Academic PLANNER (2015-16)
advertisement

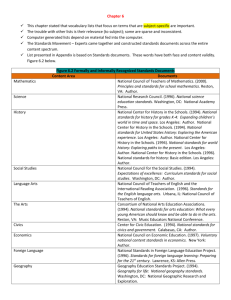
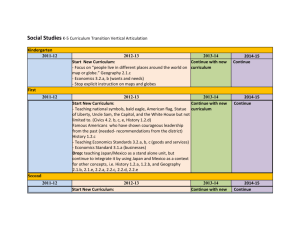
ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) CLASS VI (SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE) MONTH APRIL-MAY JULY AUGUST SEPTEMBER OCTOBERS NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY CHAPTER NAME History What, Where, How and When? On the trail of the earliest people Geography The Earth in the Solar System Civics Unity in Diversity History From Gathering to Growing Food Geography Latitude and Longitude Civics Diversity and Discrimination History History-In the earliest cities What books and burials tell us Geography Motions of the earth Civics What is Government History – Kingdoms, Kings and an early republic History – New questions and ideas Geography – Maps Civics – Key elements of a democratic government History – Ashoka, the emperor who gave up war. Geography – Major domains of the earth Civics – Panchayati Raj History – Vital villages thriving towns Traders, Kings and Pilgrims Geography – Major land from of the earth Civics – Rural Administration and Urban Administratio History – New empires and Kingdoms Geography – Climate, Vegetation and Wildlife Civics – Rural and Urban livelihoods History – Buildings, Paintings and books & REVISION ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) CLASS VII (SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE) Month APRIL-MAY JULY History – Chapter name Ch.1. Tracing Changes a Thousand years Geography- Ch.1.Environment Ch.2.Inside the Earth Civics- Ch.1 On Equality Ch.10 Struggles for equality Ch.2. New Kings and Kingdom Ch.3. The Sultans of Delhi History- Geography- Ch.3.Our Changing Earth CivicsHistory- Ch.2.Role of government in health Ch.4. The Creation of Mughal Empire Ch.5.Rulers and Buildings Geography- Ch-4. Air CivicsCivics- Ch.3.How the state government works Ch.4.Growing up as boys and girls History – Geography – Ch.6.Towns,Traders and Crafts persons Ch.5.Water Ch.6. Natural vegetation and wildlife Civics – History – Ch.5.Women change the world Ch. 7 – Tribes, Nomads and settled communities Geography – Ch.7. Transport and Communication Ch.8. Human Environment-Interactions DECEMBER Civics – History – Geography – Civics – Ch.6.&7. Understanding Media and advertising Ch. 8 - Devotional paths to the divine Ch.9- Life in the Temperate Grasslands Ch.8 &9. Markets JANUARY History – AUGUST SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER Geography – Ch. 9. Making of Regional cultures Ch. 10– Eighteenth Century political Formations Ch.10-Life in the Deserts. ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) CLASS VIII (SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE) Month APRIL-MAY Chapter name History – Ch.1. How, Where and When Ch.2. From Trade to Territory Geography- Ch.1.Resources CivicsCh.1.The Indian Constitution JULY History Ch.3. Ruling the Countryside Ch.4. Tribals, Dikus and the Vision Geography- Ch-2.Land ,water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources CivicsCh.2.Understanding Secularism AUGUST History- Ch.5. When People Rebel Geography- Ch. 3. Mineral and Power Resources Civics Ch.3.Why do we need a Parliament? Ch.4. Understanding Laws SEPTEMBER History- Ch.6.Colonialism and the city & Revision OCTOBER History – Ch.7. Weavers, Iron Smelter and Factory Owners Ch.8.Civilising the “Native” , Education the Nation Geography – Ch.4.Agriculture Civics – Ch.4.Judiciary NOVEMBER History – Ch. 9.Woem, Caste and Reform Ch.10. The Changing world of Visual Arts Geography – Ch.5.Industries Civics – Ch.5. Understanding our Criminal Justice system DECEMBER History – Ch. 11. The Making of National Movement Geography – Ch. 6.Human Resources Civics – Ch.6 & 7 Understanding marginalisation and Confronting Marginalisation JANUARY History – Civics – Ch.12. India After Independence Ch.9 & 10 Public Facilities and Law and Social Justice ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) CLASS IX Month APRIL-MAY JULY AUGUST SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY (SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE) Chapter name History – Ch.1. The French Revolution Geography Ch.1.India –size and the location History Ch.3. Nazism and the Rise of Hitler Geography Ch.2.Physical Features of India Civics Ch.1.Democracy in the contemporary world Economics Ch.1.The story of village Palamur Geography Ch-3. Drainage Civics Ch.2. What is Democracy ? Ch.3. Why Democracy? Economics Ch. 2. People as a resource. Civics Ch.3. Constitutional Design History – Ch.5.Forest society and Colonialism Geography – Ch.4.Climate Civics Ch.4.Electoral Politics in Democracy History – Ch.6.Farmers and Peasants Geography – Ch.5.Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Civics – Ch.5.Institutions of Parliamentary Democracy. Economics Ch.3.Poverty as a Challenge History – Ch. 7. Sports and Politics Geography – Ch. 6.Population Civics – Ch.4. Food Security of India Civics Ch.6.Citizens Right in Democracy Revision ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) CLASS X Month APRIL-MAY Political Science- (SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE) Chapter name Ch.1. Power sharing Ch.2. Federalism. Geography- Ch.1.Resources and Natural Resources JULY HistoryGeographyPolitical ScienceEconomics- Industrialisation 1850-1950 Ch-2.Forest and wild life resources Ch.3.Democracy and Diversity The story of Development AUGUST History- Ch.7. Print Culture and Nationalisation GeographyEconomics- Ch.3.Water Resources Ch.4. Agriculture and Revision. The role of Service sector in Indian Economy Political ScienceHistory – Ch.4.Gender,Religion and Caste Ch.3. Nationalism in India Geography – Political ScienceEconomics- Ch.5. Mineral and power resources Ch.5.Popular Struggles and Movements Ch.3.Money and Credit NOVEMBER History – Geography – Civics – Economics- Ch. 1. Nationalism in Europe Ch.6.Manufacturing Industries Ch.6.Political Parties 4.Globalisation DECEMBER Geography – EconomicsPolitical Science- JANUARY Political Science- FEBRUARY Revision SEPTEMBER OCTOBER Ch.9.Transport and Communication Ch.5. Consumer Rights Ch.7.Outcomes of democracy Ch.8. Challenges in Democracy. ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) GRADE XI MONTHS APRIL- MAY JULY AUGUST AUGUST SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER DECEMBER (SUBJECT : HISTORY) CHAPTERS I: Early Societies 1. From the Beginning of Time Focus: Africa, Europe till 15000 BC (a) Views on the origin of human beings. (b) Early societies. Debate on present-day hunter-gatherer societies 2. Early Cities Focus: Iraq, 3rd millennium BC (a) Growth of towns. (b) Nature of early urban societies. Debate on uses of writing 3. An Empire across Three Continents Focus: Roman Empire, 27 BC to AD 600. (a) Political evolution (b) Economic expansion (c) Religion (d) Late Antiquity. Debate on the institution of slavery 4. Central Islamic Lands Focus: 7th to 12th centuries. (a) Polity (b) Economy (c) Culture. Debate on the nature of the crusades 5. Nomadic Empires Focus: the Mongol, 13th to 14th century (a) The nature of nomadism. (b) Formation of empires. (c) Conquests and relations with other states. Debate on nomadic societies and state formation 6. Three Orders Focus: Western Europe, 9th-16th century (a) Feudal society and economy. (b) Formation of states. (c) Church and society. Debate on decline of feudalism 7. Changing Cultural Traditions Focus on Europe, 14th to 17th century. (a) New ideas and new trends in literature and arts. (b) Relationship with earlier ideas (c) The contribution of West Asia. Debate: Is the notion ‘European ‘Renaissance’ valid? 8. Confrontation of Cultures Focus on the Americas, 15th to 18th century. (a) European voyages of exploration. (b) Search for gold; enslavement, raids, extermination. (c) Indigenous peoples and cultures – the Arawaks, the Aztecs, the Incas. (d) The history of displacements. Debate on the slave trade 9. Displacing Indigenous Peoples Focus on North America and Australia, 18th-20th century. JANUARY JANUARY (a) European colonists in North America and Australia. (b) Formation of white settler societies. (c) Displacement and repression of local people.Debate on the impact of European settlement on indigenous populations 10. The Industrial Revolution Focus on England, 18th and 19th century. (a) Innovations and technological change. (b) Patterns of growth. (c) Emergence of a working class. Debate: Was there an Industrial Revolution? 11. Paths to Modernization Focus on East Asia. Late 19th and 20th century. (a) Militarization and economic growth in Japan. (b) China and the Communist alternative. Debate on the meaning of Modernisation ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) GRADE : XI SUB: ECONOMICS THEORY Months April/May TOPIC Statistics for Economics Introduction- Economic activities Indian Economic Development Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence Indian Economy(1950-1990) JULY Statistics for Economics Collection of Data Measures of Central Tendency Indian Economic Development Liberalisation, Privatisation, Globalisation: An Appraisal Poverty AUGUST Statistics for Economics Organisation of Data Human Capital Formation Indian Economic Development Rural Development SEPTEMBER Statistics for Economics Presentation of Data Indian Economic Development Employment: Growth, Informalisation and other issues OCTOBER Statistics for Economics Measures of Dispersion Inflation NOVEMBER Statistics for Economics Correlation Indian Economic Development Infrastructure DECEMBER Statistics for Economics Index Number Indian Economic Development Environment and sustainable Development Comparative Development Experiences of India and its neighbours JANUARY Statistics for Economics Use of Statistical Tools Indian Economic Development Development and Projects in Economics FEBRUARY & MARCH REVISION & FINAL EXAMINATION ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) GRADE : XI SUBJECT : POLITICAL SCIENCE (THEORY) Months April/May TOPIC Indian Constitution at Work Constitution Why and How and Philosophy of the Constitution Rights in the Indian Constitution Political Theory Political Theory : An Introduction JULY Indian Constitution at Work Election and Representation The Executive Political Theory Freedom Equality AUGUST Indian Constitution at Work The Legislature Political Theory Social Justice Rights SEPTEMBER REVISION & TERM I EXAMINATION OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY Indian Constitution at Work The Legislature Political Theory Citizenship Indian Constitution at Work The Judiciary Political Theory Nationalism Secularism Indian Constitution at Work Federalism Local Governments Political Theory Peace Development Indian Constitution at Work Local Governments Constituion as Living document REVISION ACADEMIC PLANNER (2015-16) GRADE : XII SUBJECT : HISTORY (THEORY) Months TOPIC PART A - MODERN INDIA India in the Late Eighteenth Century Coming of the Europeans and the Rise of the British April/May Part B – CONTEMPORARY WORLD Introduction The world from the end of the 19th Century to the end of the First World War PART A - MODERN INDIA India Under East India Company ( 1957-1857) Uprising of 1857 JULY PART B – CONTEMPORARY WORLD The World from 1919 to 1939 The Second World War AUGUST PART A - MODERN INDIA Changing after 1857 Social Cultural and Religious Awaking in the 19th Century PART B – CONTEMPORARY WORLD The World after Second World War SEPTEMBER OCTOBER REVISION & TERM I EXAMINATION PART A - MODERN INDIA Indian National Congress (1885-1905) Growth of Nationalism (1905-1918) Part B – CONTEMPORARY WORLD Development in Asia and Africa PART A - MODERN INDIA Rise of Gandhi in India Political scene (1915-20) NOVEMBER PART B – CONTEMPORARY WORLD Khurschev Era in U.S.S.R PART A - MODERN INDIA Struggle for Swaraj and making of Indian Constitution DECEMBER Part B – CONTEMPORARY WORLD Development in Science and Technology or development in Art , Literature, Media and Cultura PART A - MODERN INDIA Map work JANUARY Part B – CONTEMPORARY WORLD Map work REVISION FEBRUARY