Decomposition of water by Electrolysis

SAFE WORK PROCEDURE
Decomposition of Water by
Electrolysis
Page 1 of 2
LOCATION
VMC
WRITTEN BY: APPROVED BY: DATE CREATED LAST REVISION
Science Team WS&H June 27, 2014 New
PERSONAL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT (PPE)
Safety glasses or face shield must be worn at all times in work areas. Long and loose hair must be tied back
Appropriate footwear must be worn. Shoe must be fully enclosed. No open toed shoes.
Close fitting/protective clothing must be worn.
Remove strings hanging from pullovers/sweaters.
Rings and jewelry (long necklaces / bracelets, etc.) must not be worn.
HAZARDS PRESENT
Chemical burns
Absorption of Chemicals.
Inhalation of Chemicals.
Ingestion of Chemicals.
Slips / trips & falls
Chemical hazards
Burns from the Bunsen burner and wooden splints
APPARATUS / MATERIALS
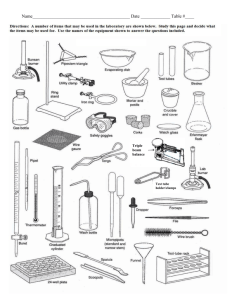
Ring stand
Marker
Beaker
Wooden splints
Small clamps
Test tubes
Graduated cylinder
Sodium carbonate
Bunsen burner
Electrodes and leads
6 volt battery
ADDITIONAL
REQUIREMENTS
Equipment orientation
WHMIS training
SAFE WORK PROCEDURE
1. Don all personal protective equipment including: safety glasses, & protective nitrile gloves
(where required). Ensure all loose clothing is either removed or tied back. Remove any jewelry and tie back long hair.
2. Half fill a 400ml beaker with water.
3. Fill the small test tubes with water and invert them into the beaker. Make sure there is no air in the test tubes.
4. Place the electrodes into the beaker and clamp the electrodes and to the sides of the test tubes on the ring stand. The electrodes should be about 2 cm apart.
5. Slide the electrodes so that they are just below the lip of the test tubes and resting on the bottom of the beaker.
6. Add 25ml of sodium carbonate solution to the beaker. NOTE: The sodium carbonate makes the water a better conductor of electricity so the reaction speeds up.
SAFE WORK PROCEDURE
Decomposition of Water by
Electrolysis
Page 2 of 2
7. Only now should the electrodes be hooked to the battery.
8. Disconnect the battery when one of the test tubes is nearly filled with gas.
9. Stopper both test tubes and remove them from the beaker. Mark the volume of gas/water in the test tubes.
10. Test the fuller test tube with a flaming splint. Observe what happens. Be careful when handling the flaming splint.
11. Test the other test tube with a glowing splint. Observe what happens.
12. Measure the volume of each gas collected by filling the test tube up the mark and then pouring the water into a graduated cylinder. Record the volume of gas in each test tube.
13. Determine the ratio of the volume of hydrogen to the volume of oxygen.
14. Clean up your workstation.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS
WS&H Act W210, Section 4, 5
Mb. Regulations 217/2006,
Part 16, (Machines / Tools & Robots) Sections 16.1-16.18)
Part 35, (WHMIS Application)
Part 36, (Chemical & Biological Substances Application)