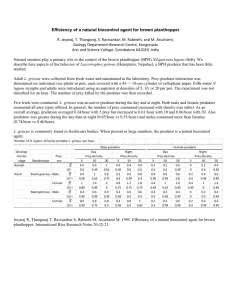
0907148
advertisement
) أنموذج ( أ ) الخاص برسائل الماجستير و اطاريح الدكتوراة ( اخر شهادة University of Baghdad College Name College of Science Department Biology department Full Name as written in Passport Hind Suhail Abdul hay e-mail hind442@yahoo.com Career Assistant Lecturer Lecturer Master Assistant Professor Professor PhD Thesis Title Study the efficacy of Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) in the control of cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) (Homoptera:Aphididae) compared with a pyrethroid insecticide. Year 2011 This study was conducted to examine the effectiveness of the predator Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae ) in controlling nymphs and adults of Abstract cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) (Homoptera: Aphididae) under both laboratory and field conditions. Also testing of the possibility in combination with Deltamethrin insecticide was studied as an integrated control program of this insect. Results showed high efficiency of the predator to attack and consum nymphs and adults of cabbage aphid. Predation efficiency increases with the progress of the larval stages up to the third (last) which was the most voracious .The 1st instar nymphs consumed by the larvae of the predator were 47,80,181.67 nymphs ,with predation rate 14.71% , 23.75% , 50.13% for 1st ,2nd and 3rd larval instars . For the purpose of predicting the predators҆ efficiency in the field the limiting factors on the attack was studied. Results showed a decreasing time for prey consumption with the advancement of the predator age. It was for 1st larval instar 7.9 , 6.1 , 5.5 , 4.8 and 3.6 times more than for 3rd larval instar, when preying on the four nymphal instars and adult stage of B.brassicae (L.),respectively. Also the movement and search area of the predator were accelerated within a specified time. This enables the predator to cover a wider area ; the speed was 5430 cm /hr., for 3rd larval instar ,which amount to an area of 814.5cm²/hr., as compared with a speed of 526.4cm/hr., and an area of 65.64cm²/ hr., for the 1 st larval instar . Regarding the effect of prey density on the numerical response of the predator, it was found that larvae of the predator had a distinct ability to survive in conditions of ) أنموذج ( أ ) الخاص برسائل الماجستير و اطاريح الدكتوراة ( اخر شهادة inadequate feeding. Increasing the amount of food consumption in the larval stage had a positive impact on the survival rate of larval instars , accelerated development and longevity of adults with a high sex ratio in favor of females as well as increase oviposition period and fecundity. Functional response was measured by offering varying densities of cabbage aphid for each individual predator. C.carnea showed type–II functional response , when the number of prey killed approaches asymptote hyperbolically as prey density increases (declining proportion of prey killed or the inverse density dependent) till it reached the stability stage determined by handling time and predator satiation . Also, the values of attack rate and handling time changed with age progress for both predator and prey. It has been observed an increase in the attack rate and reduction in handling time with the progress of the predator age when feeding on a particular nymphal instar. The attack rates of the predator was 1.779,3.406 and 4.219 ,while handling time was 0.015,0.010 and 0.008(days) for 1st,2nd,3rd larval instars respectively, when fed on 1st nymphal instar. Also attack rates decreased and increases handling time with the progress in the prey. The attack rates were 1.779,1.392,1.096 and 1.059 ,due to an increase in size of the predator and in the growing efficiency in hunting the prey as well as in the increase in size of the prey and in developing its ability to defend itself and escape. The results also showed that the increase in population density of the predator led to increasing conflicts and encounters among predators in the search area ,this reduces the encounter with the prey, as well as increased cannibalism, thus, reflected negatively on the efficiency of predator search. Assessing the effect of Deltamethrin on the predator and prey on the basis of LC 50 values, laboratory data have indicated a positive correlation between these values and the progress of B. brassicae (L.) life cycle . The adults were more resistant to the insecticide than the nymphal instars . The LC50 and LC90 values for the 4th nymphal instar were 1.8 and 1.6 times more than 1st instar; also, the alatae were more susceptible than the apterae for Deltamethrin . Deltamethrin showed selectivity among C.carnea stage, where LC50 for the 1st larval instar was 4 times for the recommended field concentration. Our results indicate that it was more toxic to eggs and adults than larval instars,which increased its tolerance as age progressed . The survey also proved that all concentrations against cabbage aphid were safe for the predator after 24 hours Field study was conducted to investigate the toxicity of Deltamethrin against cabbage aphid .Population density was determined before spray, then mortality was followed at intervals of : 1 , 4 , 7 , 15 , 21 and 30 days after spray .The results indicate a very high ) أنموذج ( أ ) الخاص برسائل الماجستير و اطاريح الدكتوراة ( اخر شهادة toxicity of about 81.9% kill after 4 days, then reached a maximum of 90.9 % after a week, and 79.3% after 15 days. Also, biological control was tested by releasing predator on B. brassicae (L.). Successful control was achieved reaching to 55% after 14 days, then gradually rose to 80.9% and 89.5% after 21 and 30 days respectively. Finally, we recommend the use of C. carnea as a prime candidate for mass release as having a high potential ability to control cabbage aphid .