Description
advertisement
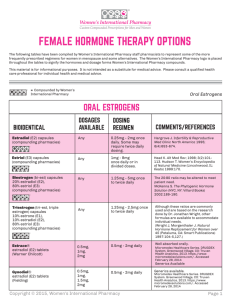
Estrogens Estrogens are synthesized mainly in the ovaries, the placenta, and the adrenal glands. A minute amount of estradiol is synthesized in the testes. Physiological actions of estrogens: Action Category Growth and development of muscular and mucosal Uterus&tube elements of Elements of the uterus and the fallopian tubes. Myometrium Stimulate the growth of the myometrium at puberty and during pregnancy. Endometrium Increase the endothelium and rebuild the endometrim In the proliferative phase Vagina Development of the epithelial layer & enhance glandular secretion.cornification and deposition of glycogen. Increase Participate in duct formation & with other hormones in preparation of the breast for lactation at puberty and pregnancy. Incresebindingof t4then decrease free →physiological goiter. Inhibits bone resorption [ ppt of calcium] Increase HDL & triglyceride but decrease LDL & cholesterol. Increase synthesis of coagulation factors Large doses decrease FSH &LH[feed back mechanism] Beast Thyroid Bone Lipids Blood Pituitary Pharmacokinetic Natural estrogen : their esterified or or conjugated derivatives are absorbed through GIT, skin and mucous membranes. Estradiol is rapidly metabolized and partially inactivated by microsomal enz. Of the liver. Micronized estradiol as N. estradiol but first pass metabolism not sufficient to lessen effectiveness when taken orally. Synthetic estrogen: these compound as ethinyl estradiol are well absorbed. Mestranol demythylated to ethinyl estradiol [fat soluble]are stored in adipose tissues. They are slowly released. The synthetic have a prolonged action and higher potency compared to N estrogen.To avoid first pass metabolism may be administrated transdermal[patch,topical gel,sprayand topical emulsion]transvaginal [tab, cream ring] or by injections. Its metabolites execreted in bile and urine. Estrogen preparations: They are divided into: Natural: Estradiol, Estrone and Estriol Semisynthetic: they include - Conjugated estrogens (ethinyl estradiol &piprazine estrone sulfate) - Esterified estrogens (estradiol cypionate , valerate ) Non steroid estrogen that include: - Synthetic: dienestrol, diethylstilbestrol, benzestrol, hexestrol, methestrol, methallenestril, and chlorotrianisene - Plant products with estrogenic activity are called phytoestrogens. - Those produced by fungi are known as mycoestrogens. Therapeutic uses: 1-Replacement therapy in cases of postmenopausal , surgical [used with progesterone to decrease risk of endometrial carcinoma associated unopposed estrogen] 1ry hypogonadism & 1ry amenorrhea, 1ry infertility. Delayed puberty & hypopitutrism & castration Menopausal syndrome[ shortest time lowest dose] ,Premature menopause, surgical menopause Bleeding,dysmenorrhea Atrophic vaginitis, osteoporosis. 2-Supression of ovulation in cases of: Dysmenorrhea ,dysfunction uterine bleeding Contraceptive pills 3-Suppress excessive androgen secretion to treat acne valgaris & hirsutism.&cancer prostate in males. 4-Suppression of postpartum lactation NB:They was used in the treatment of atherosclerosis but they are now obsolete due to high side effects. Adverse effects: Breakthrough bleeding. Breast tenderness. Thromboembolic disorders. Hypertension. Cholestasis. Increase incidence of certain types of cancer eg cancer breast , endometrium and vaginal adenocarcinoma in young women whose mothers were treated with diethylstilbestrol in an effort to prevent miscarriage. Nausea ,peripheral edema ,headach. Commonly Used Estrogens. Preparation Average Replacement Dosage Ethinyl estradiol 0.005–0.02 mg/d Micronized estradiol 1–2 mg/d Estradiol cypionate 2–5 mg every 3–4 weeks Estradiol valerate 2–20 mg every other week Estropipate Semisythetic 1.25–2.5 mg/d Conjugated, esterified, or mixed estrogenic substances: Oral 0.3–1.25 mg/d Injectable 0.2–2 mg/d Transdermal Patch Quinestrol 0.1–0.2 mg/week Chlorotrianisene 12–25 mg/d Methallenestril Mestranol 3–9 mg/d 0.05 mg/d --------------------------------------------------- Antiestrogens 1-Estrogen receptor antagonists[pituitary gonadal axis must be intact] Partial agonists: [non stroid] Clomophene (clomid) and tamoxifen (nolvadex) modify or inhibit the action of estrogens. Pure antagonists: Fulvestrant Mechanism of action: a. They bind to the cytoplasmic estrogen receptors that are then translocated to the nucleus so, interfering with the physiologic action of estrogens in pitutary. b. By interfering with the normal hypothalamic and hypophyseal feedback inhibition of estrogen synthesis, these agents cause increased secretion of luteinizing honnone-releasing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone-releasing bonnone, and gonadotropines. This leads to ovarian stimulation and ovulation. Therapeutic uses • Clomiphene is a partial agonist, a weak estrogen that also acts as a competitive inhibitor of endogenous estrogens It has found use as an ovulation-inducing agent in treatment of female infertility due to overian causes.Side effect:polycyctic ovary,multiple pregnancy,hot flushes • Tamoxifen a competitive partial agonist inhibitor of estradiol at the estrogen receptors [ more agonist] .It is extensively used in the palliative treatment of breast estrogen sensetive cancer in postmenopausal women and is approved for chemoprevention of breast cancer in high-risk women in a dose of 10–20 mg twice daily, vaginal tumour .Side effects Hot flushes and nausea vomiting, osteoporosis and increase incidence of cancer in contralateral breast if used for more than 5 years. Toremifene is a structurally similar compound with very similar properties, indications, and toxicities.It increase incidence of cancer uterus due to agonist effect on endometrium. Raloxifene is another partial estrogen agonist-antagonist It has similar effects on lipids and bone but appears not to stimulate the endometrium or breast. Fulvestrant is used in treatment of cancer breast. 2-Inhibitors of estrogen synthesis Anastrozole & Letrozole & Fadrozole are non steroidal inhibitor of aromatase enzyme Exemestane, a steroid molecule, is an irreversible inhibitor of aromatase