2013 Yr 10 Biology – Exam 1 – answers
advertisement
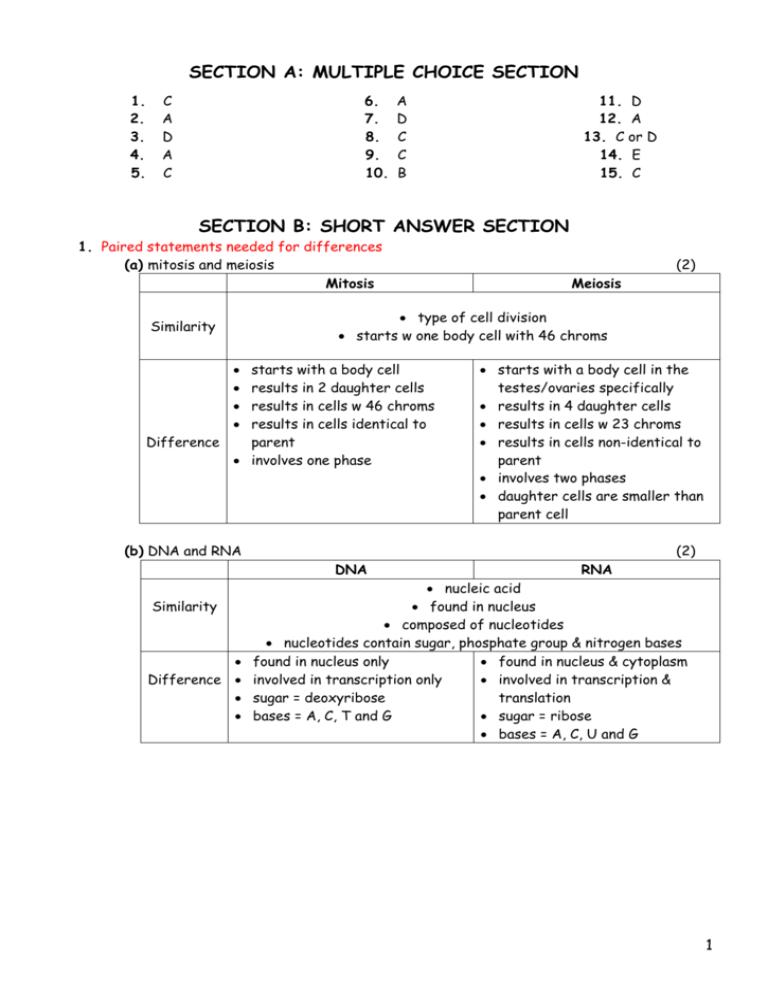
SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C A D A C 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. A D C C B 11. D 12. A 13. C or D 14. E 15. C SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER SECTION 1. Paired statements needed for differences (a) mitosis and meiosis Mitosis (2) Meiosis type of cell division starts w one body cell with 46 chroms Similarity starts with a body cell results in 2 daughter cells results in cells w 46 chroms results in cells identical to Difference parent involves one phase starts with a body cell in the testes/ovaries specifically results in 4 daughter cells results in cells w 23 chroms results in cells non-identical to parent involves two phases daughter cells are smaller than parent cell (b) DNA and RNA (2) DNA Similarity Difference RNA nucleic acid found in nucleus composed of nucleotides nucleotides contain sugar, phosphate group & nitrogen bases found in nucleus only found in nucleus & cytoplasm involved in transcription only involved in transcription & sugar = deoxyribose translation bases = A, C, T and G sugar = ribose bases = A, C, U and G 1 (c) Transcription and Translation Transcription Translation both involved in protein synthesis both involve RNA both require enzymes Similarity Difference (2) occurs in nucleus requires DNA produces mRNA does not require ribosomes does not require tRNA occurs in cytoplasm does not require DNA produces polypeptides requires ribosomes requires tRNA (Total = 6 marks) 2. a. Somatic. Cells are in pairs and gametes do not have homologous pairs of chromosomes. (2) b. 0.5 mark for each correct answer; 0.5 mark for each reason i. Domestic fowl b/c have a range of chrom sizes & a similar number (1) ii. Fruit fly b/c have a very low no of chroms compared to humans (1) (Total = 4 marks) 3. Template Strand of DNA A T G G G C C T G T G G T A G When this strand of DNA is transcribed, the resulting mRNA sequence is: A U G - G G C - C U G - U G G - U A G When this mRNA sequence is translated, the resulting amino acid sequence is: Met - Gly - Leu - Trp - Stop (Total = 2 marks) 2 4. M1 = correctly labelled base, sugar & phosphate M2 = structure; phosphate and base shown linked to correct carbon atoms on sugar; M3 = covalent bond(s) labelled between sugar and phosphate / between sugar and base; M4 = base options and sugar options identified. (Total = 4 marks) 5. (a) inheritance of genes located on the autosomes (chroms 1-22) (1) (b) no gender bias of M:F affected son from affected father (2) (c) A=ACHOO syndrome; a = unaffected Individual II–1 = AA or Aa + working (2) (d) Individual III–4 = aa + working . (2) (Total = 7 marks) 6. (a) Identify the type of inheritance described by this relationship. 0.5 mark - Complete dominance or recessive inheritance 0.5 mark - Autosomal inheritance (1) (b) error in marks (2) A and B alleles are both dominant over O Parents: AO x BO Possible phenotypes of offspring: 25% A : 25% B : 25% AB : 25% O (c) No. Could only be A, B or O They are homozygous O – so they will only ever be able to contribute an O allele (3) (Total = 6 marks) 3 7. Outline the evidence provided by DNA for the common ancestry of living organisms. DNA/genetic code is universal; same structure of double helix of complementary strands; same base pairing rule - always pairing of AT and GC; small differences in DNA show closer relationships; identified through DNA hybridisation humans have the same biochemistry as all organisms so part of same evolution/common ancestry; (Total = 3 marks) 8. Outline the evidence for evolution provided by homologous structures. comparative anatomy of groups of animals or plants shows certain structural features are basically similar; homologous structures are those that are similar in shape in different types of organisms; structural similarities imply a common ancestry; (homologous structures) used in different ways; example is pentadactyl limb in vertebrates / modification of ovary wall or pericarp to aid seed dispersal / other suitable example; adapted to different mode of locomotion in particular environment / example of two differences such as bat’s wing and human hand; illustrates divergent evolution since basic plan adapted to different niches; the more exclusive the shared homologies the closer two organisms are related; certain homologous structures in some species with no apparent function such as human appendix (homologous with functional appendix in herbivores); (Total = 3 marks) 9. Explain how natural selection leads to evolution. parents produce more offspring than required to keep numbers constant; more are produced than the environment can support; example of an environmental condition; these offspring show variation; some are better adapted than others to the environment; these tend to survive to breed themselves; characteristics are inheritable; so the new generation has these characters too; this leads to changes in the population as a whole; these changes constitute evolution; (Total = 5 marks) 4








