Grade K - Math Essential Skills Alignment Focus
advertisement

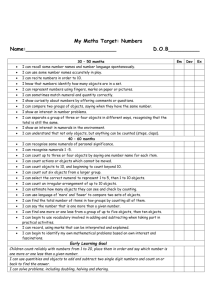
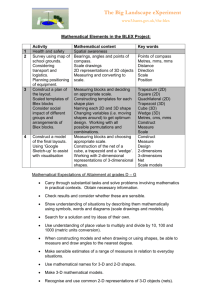
Math Standard: K.CC.1 Count to 100 by ones and by tens. Essential MATH Skills Alignment – Math Standards Content Source: 2013-2014 Iredell-Statesville Schools– Format Design: Grade: Kindergarten– Counting and Cardinality Math Standard: K.CC.2 Count forward beginning from a given number within the known sequence (instead of having to begin at 1). OASIS, LLC The academic vocabulary or content language is listed under each standard. There are 30-40 words in bold that should be taught to mastery. Math Standard: K.CC.3 Write numbers from 0 to 20. Represent a number of objects with a written numeral 0-20 (with 0 representing a count of no objects). K.CC.3 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Write numbers from 0-20 trace the shape of numbers 0-5 trace the shape of numbers 0-10 trace the shape of numbers 0-15. write the numbers 0-5 in random order from memory write the numbers 0-10 in random order from memory write the numbers 0-15 in random order from memory write the numbers 0-20 in random order from memory 2. Count a group of objects and write the matching number up to 20 count a group of objects match the amount of objects to the number by writing or using a number tile K.CC.1 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Count aloud by 1’s to 100 begin at 1 and count to 25 by 1’s begin at 1 and count to 50 by 1’s begin at 1 and count to 75 by 1’s begin at 1 and count to 100 by 1’s 2. Count aloud by 10’s to 100 begin at 0 and count to 100 by 10’s K.CC.2 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Count forward from any number that is not 1 From 1-25. From 1-50. From 1-75. From 1-100 Mathematical Language: number words (zero - one hundred) Mathematical Language: number words (zero - one hundred Mathematical Language: number words (zero - one hundred) Math Standard: K.CC.4 Understand the relationship between numbers and quantities; connect counting to cardinality. Math Standard: K.CC.5 Count to answer “how many?” questions about as many as 20 things arranged in a line, a rectangular array, or a circle, or as many as 10 things in a scattered configuration; given a number from 1–20, count out that many objects. Math Standard: K.CC.6 Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group, e.g., by using matching and counting strategies. Include groups with up to ten objects. a. When counting objects, say the number names in the standard order, pairing each object with one and only one number name and each number name with one and only one object. b. Understand that the last number name said tells the number of objects counted. The number of objects is the same regardless of their arrangement or the order in which they were counted. c. Understand that each successive number name refers to a quantity that is one larger. Essential MATH Skills Alignment – Math Standards Content Source: 2013-2014 Iredell-Statesville Schools– Format Design: Grade: Kindergarten– Counting and Cardinality K.CC.4 Essential Skills and Concepts: K.CC.5 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Use one counting word for every object in a set 1. Choose the best way for me to count a group of say a number for each object I touch without objects up to 20 touching any object twice use touching and moving to count a group of - 0-5 objects objects - 0-10 objects organize objects in a line - 0-15 objects touch and count the objects - 0-20 objects find a starting point 2. Understand the last number I say tells the number count around the circle stopping where I of objects counted started use the touching strategy to count a group of touch to count a scattered group of objects 0-10 objects use my eyes to count the objects in a group of 010 answer the question, “How many are there?” answer the question, “ how many?” using a - 0-5 objects counting strategy for sets up to 20 - 0-10 objects - 0-15 objects - 0-20 objects 3. add 1 more to a group (0-9) and tell how many there are count a set of 0-9 objects add 1 more to the group tell how many now think of a number 0-9 add 1 more to the group tell how many now Mathematical Language: number words (zero - one hundred) Mathematical Language: hundred) Math Standard: K.CC.7 Compare two numbers between 1 and 10 presented as written numerals. K.CC.7 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Look at two numbers and tell which one is more, less or equal. use what I know about numbers to decide if K.CC.7 Essential Skills and Concepts: (continued) they are more/less/equal. • Larger number is more • Smaller number is less • Same number is equal number words (zero - one OASIS, LLC The academic vocabulary or content language is listed under each standard. There are 30-40 words in bold that should be taught to mastery. K.CC.6 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Use matching to decide if a group is more, less or equal make as many partners as can with the two groups decide if they are more/less/equal by looking at the partner groups • If they all have a partner they are equal • The group that has extra objects is more • The group that doesn’t have extras is less 2. Use counting to decide if a group is more, less or equal count each group use what is known about numbers to decide if it is more/less/equal • Larger number is more • Smaller number is less • Same number is equal 3. Use take away to decide if a group is more, less or equal put each group in a pile take away one object from each group keep taking away one object until one group has none left decide if they are more/less/equal using what is known • If both have none they are equal • The group that has some left is more • The group that has none left is less 4. Choose the best way for me to decide if a group is more, less or equal each student decides for themselves which of the strategies works best for them Mathematical Language: more, less, fewer, equal, same amount K.CC.7: Mathematical Language: greater, more, less, fewer, equal, same amount The academic vocabulary or content language is listed under each standard. There are 30-40 Essential MATH Skills Alignment – Math Standards words in bold that should be taught to mastery. Content Source: 2013-2014 Iredell-Statesville Schools– Format Design: OASIS, LLC Grade: Kindergarten– Operations and Algebraic Thinking Math Standard: K.OA.1 Math Standard: K.OA.2 Math Standard: K.OA.3 Represent addition and subtraction with objects, Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and Decompose numbers less than or equal to 10 into fingers, mental images, drawings, sounds (e.g., claps), add and subtract within 10, e.g., by using objects or pairs in more than one way, e.g., by using objects or acting out situations, verbal explanations, expressions, drawings to represent the problem. drawings, and record each decomposition by a or equations. drawing or equation (e.g., 5 = 2 + 3 and 5 = 4 + 1). Drawings need not show details, but should show the mathematics in the problem. (This applies wherever drawings are mentioned in the Standards.) K.OA.1 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Make a group bigger by adding objects put more objects in a group and tell how many all together show someone how to add objects to a group and explain what happens to the group 2. Make a group smaller by taking away objects take objects from a group and tell how many are left show someone how to add objects to a group and explain what happens to the group Mathematical Language: join, add, separate, subtract, and, same amount as, equal, less, more, total Math Standard: K.OA.4 For any number from 1 to 9, find the number that makes 10 when added to the given number, e.g., by using objects or drawings, and record the answer with a drawing or equation. K.OA.4 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Break apart a group of 10 in different ways break apart a group of 10 in different ways 2. figure out how many more is needed when there is 10 in all 3. Given a number, find the missing part that makes 10 use one of the following strategies to solve the problem. • a ten frame • take away • basic facts K.OA.2 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Find the answer when two groups are added together 2. Figure out how many are added to a group when I know how many in all 3. Figure out how many I started with when I know how many are added and how many in all listen to the story problem use objects to show what I know from the story OR draw what is known from the story figure out what the question is asking use the number strategies to figure out the answer Mathematical Language: join, add, separate, subtract, and, same amount as, equal, less, more, total K.OA.3 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Take a number and break it apart in different ways take a number and break it apart in different ways Mathematical Language: join, add, separate, subtract, and, same amount as, equal, less, more, total Students should be exposed to the symbols (+, -, =) and numerical equations to be prepared for 1st grade Math Standard: K.OA.5 Fluently add and subtract within 5. K.OA.4: Mathematical Language: add, separate, subtract, and, same amount as, equal, less, more, total K.OA.5 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Use strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems up to 5 with a few steps to the get correct answer use manipulatives (counters, fingers, linking cubes, base ten blocks, etc) to solve equations quickly and correctly use a tens frame to solve equations quickly and correctly use the part-part whole mat (Envision) to solve equations quickly and correctly Mathematical Language: join, add, separate, subtract, and, same amount as, equal, less, more, total Essential MATH Skills Alignment – Math Standards Content Source: 2013-2014 Iredell-Statesville Schools– Format Design: OASIS, LLC Grade: Kindergarten– Number and Operations in Base Ten Math Standard: K.NBT.1 Compose and decompose numbers from 11 to 19 into ten ones and some further ones, e.g., by using objects or drawings, and record each composition or decomposition by a drawing or equation (e.g., 18 = 10 + 8); understand that these numbers are composed of ten ones and one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones. K.NBT.1 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Build a set from 11-19 using tens and ones 2. Break apart a set from 11-19 into groups of ten and count how many are left make a set of 10 from my group of objects count how many are left Mathematical Language: number words (one, two… thirteen, fourteen, … nineteen), leftovers The academic vocabulary or content language is listed under each standard. There are 30-40 words in bold that should be taught to mastery. Essential MATH Skills Alignment – Math Standards Content Source: 2013-2014 Iredell-Statesville Schools– Format Design: Grade: Kindergarten– Measurement and Data Math Standard: K.MD.1 Math Standard: K.MD.2 Describe measurable attributes of objects, such as Directly compare two objects with a measurable length or weight. attribute in common, to see which object has “more Describe several measurable attributes of a single of”/”less of” the attribute, and describe the object. difference. For example, directly compare the heights of two children and describe one child as taller/shorter. OASIS, LLC The academic vocabulary or content language is listed under each standard. There are 30-40 words in bold that should be taught to mastery. K.MD.1 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Use words like big and little to talk about the size of something tell about an object using words to describe its size 2. Use words like long and short to talk about the length of something tell about an object using words to describe its length 3. Use words like heavy and light to talk about the weight of something tell about an object using words to describe its weight K.MD.2 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Tell the difference in 2 objects using the length line up the objects so the ends of the objects are in the same place tell the difference in 2 objects using my math vocabulary (long/short) Math Standard: K.MD.3 Students identify similarities and differences between objects (e.g., size, color, shape) and use the identified attributes to sort a collection of objects. Once the objects are sorted, the student counts the amount in each set. Once each set is counted, then the student is asked to sort (or group) each of the sets by the amount in each set. Thus, like amounts are grouped together, but not necessarily ordered. K.MD.3 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Use an attribute to sort groups and then compare groups using least to greatest sort objects by given attribute count the groups sorted group any sets with like amounts Mathematical Language: length, weight, heavy, long, more of, less of, longer, taller, shorter Mathematical Language: length, weight, heavy, long, more of, less of, longer, taller, shorter Mathematical Language: color words (e.g., blue, green, red, etc.), descriptive words (e.g., small, big, rough, smooth, bumpy, round, flat, etc.), more, less, same amount Essential MATH Skills Alignment – Math Standards Content Source: 2013-2014 Iredell-Statesville Schools– Format Design: Grade: Kindergarten– Geometry Math Standard: K.G.1 Math Standard: K.G.2 Describe objects in the environment using names of Correctly name shapes regardless of their orientations shapes, and describe the relative positions of these or overall size. objects using terms such as above, below, beside, in front of, behind, and next to. K.G.1 Essential Skills and Concepts: K.G.2 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Tell about shapes in my world 1. Name a circle, square, triangle, rectangle, hexagon, use shapes to describe things in my world cube, cone, cylinder, and sphere 2. Tell where objects are using positional words name a shape when asked by teacher use my positional words to tell where objects are located Mathematical Language: squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, spheres, flat, solid, side, vertex, angle, edge, face, positional vocabulary (e.g., above, below, beside, in front of, behind, next to, same, different, between, around, left, right) OASIS, LLC The academic vocabulary or content language is listed under each standard. There are 30-40 words in bold that should be taught to mastery. Math Standard: K.G.3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, “flat”) or three dimensional (“solid”). K.G.3 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Recognize flat shapes pick out flat shapes from a group of objects 2. Recognize solid shapes pick out solid shapes from a group of objects 3. Sort/group objects by flat and solid sort objects by flat and solid Mathematical Language: squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, spheres, flat, solid, side, corner, angle, edge, face, positional vocabulary (e.g., above, below, beside, in front of, behind, next to, same, different, etc.) Mathematical Language: squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, spheres, flat, solid, side, corner, angle, edge, face, positional vocabulary (e.g., above, below, beside, in front of, behind, next to, same, different, etc.) Math Standard: K.G.4 Analyze and compare two- and three-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations, using informal language to describe their similarities, differences, parts (e.g., number of sides and vertices/“corners”) and other attributes (e.g., having sides of equal length). K.G.4 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Tell how 2-D & 3-D shapes are alike 2. Tell how 2-D & 3-D shapes are different name the shapes tell how shapes are alike and different by using my math vocabulary: sides length shape names angles equal Math Standard: K.G.5 Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components (e.g., sticks and clay balls) and drawing shapes. Math Standard: K.G.6 Compose simple shapes to form larger shapes. For example, “Can you join these two triangles with full sides touching to make a rectangle?” K.G.5 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Draw shapes trace shapes draw shapes all by myself 2. Build shapes build shapes by watching my teacher build shapes all by myself K.G.6 Essential Skills and Concepts: 1. Make a shape by using other shapes join shapes to other shapes Mathematical Language: squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, spheres, flat, solid, side, corner, angle, edge, face, positional vocabulary (e.g., above, below, beside, in front of, behind, next to, same, different, etc.) Mathematical Language: squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, spheres, flat, solid, side, corner, angle, edge, face, positional vocabulary (e.g., above, below, beside, in front of, behind, next to, same, different, etc.) Mathematical Language: squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, spheres, flat, solid, side, corner, angle, edge, face, positional vocabulary (e.g., above, below, beside, in front of, behind, next to, same, different, etc.)