class 7 humidity and rainfall
advertisement

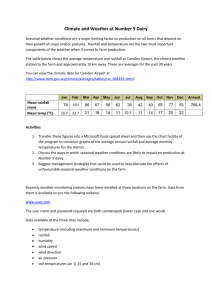
CH: 25 HUMIDITY AND RAINFALL Answer the following questions in one or two sentences. 1. Define humidity. The amount of water vapour in the atmosphere is called humidity. 2. What is condensation? Condensation is the process in which water vapour in the air changes into water. 3. Define precipitation. Precipitation is the process in which condensed water vapour falls down on the surface of the earth in various forms such as rain, snow, sleet and hail. 4. What do you understand by dew point. The temperature at which condensation takes place is called the dew point. 5. What is sleet? Sleet is a form of precipitation which is a combination of snow fl akes and rain falling together. Answer the following questions in four or five sentences. 1. What is fog? How is it different from mist? During winters humid air comes into contact with the cold surface of the earth due to which condensation takes around floating dust particles forming a cloud at ground level. This is called fog. Thin fog is termed as mist. Fog reduces visibility and often causes accidents. 2. Explain relief rainfall. Relief or orographic rainfall is the type of rainfall that takes place when moisture-laden wind from the sea is forced to rise above a hill or a mountain range. On rising, the wind cools and drops most of its moisture on the mountain side facing the wind. The other side remains relatively dry. For example, Mumbai on the west coast being on the wind facing side or the windward side of the Western Ghats receives more rain during monsoons than Pune which is on the opposite or the leeward side. 3. Differentiate between relief rainfall and convectional rainfall. Relief rainfall takes place due to the relief or height of a place. When moisture-laden wind from the sea is forced to rise above a hill or a mountain range, the wind cools and drops most of its moisture on the mountain side facing the wind. Convectional rainfall, on the other hand, is caused by local heating due to which air rises vertically. On reaching a certain height, condensation takes place, which is followed by precipitation at the same place. Such rainfall occurs mainly in equatorial areas. 4. What is cyclonic rainfall? This type of rainfall takes place when a cold air mass and a warm air mass strike each other face to face. As cold air is denser, it remains close to the ground, while the warm air rises above it. As it rises, it expands and cools resulting in rainfall. Rainfall of this type is mostly seen in the tropical and temperate regions where cold polar winds meet the warm westerly winds. 5. Explain the occurrence of hail. When falling raindrops are thrown back high above the clouds by rising air currents, they freeze and become ice pellets. If the tossing process takes place many times then more layers of ice form around the pellets giving them an onion like pattern. When these pellets become heavy they fall down as hailstones. 6. What do you understand by windward and leeward sides? The side of a mountain that faces the rain bearing winds from the sea is called the windward side. It receives heavy rain. Winds after crossing the mountain are left with little moisture for the other side of the mountain which remains relatively dry. This dry side is called the leeward or the rain shadow side of the mountain.