Lecture Notes

October 22nd - Filters
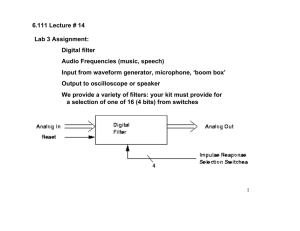
Digital filter design: IIR and FIR filters Analog EQ, Digital EQ
A Concise History of EQ
Variables in filters
Types o o o
Low Pass
High Pass
Band Pass o
Parameters
Q o o
Band Reject
Stands for ‘Quality Factor’
Defines the bandwidth and shape of the filter where a lower Q value is a broader shape across a wider range around the center frequency, and a higher Q value is a more narrow shape
Gain or Attenuation Amount
Center frequency
Analog
-no aliasing
-filters signals ahead of the ADC
-affects the phase of the signal. 45 degrees per pole (denominator)
Additional Resource on Analog Filter Design
Digital
-can be phase linear/constant time delay (FIR only)
-programmable with fine controls
-not influenced by temperature and tolerances
-only as good as the ADC
Source
Bessel Filters
-constant time delay in the pass band, but not surrounding bands
State-Variable Filters
pre-massenberg parametric allowed for the development of the modern console
show schematic where you pick up the signal in the circuit determines LP, HP, BP
combine LP & BP to get band rejection show the LP/HP/BP/BR in a highlighted schematic filter resonance
Review of Transfer functions & Fourier analysis http://sites.tufts.edu/andrewrosen/files/2013/04/es3_final.pdf
Digital Filter Design (Pirkle, Chapters 6 & 8)
coefficients of a filter determine its frequency response and other characteristics delay elements create phase shift as opposed to reactive components in analog circuits
filters are often discussed in the visual domains; they are very similar (think instagram, photoshop, etc.) but utilized in a different part of the spectrum
IIR Filters
infinite impulse response
of called ‘linear filters’ essentially the same as SVF analog designs and interchangeable using BZT
represent similar timbral and phase characteristics to analog filters
problems: can easily become unstable and oscillate curve types (linkwitz-riley, butterworth, etc.)
FIR
finite impulse response
linear phase response non-linear filters
most often implemented using convolution problems: pre-ringing
Additional resources:
Will Pirkle’s books, musicdsp.org
, webaudioapi , MATLAB for Audio, KVR developer’s section
Online Books, lecture links and class notes from CCRMA faculty http://mmckegg.github.io/web-audio-school/