Polynomial Functions - sandbox
advertisement

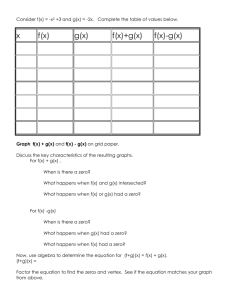
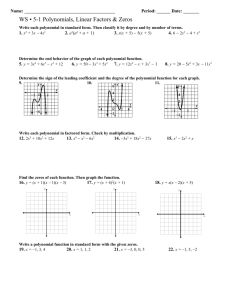
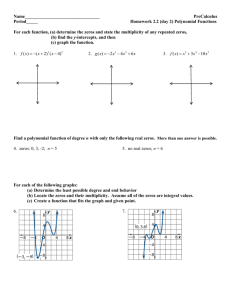
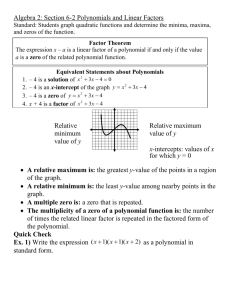
Polynomial Functions NOTE: Some problems in this file are used with permission from the engageny.org website of the New York State Department of Education. Various files. Internet. Available from https://www.engageny.org/ccss-library. Accessed August, 2014. Properties of Exponents: Class Work Simplify the following expressions. 1. (−4𝑔3 ℎ2 𝑗 −2 )−3 4. (5r 3 s4 t 2 )(2r 3 s−3 )4 4𝑘 3 2 2. (3𝑚𝑛2 ) 5. (3u2 v −4 )3 (6u4 v3 )−2 −2 3p7 q3 3. ((2p2 q2 )3 ) 6. ( −3 8w2 x−3 y4 z5 ) 12w3 x−4 y5 z−6 Properties of Exponents: Homework Simplify the following expressions. 7. (−3𝑔−4 ℎ3 𝑗 −3 )−4 4𝑘 4 10. 4(5r10 s12 t 8 )(2r 4 s−5 )−3 2 8. (6𝑚3 𝑛−4 ) 8p7 q9 11. (6u6 v −3 )3 (9u5 v−6 )−2 −2 6w−3 x−4 y5 z6 9. ((2p2 q2 )4 ) Algebra II - Polynomials −2 12. (15w3 x−4 y5 z−6 ) ~1~ NJCTL.org Operations with Polynomials: Class Work Determine if each function is a polynomial function. If so, write it in standard form, name its degree, state its type based on degree and based on number of terms, and identify the leading coefficient. 13. 2𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 2 4 14. 7 𝑦 − 3𝑦 2 + 3𝑦 15. 5𝑎3 − 2𝑎 − 4𝑎 + 3 16. 6𝑎 2 𝑏 − 5𝑎𝑏 2 + 2𝑎𝑏 2 17. (2𝑥 −2 − 4) + (−5𝑥 −2 − 3) Perform the indicated operations. 18. (4g 2 − 2) − (3g + 5) + (2g 2 − g) 19. (6𝑡 − 3𝑡 2 + 4) − (𝑡 2 + 5𝑡 − 9) 20. (7𝑥 5 + 8𝑥 4 − 3𝑥) + (5𝑥 4 + 2𝑥 3 + 9𝑥 − 1) 21. (−10𝑥 3 + 4𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 + 9) − (2𝑥 3 − 2𝑥 2 + 𝑥 + 12) 22. The legs of an isosceles triangle are (3x2+ 4x +2) inches and the base is (4x-5) inches. Find the perimeter of the triangle. 23. −2𝑎(4𝑎2 𝑏 − 3𝑎𝑏 2 − 6𝑎𝑏) 27. (m − 3)(2m2 + 4m − 5) 24. 7𝑗𝑘 2 (5𝑗 3 𝑘 + 9𝑗 2 − 2𝑘 + 10) 28. (2𝑓 + 5)(6𝑓 2 − 4𝑓 + 1) 25. (2x − 3)(4x + 2) 29. (3t 2 − 2t + 9)(4t 2 − t + 1) 26. (𝑐 2 − 3)(𝑐 + 4) Algebra II - Polynomials ~2~ NJCTL.org 30. The width of a rectangle is (5x+2) inches and the length is (6x-7) inches. Find the area of the rectangle. 31. The radius of the base of a cylinder is (3x + 4) cm and the height is (7x + 2) cm. Find the volume of the cylinder (V = 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ). 32. A rectangle of (2x) ft by (3x-1) ft is cut out of a large rectangle of (4x+1)ft by (2x+2)ft. What is area of the shape that remains? 33. A pool that is 20ft by 30ft is going to have a deck of width x ft added all the way around the pool. Write an expression in simplified form for the area of the deck. Multiply and simplify: 34. (𝑏 + 2)2 36. (2𝑑 + 4𝑒)2 35. (𝑐 − 1)(𝑐 − 1) 37. (5𝑓 + 9)(5𝑓 − 9) 38. What is the area of a square with sides (3x+2) inches? Expand, using the Binomial Theorem: 39. (2𝑥 + 4𝑦)5 40. (7𝑎 + 𝑏)3 41. (3𝑥 − 4𝑧)6 42. (𝑦 − 5𝑧)4 Algebra II - Polynomials ~3~ NJCTL.org Operations with Polynomials: Homework Determine if each function is a polynomial function. If so, write it in standard form, name its degree, state its type based on degree and based on number of terms, and identify the leading coefficient. 43. √2𝑥 2 + 0.4𝑥 3 4 44. 7𝑦 − 8𝑦 2 + 9𝑦 45. 11𝑎4 − 2𝑎3 + 7𝑎2 − 8𝑎 + 9 46. 6𝑎 2 11 − 5𝑎 9 +2 2 47. (2𝑥 3 − 4) + (−5𝑥 2 − 3) Perform the indicated operations: 48. (3n − 13) − (2n2 + 4n − 6) − (5𝑛 − 4) 49. (5g 2 − 4) − (3g 3 + 7) + (5g 2 − 5g) 50. (−8𝑥 4 + 7𝑥 3 − 3𝑥 + 5) + (5𝑥 4 + 2𝑥 2 − 16𝑥 − 21) 51. (17𝑥 3 − 9𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 − 18) − (11𝑥 3 − 2𝑥 2 − 19𝑥 + 15) 52. The width of a rectangle is (5x2+6x +2) inches and the length is (6x-7) inches. Find the perimeter of the rectangle. 53. 4𝑥(3𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 − 2) 58. (2𝑐 2 − 4)(3𝑐 + 2) 54. −6𝑎(3𝑎2 𝑏 − 5𝑎𝑏 2 − 7𝑏) 59. (2m − 5)(3m2 − 6m − 4) 55. 8𝑗 2 𝑘 3 (2𝑗 3 𝑘 + 6𝑗 2 − 5𝑘 + 11) 60. (3𝑓 + 4)(6𝑓 2 − 4𝑓 + 1) 56. (4x + 5)(6x + 1) 61. (2𝑝2 − 5)(𝑝2 + 8𝑝 + 2) 57. (2𝑏 − 9)(4𝑏 − 2) 62. (5t 2 − 3t + 6)(3t 2 − 2t + 1) Algebra II - Polynomials ~4~ NJCTL.org 63. The width of a rectangle is (4x-3) inches and the length is (3x-5) inches. Find the area of the rectangle. 64. The radius of the base of a cone is (9x - 3) cm and the height is (3x + 2) cm. Find the volume of the 1 cylinder (V = 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ). 3 65. A rectangle of (3x) ft by (5x-1) ft is cut out of a large rectangle of (6x+2)ft by (3x+4)ft. What is area of the shape that remains? 66. A pool that is 25ft by 40ft is going to have a deck of width (x + 2) ft added all the way around the pool. Write an expression in simplified form for the area of the deck. Multiply and simplify: 67. (3𝑎 − 1)(3𝑎 + 1) 70. (3𝑑 − 5𝑒)2 68. (𝑏 − 2)2 71. (5𝑓 + 9)(5𝑓 + 9) 69. (𝑐 − 1)(𝑐 + 1) 72. What is the area of a square with sides of (4x-6y) inches? Expand the following using the binomial Theorem: 73. (2𝑎 − 𝑏)6 74. (3𝑥 + 2𝑦)3 75. (5𝑦 − 4𝑧)5 76. (𝑎 + 7𝑏)4 Algebra II - Polynomials ~5~ NJCTL.org Factoring I Classwork Factoring I Homework Factoring out the GCF Factoring out the GCF 77. 6x3y2 – 3x2y 91. 8x3y – 4x2y2 78. 10p3q – 15p3q2 – 5p2q2 92. 8m3n3 – 4m2n3 – 32mn3 79. 7m3n3 – 7m3n2 + 14m3 93. -18p3q2 + 3pq Factoring ax2 + bx + c Factoring ax2 + bx + c 80. x2 – 5x – 24 94. m2 – 2m – 24 81. m2 – mn – 6n2 95. a2 – 13a + 12 82. x2 – 2xy + y2 96. n2 + n – 6 83. a2 + ab – 12b2 97. x2 – 10xy + 21y2 84. x2 – 6xy + 8y2 98. x2 + 11xy + 18y2 85. 2x2 + 7x + 3 99. 6x2 – 5x + 1 86. 6x2 – x – 2 100. 15p2 – 22p – 5 87. 5a2 + 17a – 12 101. 10m2 + 13m – 3 88. 6m2 - 5mn + n2 102. 12x2 – 7xy + y2 89. 6p2 + 37p + 6 103. 4p2 + 24p + 35 104. 15m2 – 13mn + 2n2 90. 4c2 + 20cd + 25d2 Spiral Review 105. Simplify: 106. Multiply: 5 – 4 [(-2) – (-2)] Algebra II - Polynomials 2 3 4 ∙4 2 3 107. Divide 2 3 4 ÷4 2 3 ~6~ 108. Evaluate, use x = 5: -2(-6x – 9) + 4 NJCTL.org 125. x4y + 12x3y + 20x2y Factoring II Classwork Factoring a2 – b2, a3 – b3, a3 + b3 Factoring II Homework 109. a3 – 1 Factoring a2 – b2, a3 – b3, a3 + b3 110. 25x2 – 16y2 126. y3 + 27 111. 121a2 – 16b2 127. 64m3 – 1 112. 27x3 + 8y3 128. p2 – 36q2 113. a3b3 – c3 129. m2n2 – 4 114. 4x2y2 – 1 130. x2 + 16 Factoring by Grouping 131. 8x3 – 27y3 115. 2xy + 5x + 8y + 20 Factoring by Grouping 116. 9mn – 3m – 15n + 5 132. 6mp – 2m – 15p + 5 117. 2xy – 10x – 3y + 15 133. 6xy + 15x + 4y + 10 118. 10rs – 25r + 6s – 15 134. 4rs – 4r + 3s – 3 119. 10pq – 2p – 5q + 1 135. 6tr – 9t – 2r + 3 120. 10mn + 5m + 6n + 3 136. 8mn + 4m + 6n + 3 137. 3xy – 4x – 15y + 20 Mixed Factoring 121. 3x3 – 12x2 + 36x Mixed Factoring 122. 6m3 + 4m2 – 2m 138. 3m3 – 3mn2 123. 3a3b – 48ab 139. -6x3 – 28x2 + 10x 124. 54x4 + 2xy3 Algebra II - Polynomials ~7~ NJCTL.org 140. 18a3b – 50ab 143. 2x2y2 – 2x2y – 2xy2 + 2xy 141. x4y + 27xy 142. -12r3 – 21r2 – 9r Spiral Review 144. Simplify: 8(-4) (2)(-1) + (4)2 145. Simplify: 146. Add: 172 - (12 - 4)2 + 2 2 3 7 5 2 +5 147. Evaluate, use x = -3, y = 2 -3x + 2y – xy + x Division of Polynomials: Class Work Simplify. 148. 6x3 −3x2 +9x 3x 149. (4𝑎4 𝑏 3 + 8𝑎3 𝑏 3 − 6𝑎2 𝑏 2 ) ÷ (2𝑎2 𝑏) 150. 6x3 −4x2 +7x+3 3x+1 151. (4𝑎4 + 8𝑎3 − 6𝑎2 + 3𝑎 + 4) ÷ (𝑎 − 1) Algebra II - Polynomials ~8~ NJCTL.org 152. Consider the polynomial function 𝒇(𝒙) = 𝟑𝒙𝟐 + 𝟖𝒙 − 𝟒. a. Divide 𝒇 by 𝒙 − 𝟐. b. Find 𝒇(𝟐). 153. Consider the polynomial function 𝒈(𝒙) = 𝒙𝟑 − 𝟑𝒙𝟐 + 𝟔𝒙 + 𝟖. a. Divide 𝒈 by 𝒙 + 𝟏. b. Find 𝒈(−𝟏). 154. Consider the polynomial 𝑃(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 10𝑥 − 10. Is 𝑥 + 1 one of the factors of 𝑃? Explain. 155. The volume a hexagonal prism is (3𝑡 3 − 4𝑡 2 + 𝑡 + 2) 𝑐𝑚3 and its height is (t+1) cm. Find the area of the base. (Use V=Bh) Division of Polynomials: Homework Simplify. 156. 16x5 −12x3 +24x2 4x2 157. (4𝑎 4 𝑏3 + 8𝑎 3 𝑏 3 − 16𝑎 2 𝑏 2 ) ÷ (4𝑎𝑏 2 ) Algebra II - Polynomials ~9~ NJCTL.org 158. (3f 3 + 18f − 12)(3f 2 )−1 159. 3x3 −3x2 +9x+2 x+3 160. Consider the polynomial function 𝒇(𝒙) = 𝒙𝟑 − 𝟐𝟒. a. Divide 𝒇 by 𝒙 − 𝟐. b. Find 𝒇(𝟐). 161. Consider the polynomial function 𝒈(𝒙) = 𝒙𝟑 + 𝟓𝒙𝟐 − 𝟖𝒙 + 𝟕. b. Divide 𝒈 by 𝒙 + 𝟏. c. Find 𝒈(−𝟏). 162. Consider the polynomial 𝑃(𝑥) = 2𝑥 3 + 5𝑥 2 − 12𝑥 + 5. Is 𝑥 − 1 one of the factors of 𝑃? Explain. Algebra II - Polynomials ~10~ NJCTL.org 163. (8f 3 )(2f + 4)−1 164. The volume a hexagonal prism is (4𝑡 3 − 3𝑡 2 + 2𝑡 + 2) 𝑐𝑚3 . The area of the base, B is (t-1) cm2. Find the height of the prism. (Use V=Bh) 165. Consider the polynomial 𝑃(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 + 3𝑥 3 − 28𝑥 2 − 36𝑥 + 144. a. Is 1 a zero of the polynomial 𝑃? b. Is 𝑥 + 3 one of the factors of 𝑃? Algebra II - Polynomials ~11~ NJCTL.org Characteristics of Polynomial Functions: Class Work For each function or graph answer the following questions: a. Does the function have even degree or odd degree? b. Is the lead coefficient positive or negative? c. Is the function even, odd or neither? 166. 167. 168. 169. Is each function below odd, even or neither? 170. 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 4 + 3𝑥 2 − 2 171. 𝑦 = 5𝑥 5 − 3𝑥 + 1 172. 𝑔(𝑥) = −2𝑥(4𝑥 2 − 3𝑥) 173. ℎ(𝑥) = 4𝑥 174. For each function in #’s 170 – 173 above, describe the end behavior in these terms: as x∞, f(x) ____, and as x -∞, f(x) _____. Is each function below odd, even or neither? How many zeros does each function appear to have? 175. Algebra II - Polynomials 176. 177. ~12~ 178. NJCTL.org Characteristics of Polynomial Functions: Homework For each function or graph answer the following questions: a. Does the function have even degree or odd degree? b. Is the lead coefficient positive or negative? c. Is the function even, odd or neither? 179. 180. 181. 182. Is each function below an odd-function, an even-function or neither. 183. 𝑓(𝑥) = 5𝑥 4 − 6𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 184. 𝑦 = 5𝑥 5 − 3𝑥 3 + 1𝑥 185. 𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥 2 (4𝑥 3 − 3𝑥) 4 186. ℎ(𝑥) = − 5 𝑥 2 + 2 187. For each function in #’s 183 – 186 above, describe the end behavior in these terms: as x∞, f(x) ____, and as x -∞, f(x) _____. Are the following functions odd, even or neither? How many zeros does the function appear to have? 188. 189. 190. 191. Analyzing Graphs and Tables of Polynomial Functions: Class Work Identify any zeros (either as an integer or as an interval of x-values) of the function. Label any relative maximum and minimum. 192. 193. Algebra II - Polynomials ~13~ NJCTL.org 194. 196. 195. x -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 f(x) 5 1 -1 0 2 1 -1 x -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 197. f(x) -4 0 2 1 -1 -3 -1 198. x -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 f(x) 2 -3 -4 -1 2 5 -2 Analyzing Graphs and Tables of Polynomial Functions: Homework Identify any zeros (either as an integer or as an interval of x-values) of the function. Label any relative maximum and minimum. 199. 200. 201. 202. 203. x -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 f(x) 6 2 1 3 1 -1 0 Algebra II - Polynomials 204. 205. x -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 f(x) 2 4 2 -2 0 3 1 ~14~ x -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 f(x) 4 -2 -3 -1 1 3 7 NJCTL.org Zeros and Roots of a Polynomial Function: Class Work For each graph below and its given degree, name the real zeros and their multiplicity, and state the number of imaginary zeros. 206. 207. 208. 4th degree 4th degree 5th degree Name all of the real and imaginary zeros and state their multiplicity. 209. 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 − 3) 212. ℎ(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 (𝑥 − 10)(𝑥 + 1) 210. 𝑔(𝑥) = (𝑥 2 − 1)(𝑥 2 + 1) 213. 𝑦 = (𝑥 2 − 9)(𝑥 + 3)2 (𝑥 2 + 9) 211. 𝑦 = (𝑥 + 1)2 (𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 − 2) Zeros and Roots of a Polynomial Function: Homework For each graph below and its given degree, name the real zeros and their multiplicity, and state the number of imaginary zeros. 214. 215. 3rd degree Algebra II - Polynomials 216. 4th degree ~15~ 6th degree NJCTL.org Name all of the real and imaginary zeros and state their multiplicity. 217. 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 1)(𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 − 3) 220. ℎ(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 (𝑥 − 7)(𝑥 − 6)𝑥(2𝑥 + 4)(𝑥 − 5) 218. 𝑔(𝑥) = (𝑥 2 − 4)(𝑥 2 + 4) 221. 𝑦 = (𝑥 + 4)2 (𝑥 2 − 16)(𝑥 2 + 16) 219. 𝑦 = (𝑥 + 7)2 (4𝑥 2 − 64) Zeros and Roots of a Polynomial Function by Factoring: Class Work Name all of the real and imaginary zeros and state their multiplicity. 222. 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 3 + 16𝑥 2 + 30𝑥 225. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 8𝑥 2 − 9 223. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 + 9𝑥 2 226. 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 16𝑥 − 15 224. 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 2 − 8𝑥 − 12 227. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 + 4𝑥 2 − 25𝑥 − 100 228. Consider the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 2 − 𝑥 − 3. a. Use the fact that 𝑥 + 3 is a factor of 𝑓 to factor this polynomial. b. Find the x-intercepts for the graph of 𝑓. c. At which 𝒙-values can the function change from being positive to negative or from negative to positive? d. For 𝒙 < −𝟑, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? e. For −𝟑 < 𝒙 < −𝟏, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? Algebra II - Polynomials ~16~ NJCTL.org f. For −𝟏 < 𝒙 < 𝟏, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? g. For 𝒙 > 𝟏, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? h. Use the information generated in parts (f)–(i) to sketch a graph of 𝒇. Zeros and Roots of a Polynomial Function by Factoring: Homework Name all of the real and imaginary zeros and state their multiplicity. 229. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 − 3𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 + 6 232. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 𝑥 2 − 30 230. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 + 𝑥 2 − 12 233. 𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑥 4 − 5𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 − 2 231. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 + 5𝑥 2 − 9𝑥 − 45 234. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 − 5𝑥 3 + 20𝑥 − 16 235. Consider the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 − 6𝑥 2 − 9𝑥 + 14. a. Use the fact that 𝑥 + 2 is a factor of 𝑓 to factor this polynomial. b. Find the x-intercepts for the graph of 𝑓. Algebra II - Polynomials ~17~ NJCTL.org c. At which 𝒙-values can the function change from being positive to negative or from negative to positive? d. For 𝒙 < −𝟐, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? e. For −𝟐 < 𝒙 < 𝟏, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? f. For 𝟏 < 𝒙 < 𝟕, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? g. For 𝒙 > 𝟕, is the graph above or below the 𝒙-axis? How can you tell? h. Use the information generated in parts (f)–(i) to sketch a graph of 𝒇. Writing Polynomials from Given Zeros: Class work Write a polynomial function of least degree with integral coefficients that has the given zeros. 236. −3, −2, 2 240. 237. −3, −1, 2, 4 Algebra II - Polynomials ~18~ NJCTL.org 238. ±√3, 1 , 3 −5 241. 3 239. 2, 3, 𝑖, −𝑖, 5 Writing Polynomials from Given Zeros: Homework Write a polynomial function of least degree with integral coefficients that has the given zeros. 242. 1, 2, 3 4 246. 243. −1, 3, 0 244. 0 (𝑚𝑢𝑙𝑡. 2), −5, 1 245. −2𝑖, 2𝑖, −5(𝑚𝑢𝑙𝑡. 3) 247. Algebra II - Polynomials ~19~ NJCTL.org UNIT REVIEW Multiple Choice 6p8 q9 −2 1. Simplify the following expression: ((2p3 q4 )3 ) a. b. c. d. 3 4pq3 9 16p2 q6 4pq3 3 16p2 q6 9 2. The sides of a rectangle are (2x2 – 11x +1) ft and (3x – 4) ft find the perimeter of the rectangle. a. (2x2 – 8x – 3) ft b. (4x2 – 16x – 6) c. (5x3 – 11x – 3) ft d. (6x3 – 41x2 + 47x – 4) ft2 3. The sides of a rectangle are (2x2 – 11x +1) ft and (3x – 4) ft find the area of the rectangle. a. (6x3 – 41x2 – 41x – 4) ft2 b. (6x3 – 25x2 + 47x – 4) ft2 c. (6x3 – 41x2 + 47x – 4) ft2 d. (6x3 – 33x – 4) ft2 4. A pool that is 10ft by 20 ft is going to have a deck (x) ft added all the way around the pool. Write an expression in simplified form for the area of the deck. a. (60x + 4x 2 )ft 2 b. (30x + x 2 )ft 2 c. (200 + 60x + 4x 2 )ft 2 d. (200 + 30x + x 2 )ft 2 5. What is the area of a square with sides (6x – 2) inches? a. (36x 2 − 4) in2 b. (36x 2 + 4) in2 c. (36x 2 − 12x − 4) in2 d. (36x 2 − 24x + 4) in2 6. 7. 27w3 x5 −12w4 x3 +24w3 x2 is equivalent 6w2 x2 9wx3 −4w2 x+4w a. 3 9wx3 b. 2 − 2w 2 x + 4w 9wx3 −4w2 x c. + 4w 3 3 2 9wx +4w x+8w d. 2 2 (2𝑎4 (𝑎 to which of the following? − 6𝑎 + 4) ÷ − 2) a. 2𝑎3 − 3𝑎 − 2 b. 2𝑎3 − 3𝑎2 − 2 c. 2𝑎3 + 4𝑎2 − 2𝑎 − 4 + d. 2𝑎3 + 4𝑎2 + 2𝑎 + 4 + Algebra II - Polynomials −4 𝑎−2 12 𝑎−2 ~20~ NJCTL.org 8. A box has volume of (3x 2 − 2x − 5) cm3 and a height of (x+1) cm. Find the area of the base of the box. a. (3x + 2) cm2 b. (3x – 2) cm2 c. (3x + 5) cm2 d. (3x – 5) cm2 9. Using the graph, decide if the following function has an odd or even degree and the sign of the lead coefficient. a. odd degree; positive b. odd degree; negative c. even degree; positive d. even degree; negative 10. Which of the following equations is of an odd-function? a. 𝑦 = 3𝑥 5 − 2𝑥 b. 𝑦 = 5𝑥 7 − 3𝑥 3 + 9 c. 𝑦 = 𝑥 5 (𝑥 7 + 𝑥 5 ) d. 𝑦 = 7𝑥 10 x f(x) 11. What value should A be in the table so that the function has 4 zeros? -2 6 a. -2 -1 A b. 0 0 2 c. 1 1 3 d. 3 2 1 3 -1 12. Name all of the real and imaginary zeros and state their multiplicity: 4 0 𝑦 = (𝑥 2 + 8𝑥 + 16)(4𝑥 2 + 64) a. Real zeros: -4 with multiplicity 2; Imaginary zeros: ± 4i each with multiplicity 1 b. Real zeros: -4 with multiplicity 3, 4 with multiplicity 1; No imaginary zeros c. Real zeros: -4 with multiplicity 4; No imaginary zeros d. Real zeros: -4 with multiplicity 2; Imaginary zeros: 2i with multiplicity 2 Extended Response 1. Graph 𝑦 = (𝑥 + 2)2 (𝑥 + 1)𝑥(𝑥 − 1)(𝑥 − 3). Name the real zeros and their multiplicity. Algebra II - Polynomials ~21~ NJCTL.org 2. Given the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 2 − 6. Write the function in factored form. 3. Name all of the real and imaginary zeros and state their multiplicity of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 − 10𝑥 2 + 11𝑥 + 70 4. Write a polynomial function of least degree with integral coefficients that has the given zeros. -4.5, -1, 0, 1, 4.5 5. Consider the graph of a degree 5 polynomial shown to the right, with 𝑥-intercepts −4, −2, 1, 3, and 5. Write an equation for a possible polynomial function that the graph represents. Algebra II - Polynomials ~22~ NJCTL.org 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Answer Key 25. 8x2-8x-6 26. c3+4c2-3c-12 27. 2m3-2m2-17m+15 28. 12f3+22f2-18f+5 29. 12t4-11t3+41t2-11t+9 30. Area = (30x2-23x-14) in.2 31. Area = 𝜋(63x3+186x2+160x+32) m2 32. Area = (2x2+12x+2) ft.2 33. Areadeck = (4x2+100x) ft.2 34. b2+4b+4 35. c2-2c+1 36. 4d2+16de+16e2 37. 25f2-81 38. (9x2+12x+4) in.2 𝑗6 −64𝑔9 ℎ6 16𝑘 6 9𝑚2 𝑛4 64𝑞 6 9𝑝2 80𝑟 15 𝑡 2 𝑠8 3 4𝑢2 𝑣 18 27𝑤 3 𝑦 3 8𝑥 3 𝑧 33 𝑔16 𝑗 12 81ℎ12 4𝑘 8 𝑛8 9𝑚6 4𝑝2 𝑞2 5𝑠 27 𝑡 8 2𝑟 2 8𝑢8 𝑣 3 39. 32x5+320x4y+1280x3y2+2560x2y3+2560xy4+1024y5 3 25𝑤 12 41. 729x6-5832x5z+19440x4z2-34560x3z3+34560x2z4- 40. 343a3+147a2b+21ab2+b3 18432xz5+4096z6 4𝑧 24 Yes, 5x2, degree: 2, monomial/quadratic, 5 4 Yes, -3y 2 +3 y, degree: 2, 7 binomial/quadratic, -3 15. Yes, 5a3 -6a+3, degree: 3, trinomial/cubic, 5 16. Not a polynomial function 17. Not a polynomial function 18. 6g2-4g-7 19. -4t 2 +t+13 20. 7𝑥 5 + 13𝑥 4 + 2𝑥 3 + 6𝑥 −1 21. −12𝑥 3 + 6𝑥 2 − 6𝑥 − 3 22. Perimeter = (6x2+12x-1) inches 23. -8a3b+6a2b2+12a2b 24. 35j4k3+63j3k2-14jk3+70jk2 Algebra II - Polynomials ~23~ 42. y4-20y3z+150y2z2-500yz3+625z4 Yes, 0.4𝑥 3 + √2𝑥 2 , degree: 3, binomial/cubic, 0.4 44. Not a polynomial function 45. Yes, already in std form, degree: 4, no specific name/quartic, 11 46. Yes, already in std form, degree: 2, trinomial/quadratic, 6/11 47. Not a polynomial function 48. -2n2-6n-3 49. -3g3+10g2-5g-11 50. -3x4+7x3+2x2-19x-16 51. 6x3-7x2+24x-33 52. Perimeter = (10x2+24x-10) inches 53. 12x3-20x2-8x 54. -18a3b+30a2b2+42ab 43. NJCTL.org 71. 16j5k4+48j4k3-40j2k4+88j2k3 24x2+34x+5 8b2-40b+18 6c3+4c2-12c-8 6m3-27m2+22m+20 18f3+12f2-13f+4 2p4+16p3-p2-40p-10 15t4-19t3+29t2-15t+6 Area = (12x2-29x+15) in.2 Area = 81x3-27x+6) m2 Area = (3x2+33x+8) in.2 Areadeck = (4x2+146x+276) ft.2 9a2-1 b2-4b+4 c2-1 9d2-30de+25e2 25f2+90f+81 72. Area = (16x2-48xy+36y2) in.2 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 94. (m - 6)(m + 4) 95. (a - 12)(a - 1) 96. (n + 3)(n - 2) 97. (x – 7y)(x – 3y) 98. (x + 9y)(x + 2y) 99. (3x – 1)(2x – 1) 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 73. 64a6-192a5b+240a4b2-160a3b3+60a2b4-12ab5+b6 74. 112. 27x3+54x2y+36xy2+8y3 113. 75. 3125y5-12500y4z+20000y3z2-16000y2z3+6400yz4-1024z5 114. 76. a4+28a3b+294a2b2+1372ab3+2401b4 115. 77. 3x2y(2xy – 1) 116. 78. 5p2q(2p – 3pq – q) 117. 79. 7m3(n3 – n2 + 2) 118. 80. (x – 8)(x + 3) 119. 81. (m – 3n)(m + 2n) 120. 82. (x – y)(x – y) 121. 83. (a + 4b)(a – 3b) 122. 84. (x – 4y)(x – 2y) 123. 85. (2x + 1)(x + 3) 124. 86. (3x – 2)(2x + 1) 125. 87. (5a – 3)(a + 4) 126. 88. (2m – n)(3m – n) 127. 89. (6p + 1)(p + 6) 128. 90. (2c + 5d)(2c + 5d) 129. 91. 4x2y(2x-y) 130. 92. 4mn3(2m2-m-8) 131. 93. 3pq(-6p2q+1) Algebra II - Polynomials 132. ~24~ (3p – 5)(5p + 1) (2m + 3)(5m – 1) (3x – y)(4x – y) (2p + 7)(2p + 5) (3m – 2n)(5m – n) 5 77 6 33 56 82 (a – 1)(a2 + a + 1) (5x – 4y)(5x + 4y) (11a – 4b)(11a + 4b) (3x + 2y)(9x2 + 6xy + 4y2) (ab – c)(a2b2 + abc + c2) (2xy – 1)(2xy + 1) (x + 4)(2y + 5) (3m – 5)(3n – 1) (2x – 3)(y – 5) (5r + 3)(2s – 5) (2p – 1)(5q – 1) (5m + 3)(2n + 1) 3x(x – 6)(x + 2) 2m(3m – 1)(m + 1) 3ab(a – 4)(a + 4) 2x(3x + y)(9x2 – 3xy + y2) x2y(x + 10)(x + 2) (y + 3)(y2 – 3y + 9) (4m – 1)(16m2 + 4m + 1) (p – 6q)(p + 6q) (mn – 2)(mn + 2) Not Factorable (2x – 3y)(4x2 + 6xy + 9y2) (2m – 5)(3p – 1) NJCTL.org 133. 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. (3x + 2)(2y + 5) (4r + 3)(s – 1) (3t – 1)(2r – 3) (4m + 3)(2n + 1) (x – 5)(3y – 4) 3m(m – n)(m + n) -2x(3x – 1)(x + 5) 2ab(3a – 5)(3a + 5) xy(x + 3)(x2 – 3x + 9) -3r(4r + 3)(r + 1) 2xy(x – 1)(y – 1) 145. 32 227 146. 7 147. 150. 16 2x2-x+3 2a2b2+4ab2-3b 2x2 – 2x + 3 151. 4a3+12a2+6a+9 + 152. a. 3𝑥 + 14 + 153. a. 𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 10 − 154. Yes, because P(-1) = 0. 155. B = (3t2-7t + 8 - 156. 4x3-3x+6 a3b+2a2b- 4a 144. 148. 149. 157. a. No b. Yes 166. Odd; positive; neither 167. Even; negative; even 168. Even; positive; neither 169. Odd; negative; neither 170. Even function 171. Neither 172. Neither 173. Odd 174. 170: ∞, ∞ 171: ∞, −∞ 172: −∞, ∞ 173: ∞, −∞ 175. Odd function; 3 zeros 176. Even function; 2 zeros 177. Neither; 3 zeros 178. Even function; 2 zeros 179. Odd; negative; neither 180. Even; negative; even 181. Even; positive; even 182. Odd; negative; odd 183. Neither 184. Odd function 185. Odd function 186. Even function 187. 184: ∞, ∞ 185: ∞, −∞ 186: ∞, −∞ 187: −∞, − ∞ 188. Even function; 2 zeros 189. Odd function; 1 zero 190. Neither; 2 zeros 191. Odd function; 1 zero 192. Zeros: between x= -2 and x= -1, at x= 0, between x=1 and x= 2; relative max at x= -1; relative min at x=1 193. Zeros: between x=-2 and x=-1, between x=-1 and x=0, between x=0 and 165. 31 35 6 4 𝑓 𝑓2 13 𝑎−1 24 b. 24 𝑥−2 6 2 𝑥+1 b. -2 ) cm.2 𝑡+1 158. f+ - 159. 3x2-12x+45 - 160. a. 𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 + 4 − 161. a. 𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 − 12 + 162. Yes, because P(1) = 0. 163. 4f2-8f+16 - 164. height = 4t2+t+3+ 133 𝑥+3 16 𝑥−2 19 b. -16 𝑥+1 b. 19 32 𝑓+2 Algebra II - Polynomials 5 𝑡−1 cm ~25~ NJCTL.org x=1, between x=1 and x=2; relative max at x=-1 and x=1; relative min at x=0 194. Zeros: at x=-2 and x=2; no relative max; relative min at x=0 195. Zeros: between x=-2 and x=-1, between x=-1 and x=0 , at x=0, between x=0 and x=1, between x=1 and 2; relative max at x≈-.5 and x≈1.5; relative min at x≈-1.5 and x≈.5 196. Zeros: between x=-1 and 0, at x=1, between x=3 and 4; relative max x=2; relative min at x=0 197. Zeros: at x=-1, between x=1 and 2; relative max at x=0; relative min at x=3 198. Zeros: between x=-2 and x=-1, between x=1 and x=2, between x=3 and x=4; relative max at x=3; relative min at x=0 199. Zero: at x=2; no relative max or min 200. Zeros: at x≈-2, x≈-1, x≈0, x≈1,and x≈2; relative max at x=-1.5 and x=.5; relative min at x=-.5 and x=1.5 201. Zeros: between x=-2 and x=-1, between x=1 and x=2; relative max at x=0; relative min at x=-1 and x=1 202. No zeros; relative max at x=0; relative min at x=-1 and x=1 203. Zeros: between x=2 and 3, and at x=4; relative max at x=1; relative min at x=0 and x=3 204. Zeros: between x=0 and 1, at x=2; relative max at x=-1 and x=3; relative min at x=1 Algebra II - Polynomials ~26~ Zeros: between x=-2 and x=-1, between x=1 and x=2; no relative max; relative min at x=0 206. Real zeros: at x=-2 and x=2 ( both mult. of 2); no imaginary zeros 207. Real zeros: at x=3 (mult. of 2); 2 imaginary zeros 208. Real zeros: at x= −3, x = -1, x=3 (all mult. of 1), x=3 (mult. of 2); no imaginary zeros 209. Real zeros: at x=-1 (mult. of 1), at x=-2 (mult. of 2) and x=3 (mult. of 1) 210. Real zeros: at x=-1 (mult. of 1), at x=1 (mult. of 1); Imaginary zeros: at x= i (mult. of 1), at x=-i (mult. of 1) 211. Real zeros: at x=-1 (mult. of 2), at x=2 (mult. of 1), at x=-2 (mult. of 1) 212. Real zeros: at x=0 (mult. of 2), at x=10 (mult. of 1), at x=-1 (mult. of 1) 213. Real zeros: at x=-3 (mult. of 3), at x=3 (mult. of 1); Imaginary zeros: at x=3i (mult. of 1), at x=-3i (mult. of 1) 214. Real zeros: at x=-2 (mult. of 1) and at x=-1 (mult. of 1) and at x = 1 (mult. of 1); no imaginary zeros 215. Real zeros: at x=-2 and x=2 (each mult. of 1); 2 imaginary zeros 216. Real zeros: at x=-1.5 (mult. of 1) x=2 (mult. of 1) and at x=3 (mult. of 2); 2 imaginary zeros 217. Real zeros: at x=1 (mult. of 1), at x=-3 (mult. of 2), at x=3 (mult. of 1) 205. NJCTL.org Real zeros: at x=2 (mult. of 1), at x=-2 (mult. of 1); Imaginary zeros: at x=2i (mult. of 1), at x=-2i (mult. of 1) 219. Real zeros: at x=-7 (mult. of 2), x=4 (mult. of 1), at x=-4 (mult. of 1) 220. Real zeros: at x=0 (mult. of 4), at x=7 (mult. of 1), at x=6 (mult. of 1), at x=-2 (mult. of 1), at x=5 (mult. of 1) 221. Real zeros: at x=-4 (mult. of 3), at x=4 (mult. of 1); Imaginary zeros: at x=4i (mult. of 1), at x=-4i (mult. of 1) 222. Real zeros: at x=0 (mult. of 1), at x=-3 (mult. of 1), at x=-5 (mult. of 1 223. Real zeros: at x=0 (mult. of 2) 2 Imaginary zeros: at x= 3i (mult. of 1), at x=-3i (mult. of 1) 224. Real zeros: at x=-1.5 (mult. of 1), at x= 2 (mult. of 1), at x=-2 (mult. of 1) 225. Real zeros: at x=-3 (mult. of 1), at x=3 (mult. of 1); 2 Imaginary zeros: at x= i (mult. of 1), at x=-i (mult. of 1) 226. Real zeros: at x=-1 (mult. of 1), at 5 x=- (mult. of 1), at x=3 (mult. of 1) 2 227. Real zeros: at x=-5 (mult. of 1), at x=-4 (mult. of 1), at x=5 (mult. of 1) 228. a. f(x) = (x + 3)(x + 1)(x – 1) b. -3, -1, 1 c. -3, -1, 1 d. Below, f(-4) is negative, OR since the degree is 3 and the leading coefficient is positive. e. Above, crosses at -3 f. Below, crosses at -1 218. Algebra II - Polynomials ~27~ g. Above, crosses at 1 h. 229. 3 Real zeros: at 𝑥 = √2 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = −√2 (mult. of 1), at x=3 (mult. of 1) 230. Real zeros: at 𝑥 = √3 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = −√3 (mult. of 1); 2 Imaginary zeros: at 𝑥 = 2𝑖 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = −2𝑖 (mult. of 1) 231. Real zeros: at x=-3 (mult. of 1), at x= 3 (mult. of 1), at x=-5 (mult. of 1) 2 Real zeros: at 𝑥 = √6 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = −√6 (mult. of 1); 232. 2 Imaginary zeros: at 𝑥 = 𝑖√5 (mult. of 233. 1), at 𝑥 = −𝑖√5 (mult. of 1) Real zero: at 𝑥 = 2 (mult. of 1) and at 1 x=− (mult. of 1); Imaginary zeros: at 𝑥 = 3 𝑖 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = −𝑖 (mult. of 1) 234. 4 Real zeros: at 𝑥 = 1 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = 4 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = −2 (mult. of 1), at 𝑥 = 2 (mult. of 1) 235. a. f(x) = (x + 2)(x – 7)(x – 1) b. -2, 1, 7 c. -2, 1 , 7 d. Below, f(-3) is negative, or since the degree is 3 and the leading coefficient is positive. e. Above, crosses at -2 NJCTL.org f. Below, crosses at 1 g. Above, crosses at 7 h. 236. 237. 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 − 2)(𝑥 − 4) 238. 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 2 − 3) (𝑥 − ) (𝑥 + 5) 239. 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 2)(𝑥 − 3)(𝑥 2 + 1) (𝑥 − 5) 240. 241. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥(𝑥 − 2)2 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 1)2 (𝑥 + 1)2 242. 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 1) (𝑥 − 4) (𝑥 − 2) 243. 244. 245. 246. 247. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥(𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 − 3) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 (𝑥 + 5)(𝑥 − 1) 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 2 + 4)(𝑥 + 5)3 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥(𝑥 − 1.5)(𝑥 + 1.5) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥(𝑥 2 − 1)(𝑥 2 − 4) 1 3 3 3 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 − 2) REVIEW 1. D 2. B 3. C 4. A 5. 6. 7. 8. D B D D 9. B 10.A 11.A 12.A 1. x = −2 (mult. of 2) x = −1 (mult. of 1) x = 0 (mult. of 1) x = 1 (mult. of 1) x = 3 (mult. of 1) 2. 3(x − 1)(x 2 + 2x + 2) 3. x = −2 (mult. of 1) x = 5 (mult. of 1) x = 7 (mult. of 1) 4. f(x) = x(x 2 − 1)(x 2 − 20.25) 5. f(x) = (x + 4)(x + 2)(x – 1)(x – 3)(x – 5) Algebra II - Polynomials ~28~ NJCTL.org