A student obtains data on the magnitude of force applied to an
advertisement
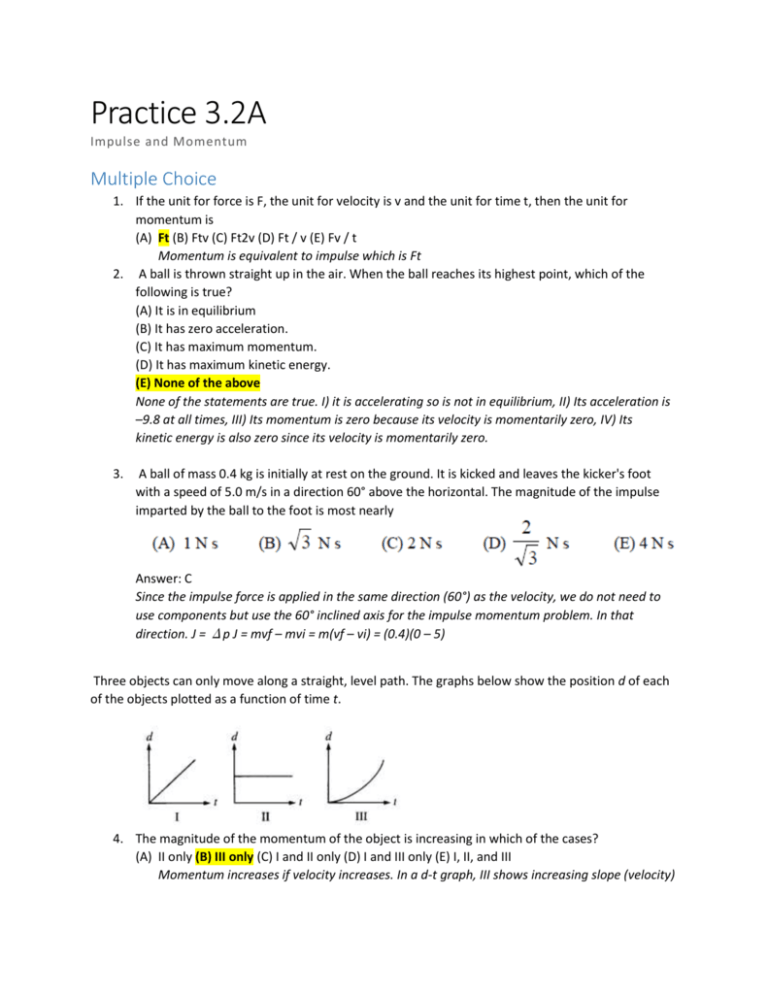
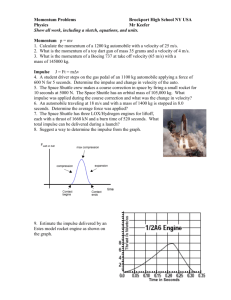
Practice 3.2A Impulse and Momentum Multiple Choice 1. If the unit for force is F, the unit for velocity is v and the unit for time t, then the unit for momentum is (A) Ft (B) Ftv (C) Ft2v (D) Ft / v (E) Fv / t Momentum is equivalent to impulse which is Ft 2. A ball is thrown straight up in the air. When the ball reaches its highest point, which of the following is true? (A) It is in equilibrium (B) It has zero acceleration. (C) It has maximum momentum. (D) It has maximum kinetic energy. (E) None of the above None of the statements are true. I) it is accelerating so is not in equilibrium, II) Its acceleration is –9.8 at all times, III) Its momentum is zero because its velocity is momentarily zero, IV) Its kinetic energy is also zero since its velocity is momentarily zero. 3. A ball of mass 0.4 kg is initially at rest on the ground. It is kicked and leaves the kicker's foot with a speed of 5.0 m/s in a direction 60° above the horizontal. The magnitude of the impulse imparted by the ball to the foot is most nearly Answer: C Since the impulse force is applied in the same direction (60°) as the velocity, we do not need to use components but use the 60° inclined axis for the impulse momentum problem. In that direction. J = Δp J = mvf – mvi = m(vf – vi) = (0.4)(0 – 5) Three objects can only move along a straight, level path. The graphs below show the position d of each of the objects plotted as a function of time t. 4. The magnitude of the momentum of the object is increasing in which of the cases? (A) II only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and III Momentum increases if velocity increases. In a d-t graph, III shows increasing slope (velocity) 5. The sum of the forces on the object is zero in which of the cases? (A) II only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and III The net force is zero if velocity (slope) does not change, this is graphs I and II A student obtains data on the magnitude of force applied to an object as a function of time and displays the data on the graph above. 6. The slope of the “best fit” straight line is most nearly (A) 5 N/s (B) 6 N/s (C) 7 N/s (D) 8 N/s (E) 10 N/s Find the slope of the line. 7. The increase in the momentum of the object between t=0 s and t=4 s is most nearly (A) 40 N∙s (B) 50 N∙s (C) 60 N∙s (0) 80 N∙s (E) 100 N∙s 8. A car of mass 900 kg is traveling at 20 m/s when the brakes are applied. The car then comes to a complete stop in 5 s. What is the average power that the brakes produce in stopping the car? (A) 1800 W (B) 3600 W (C) 7200 W (D) 36,000 W (E) 72,000 W 9. A ball with a mass of 0.50 kg and a speed of 6 m/s collides perpendicularly with a wall and bounces off with a speed of 4 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the magnitude of the impulse acting on the ball? (A) 13 J (B) 1 Ns (C) 5 Ns (D) 2 m/s (E) 10 m/s Use J=Δp J = mvf – mvi J = (0.5)(– 4) – (0.5)(6) Problem 1 Force displacement graph, asks questions about energy, work and momentum change 1997B1. A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line. The net force acting on the object varies with the object's displacement as shown in the graph above. The object starts from rest at displacement x = 0 and time t = 0 and is displaced a distance of 20 m. Determine each of the following. a. The acceleration of the particle when its displacement x is 6 m. b. The time taken for the object to be displaced the first 12 m. c. The amount of work done by the net force in displacing the object the first 12 m. d. The speed of the object at displacement x = 12 m. e. The final speed of the object at displacement x = 20 m. f. The change in the momentum of the object as it is displaced from x = 12 m to x = 20 m Problem 1 Solution Problem 2 2002B1. A model rocket of mass 0.250 kg is launched vertically with an engine that is ignited at time t = 0, as shown above. The engine provides an impulse of 20.0 N•s by firing for 2.0 s. Upon reaching its maximum height, the rocket deploys a parachute, and then descends vertically to the ground. (a) On the figures below, draw and label a free-body diagram for the rocket during each of the following intervals. (b) Determine the magnitude of the average acceleration of the rocket during the 2 s firing of the engine. (c) What maximum height will the rocket reach? (d) At what time after t = 0 will the maximum height be reached? Problem 2 Solution