Factors that Influence Climate
advertisement

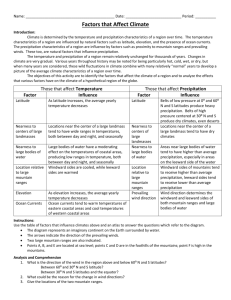
Factors that Influence Climate Climate is determined by the temperature and precipitation characteristics of a region over long periods of time. Climate is an average of all of the daily weather phenomena for a region based on a large number of factors including latitude, elevation, ocean currents, proximity to mountain ranges, prevailing winds, etc. The temperature and precipitation characteristics of a region remain relatively unchanged for thousands of years. Changes in climate are very gradual. Various years throughout history may be noted for being particularly hot, cold, wet or dry, but when many years are considered, these wild fluctuations in climate combine with many relatively normal years to develop a picture of the average climate characteristics of a region over time. Objectives: To identify the factors that affect the climate of a region To identify and analyze the effects the various factors have on the climate of a hypothetical region. Important terms: climate; latitude; windward; leeward; elevation; altitude; precipitation; prevailing winds, global winds, mountain breeze, valley breeze, sea breeze, land breeze, orographic lifting, rain shadow effect Procedures: 1. Review the table entitled “Factors that Influence Climate”. 2. Understand the application of important terms above in climate. 3. Use the table of factors to answer questions about the imaginary continent in this packet. Note: a) b) c) d) The continent is surrounded by water. The arrows represent the direction of the prevailing winds. Two large mountain ranges are indicated by ^ symbols. Points A, B and E are at sea level. C and D are in the foothills of the mountains; F is high in the mountains. 4. Use the internet to find cities in similar locations on our planet. Give the name of the city, its continent, latitude and longitude coordinates, along with a description of the climate and specific factors in that location that affect the climate. Analysis and Comprehension 1. What is the direction of the wind in the region above and below 60̊ N and S. latitudes? 2. What is the direction of the wind between 60̊ and 30̊ N and S latitude? 3. What is the direction of the wind between 30̊ N and S and the equator? 4. What could be the reason for the change in wind directions? 5. Give the locations of the 2 mountain ranges including latitude ranges, cardinal directions and descriptions of windward and leeward sides of the continent. 6. Which city on the imaginary continent probably has the same type of weather year round? Why? a. Use the internet to find a real city in a similar location on the globe. City name: Latitude and Longitude coordinates: Continent: Climate: Factors that affect its climate: 7. What factor would cause location F to have colder yearly climate than any other location? Why? a. Use the internet to find a real city in a similar location on the globe. City name: Latitude and Longitude coordinates: Continent: Climate: Factors that affect its climate: 8. What three factors would cause location E to have the greatest annual rainfall? a. Use the internet to find a real city in a similar location on the globe. City name: Latitude and Longitude coordinates: ___________________________ Continent: _____________________ Climate: ____________________________________________________ Factors that affect its climate: 9. Which location, C or D, would you expect to have the greater annual rainfall? Why? 10. Which location, A or B, would you expect to have the greater range in temperatures during the year? Explain your answer. 11. Location A is the center of a large desert. What factor could account for its low annual precipitation? a. Find a city in the U.S. that experiences that same climate due to the same factors. What is the name of the city and the state? b. What are the geographical features that affect its climate? 12. What three factors would cause the climate in location D to be cooler than at location B? a. Find two cities in the U.S. that experiences that same climates D and B due to the same factors. What is the name of the cities and the states they are found in? b. What are the geographical features that affect their respective climates? 13. Imagine that this is an El Niño year and this imaginary continent was in the Western Hemisphere. Explain how the climate would change and why the changes would occur. 14. Imagine this is an El Niño year and this imaginary continent was in the Eastern Hemisphere. Explain how the climate would be change and why the changes would occur. 15. Imagine this is a La Niña year and this imaginary continent was in the Western Hemisphere. Explain how the climate would change and why the changes occur. 16. Imagine this is a La Niña year and this imaginary continent was in the Eastern Hemisphere. Explain how the climate would be change and why the changes would occur. Factors that Affect Climate: Temperature Precipitation Latitude As latitude increases, the average yearly Belts of low pressure at 0̊ and 60̊N and S temperature decreases produce heavy precipitation. Belts of high pressure at 30̊ N and S produce dry climates, even deserts Nearness to centers of large landmasses Locations near the center of a large Locations near the center of large land landmass tend to have wide ranges in masses tend to have dry climates. temperatures, between day and night and seasonally. This is because land heats and cools faster than water. Nearness to large bodies of water Large bodies of water tend to have a Areas near large bodies of water tend to moderating effect on the temperatures of have higher than average precipitation, coastal areas, producing low ranges in especially on the leeward side of the temperature, both between day and night water. and seasonally. Location relative to large mountain ranges Windward sides are cooled, while Windward sides of mountains tend to leeward sides are warmed. receive higher than average precipitation; leeward sides tend to receive lower than average precipitation. Elevation As elevation increases, the average Because air pressure decreases with yearly temperature decreases altitude, there tends to be less water vapor in the air. As a result, precipitation may decrease seasonally, but will be in the form of snow. Ocean Currents Eastern coastal areas tend to have Cold ocean currents are claimed to warmer temperatures, while western prevent clouds from forming, lowering coastal areas tend to have cooler precipitation rates. Warm currents bring temperatures. air masses, increasing humidity, which increases the number of clouds and hence, precipitation. Prevailing Winds Direction Prevailing winds moving from oceans Wind direction determines windward and toward land moderate temperatures. leeward sides of both mountain ranges Relatively cool summer temps and warm and larges bodies of water. winter temps. Winds that originate from Prevailing winds originating over water lower latitudes are warm; winds that are moist, while prevailing winds over originate from upper latitudes are land are dry. Winds formed by rising cool/cold. warm air bring precipitation; winds formed by sinking cool air bring dry conditions.