Neuropathic Symptoms Neuropathic symptoms at follow up
advertisement
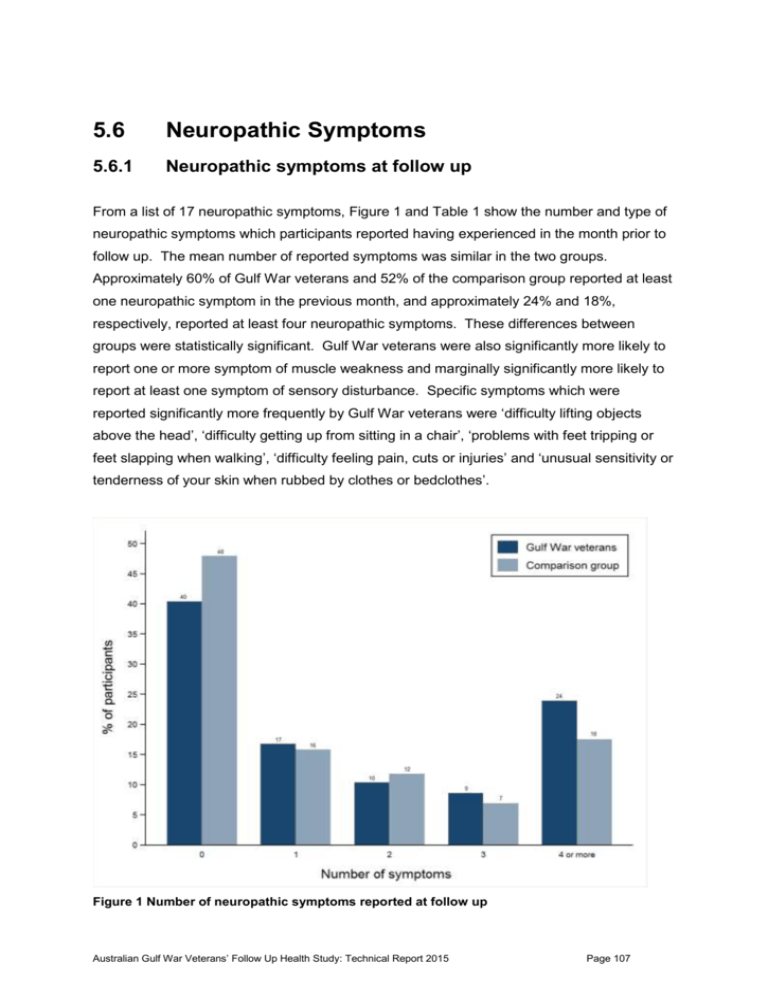
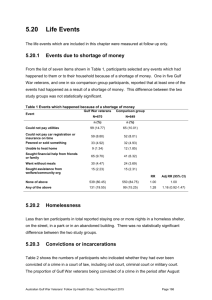
5.6 Neuropathic Symptoms 5.6.1 Neuropathic symptoms at follow up From a list of 17 neuropathic symptoms, Figure 1 and Table 1 show the number and type of neuropathic symptoms which participants reported having experienced in the month prior to follow up. The mean number of reported symptoms was similar in the two groups. Approximately 60% of Gulf War veterans and 52% of the comparison group reported at least one neuropathic symptom in the previous month, and approximately 24% and 18%, respectively, reported at least four neuropathic symptoms. These differences between groups were statistically significant. Gulf War veterans were also significantly more likely to report one or more symptom of muscle weakness and marginally significantly more likely to report at least one symptom of sensory disturbance. Specific symptoms which were reported significantly more frequently by Gulf War veterans were ‘difficulty lifting objects above the head’, ‘difficulty getting up from sitting in a chair’, ‘problems with feet tripping or feet slapping when walking’, ‘difficulty feeling pain, cuts or injuries’ and ‘unusual sensitivity or tenderness of your skin when rubbed by clothes or bedclothes’. Figure 1 Number of neuropathic symptoms reported at follow up Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 107 Table 1 Number and type of neuropathic symptoms at follow up Gulf War veterans N=686 Comparison group N=651 Mean (sd) Mean (sd) Ratio of means* Adj ratio of means† 2.2 (3.0) 1.7 (2.5) 1.21 1.14 (0.96 – 1.36) n (%) n (%) RR Adj RR (95% CI)b One or more 409 (59.62) 339 (52.07) 1.14 1.13 (1.03-1.25) Four or more 164 (23.91) 114 (17.51) 1.37 1.32 (1.07-1.64) One or more symptom of muscle weakness 307 (44.05) 234 (35.51) 1.24 1.23 (1.08-1.41) Difficulty lifting objects above head 161 (23.10) 105 (15.93) 1.45 1.42 (1.13-1.79) Difficulty undoing buttons 45 (6.46) 29 (4.40) 1.47 1.38 (0.86-2.20) Difficulty turning doorknobs/unscrewing jars 68 (9.78) 48 (7.32) 1.34 1.28 (0.89-1.83) 234 (33.77) 179 (27.37) 1.23 1.25 (1.06-1.48) Problems with tripping or feet slapping while walking 48 (9.60) 20 (3.05) 1.62 1.54 (1.07-2.22) Difficulty swallowing food (more than occasionally) 25 (3.59) 15 (2.29) 1.57 1.65 (0.83-3.28) 316 (45.34) 259 (39.30) 1.15 1.14 (>1.00-1.29) Difficulty recognising hot from cold water 11 (1.58) 2 (0.31) 5.18 4.59 (0.96-21.91) Difficulty feeling pain, cuts or injuries 33 (4.74) 9 (1.37) 3.45 3.25 (1.45-7.30) Numbness, “asleep feeling” or prickling sensation in hands or arms 198 (28.49) 156 (23.85) 1.19 1.14 (0.95-1.37) Numbness, “asleep feeling” or prickling sensation in feet or legs 160 (23.02) 129 (19.69) 1.17 1.13 (0.92-1.39) Burning, deep aching pain or tenderness in hands or arms 76 (10.95) 55 (8.40) 1.30 1.19 (0.85-1.66) Burning, deep aching pain or tenderness in feet or legs 103 (14.80) 91 (13.89) 1.07 1.02 (0.78-1.34) Unusual sensitivity or tenderness of your skin when clothes or bedclothes rub against you 48 (6.90) 20 (3.05) 2.26 2.07 (1.23-3.46) Feeling unsteady walking on even ground 83 (11.93) 65 (9.92) 1.20 1.18 (0.87-1.61) Feeling unsteady walking in the dark 75 (10.79) 57 (8.70) 1.24 1.16 (0.83-1.63) Feeling like you might fall over because of unsteadiness 60 (8.62) 42 (6.42) 1.34 1.18 (0.80-1.73) 97 (13.94) 64 (9.77) 1.43 1.34 (0.99-1.83) Number of neuropathic symptoms Symptoms of muscle weakness Difficulty getting up from sitting in a chair Symptoms of sensory disturbance One or more symptom of sensory disturbance Symptom of autonomic dysfunction Feeling faint when standing up from lying or sitting * Obtained using zero-inflated negative binomial regression † Adjusted for age (<20; 20-24; 25-34; >=35 years), service branch (Navy; Army; Air Force) and rank (CO, NCO, enlisted ranks), each estimated as at August 1990, and alcohol (AUDIT score > 10) and self-reported doctor-diagnosed diabetes Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 108 5.6.2 Association between Gulf War deployment characteristics and neuropathic symptoms in veterans at follow up Table 2 shows that, relative to Officers, Gulf War veterans who served under the two lower rank categories; ‘other rank supervisory’ and ‘other rank-non supervisory’; reported a significantly higher average number of neuropathic symptoms at follow up. There was no association between average number of neuropathic symptoms reported at follow up and service branch or age category during the Gulf War. Table 2 Association between Gulf War deployment characteristics and average number of neuropathic symptoms at follow up in Gulf War veterans Gulf War deployment characteristic Total number of neuropathic symptoms at follow up in Gulf War veterans N mean (SD) ratio Adj ratio* (95% CI) Age at deployment < 20 62 2.5 (3.4) 1.00 1.00 20-24 166 2.0 (3.6) 0.87 0.93 (0.61 – 1.44) 25-34 358 2.2 (3.0) 0.87 0.95 (0.61 – 1.50) >=35 100 2.5 (2.6) 0.77 0.96 (0.57 – 1.61) Navy 589 2.2 (3.0) 1.00 1.00 Army 46 2.8 (3.5) 1.15 1.19 (0.79 – 1.77) Air Force 51 1.6 (2.1) 0.77 1.00 (0.64 – 1.56) Officer 147 1.4 (2.4) 1.00 1.00 Other rank-supervisory 348 2.3 (3.0) 1.38 1.50 (1.07 – 2.11) Other rank - non supervisory 190 2.6 (3.2) 1.50 1.64 (1.07 – 2.51) Service branch Rank category *Adjusted for age (<20; 20-24; 25-34; >=35 years), service branch (Navy; Army; Air Force) and rank (CO, NCO, enlisted ranks), each estimated as at August 1990, alcohol (AUDIT score > 10) and self-reported doctor-diagnosed diabetes 5.6.3 Key findings The mean number of neuropathic symptoms in the previous month, reported by both study groups, was approximately two of the 17 symptoms measured. Gulf War veterans were significantly more likely than the comparison group to report at least one neuropathic symptom (60% vs 52%), or at least four neuropathic symptoms (24% vs 18%), one or more symptom of muscle weakness (44% vs 36%) and one or more symptom of sensory disturbance (45% vs 39%). Individual symptoms which were reported significantly more frequently by Gulf War veterans were ‘difficulty lifting objects above the head’, ‘difficulty getting up from sitting in a chair’, ‘problems with feet tripping or feet slapping when walking’, ‘difficulty feeling pain cuts or injuries’ and ‘unusual sensitivity or tenderness of your skin when rubbed by clothes or bedclothes’. Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 109 In Gulf War veterans, increasing number of neuropathic symptoms reported at follow up was associated with lower rank category during the Gulf War, but it was not associated with service branch or age category during the Gulf War. Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 110