SS8 Topographic Profiles
advertisement

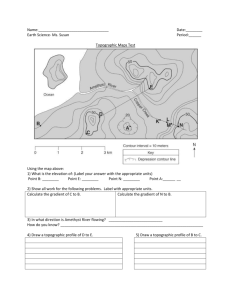
SS8: Mapping Unit How do We Show Elevation on Maps? Contour lines are a map’s way of showing elevation (how high the land is). They join together places of the same height and form patterns that help us to imagine what the land actually looks like. ‘Naismith’s rule’ Remember that the closer together the contour lines are, the steeper the land. Contour lines that are wide apart show us that the land is flatter. When you're travelling across steep landscapes (where contour lines are very close together) it will add time on to your journey. Naismith said that you should allow an extra minute of walking time for every 10 metres of height that you climb. Contour lines are usually drawn at 10 metre intervals on a 1:50 000 scale map and at 5 metre intervals on a 1:25 000 scale map. Page 1 SS8: Mapping Unit Drawing Topographic Profiles A topographic profile is taking a flat image of a topographic map and producing an image of the map from the side. Essentially this is taking a view of a mountain from on top and then drawing it from the side. This is a fairly simple concept to understand and once understood is quick and simple to do. When drawing a profile first you need a section of map that your going to draw your profile on. (Line A-B) Next you take a sheet of paper and mark off each line that intersects the A-B line. Looking at the original contour lines, you can see that only two of them were marked, but since you can see that there are 5 lines between each marked line you can figure out that each line is 10 apart. Page 2 SS8: Mapping Unit After the lines are copied and labeled you then copy this onto a topographic profile. Then connect the points together to form a smooth curve. Notes: 99% of all hills don't have flat tops so don't give yours one. If it doesn't cross a contour line don't make the profile cross one. Congratulations! You now have a topographic profile. Page 3 SS8: Mapping Unit Topographic Profiles Base your answers to the following questions on the topographic map below. Points A, B, C, D, and X represent locations on the map. Elevations are measured in metres. ROCK MOUNTAIN 0 2 4 6 N km 1. What is the elevation of each of the following points? A. _____________ B. _____________ C. _____________ D. _____________ X. _____________ 2. In what direction does Fish Creek Flow? _______________________ 3. Which side of Rock Mountain is the steepest? (compass direction) ____________________ 4. Which side of Rock Mountain has the gentlest slope? (compass direction) __________________ 5. Label the Spur on Rock Mountain. 6. Think about BOLTSS. What is our map missing? Page 4 SS8: Mapping Unit 7. On the grid below, construct a topographic profile (“draw the hill”) from point A to point B by following the directions below. a. Plot the elevation along line AB by marking with a each point where a contour line is crossed by line AB. Points A and B have been plotted for you. b. Complete the profile by correctly connecting the plotted points with a smooth, curved line. Elevation (metres) Distance (kilometres) Page 5