /Plant Cell or Both Heredity: What is Heredity? Passage of inherited traits from generation to generation. Chromosomes – the X structures in the cell that contains genetic information DNA – the ladder like structure in the chromsomes that holds genes Gene - found on the DNA and Chromosmes with genetic information Dominate Gene – strong gene, written as a Capital letter…example B,D, T Recessive Gene – the weaker gene, written as a lowercase letter, example b,d,t (must have both recessive for trait to show. Genotype – The letter combination one from male and one from female to represent trait. Example BB,Bb or bb Phenotype – the physical appearance of the trait… example brown hair Inherited Traits – characteristics you get from parents Acquired Traits – Learned behavior Homozygous Genes –genes on genotypes are either both dominate or both recessive –BB, dd Heterozygous Genes – genes on the genotypes – One is dominate and one is recessive – Dd, Bb




![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)