Mitosis and Meiosis book
advertisement

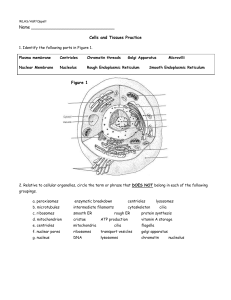
Mitosis: A Division process of somatic cells. Following the teacher’s instructions use three pieces of paper to make your Cell Division Book. When the book is closed (folded) the sides facing the outside will become your title page and end page. Title page (cover) write your title, your first and last name and period you have Biology. Your job is to chronologically organize both the pictures and the descriptions neatly into your Cell Division book. In your book you will be pasting the cells, previously cut, from left to right and top to bottom in the order each event would occur in the cell cycle. There are nine pictures (there may be several that represent the progression of chromosomal movement for each phase). The pictures are not in order. 1 3 Title Author Period 2 7 4 6 5 9 8 Match each of the processes and descriptions below with the appropriate picture. The processes below are not in chronological order. You will have the following phases to include: Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase and Cytokinesis. There may be several descriptions for each phase/picture. ____________________: Cell is carrying on ALL of life’s functions. * growing, * synthesizing DNA, * organelle duplication, *protein synthesis. Preparation for Mitosis. Cell spends most of it’s time in this phase. ____________________: Cell Prepares to divide. Chromatin condenses to form X-shaped chromosomes made of sister chromatids. Centrioles move to the poles. Spindle fibers form. ____________________: chromosomes line up in the middle at the cell equator. ____________________: chromosomes move around in preparation for metaphase. ____________________: chromosomes now totally apart. Nuclear membrane reforms. Spindle fibers break down. Cell membrane begins to pinch in the middle (animal cells only). Cytokinesis begins. ____________________: nuclear membrane disappears, nucleolus disappears, spindle fibers attach to centromeres. ____________________: Result of Cell Division- 2 new daughter cells with genetic makeup identical to the parent cell. Chromosomes uncondensed into chromatin, nuclear membrane reforms. Two new daughter cells. They are identical. ____________________: Sister chromatids are pulled apart toward the opposite poles. ____________________: sister chromatids move away from each other. Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart and split the centromere. Meiosis: A Doubly Division process of gametic cells. Following the teacher’s instructions use three pieces of paper to make your Cell Division Book. When the book is closed (folded) the sides facing the outside will become your title page and end page. The opposite side of the book is where all of the Meiosis information will go. Title page (cover) write your title, your first and last name and period you have Biology. Your job is to chronologically organize both the pictures and the descriptions neatly into your Cell Division book. In your book you will be pasting the cells, previously cut, from left to right and top to bottom in the order each event would occur in the cell cycle. There are 11 pictures. The pictures are not in order. 2 5 Title and Interphase (1) 10 6 8 9 3 7 Meiosis Summary 11 4 Match each of the processes and descriptions below with the appropriate picture. The processes below are not in chronological order. You will have the following phases to include: Interphase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Cytokinesis I, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II, and Cytokinesis II. There is also Summary (which has two parts) information for the last square. _______________________: After meiosis one sperm and one egg will unite in a process called fertilization- 1n + 1n = 2n. This forms a zygote (2n) which will develop into a new organism. _______________________: Cell doubles in size (grows), DNA synthesizes, (cell is diploid 2n) organelles synthesize, cell carries on all life’s functions. _______________________: Cell prepares to divide, chromatin condenses, centrioles move to poles and spindle fibers form, nuclear membrane disappears. Synapsis forms between homologous chromosomes pairs making a tetrad (4 chromatids). Crossing over occurs increasing genetic variability. _______________________: Chromatin condenses to from chromosomes, new spindle fibers form, centrioles move to poles, nuclear membrane disappears. *DNA does NOT replicate again. _______________________: Cytoplasm splits, Result is 2 haploid daughter cells. Chromosomes uncondensed. _______________________: Cytoplasm splits, Result is 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells. Chromosomes uncondensed. _______________________: Homologous chromosomes (tetrads) line up on the cell equator. _______________________: Homologous chromosomes are totally apart. Nuclear membrane reforms, spindle breaks down and cell membrane begins to pinch _______________________: Homologous chromosomes pull apart and move towards the poles. _______________________: Purpose: To perform 2 nuclear divisions 2n 1n. To produce 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells. Occurs in gametes to generate sperm (male) or egg (female). _______________________: Sister chromatids are totally apart, spindle dissolves, nuclear membrane reforms, cell membrane begins to pinch. _______________________: Sister chromatids pull apart and move toward the poles. _______________________: Spindle fibers move chromosomes to cell equator. Cut out each phase of Meiosis and paste in chronological order in your Cell Division book.