11x17Answers
advertisement

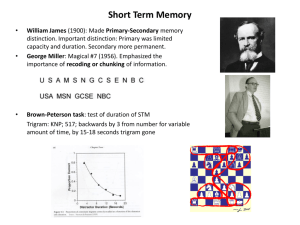
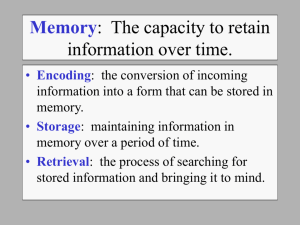
Page 71-72 3. Encoding is how memories are created; storage is the process by which memories are retained; retrieval is how that information is used in the future 5. Interference theory, decay theory, aging, stress, lack of sleep 8. Working memory (7-9 items). Often used with lists, sequences. 9. Decay theory as we no longer use information, it is forgotten; Interference theory old learning is ‘pushed out’ by new learning. 10. If we do not rehearse, or practice, new learning then it will not be transferred into longer-term memory. 11. Primacy information learned at the beginning of a list or sequence is transferred into longer-term memory; Recency information learned at the end of a list is still accessible via short-term memory Page 72-74 1. Working; long-term 3. Encoding 5. Storage, retrieval 11. Decay 15. Primacy, recency 16. Organization, chunks 18. Working 20. Mnemonics 33. Interference 52. amygdala Page 75- 1. 3. 5. 6. 7. 8. 10. 12. 13. 16. 20. 21. 22. 12. Chunking information involves grouping similar information together so that there are fewer ‘items’ to remember: Ex: remembering 1918 instead of 1 and 9 and 1 and 8. Chunks are created by the brain organizing information 17. Chunking and reorganization help the memory by encoding fewer items into memory, thereby aiding in recall 18. Mnemonics are cues that are used to remember lists/complex patterns of information (Ex: ROY G. BIV for Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet in the rainbow) 28. Interference theory new information clouds out old; Decay Unused information is forgotten 36. Eyewitness testimony is not always reliable, memory recall does not always match past events C B B C D D D B C C B B B 78