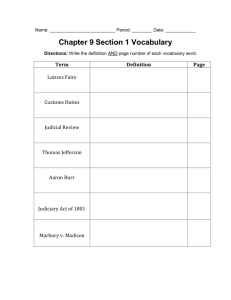
Mathematics Core 1
advertisement
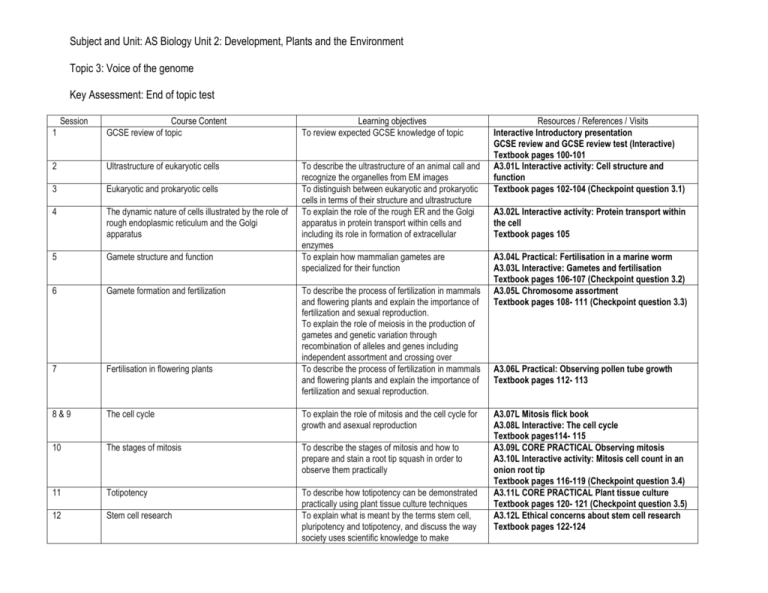
Subject and Unit: AS Biology Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment Topic 3: Voice of the genome Key Assessment: End of topic test 1 Session Course Content GCSE review of topic Learning objectives To review expected GCSE knowledge of topic 2 Ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells 3 Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells 4 The dynamic nature of cells illustrated by the role of rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus 5 Gamete structure and function To describe the ultrastructure of an animal call and recognize the organelles from EM images To distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in terms of their structure and ultrastructure To explain the role of the rough ER and the Golgi apparatus in protein transport within cells and including its role in formation of extracellular enzymes To explain how mammalian gametes are specialized for their function 6 Gamete formation and fertilization 7 Fertilisation in flowering plants 8&9 The cell cycle To explain the role of mitosis and the cell cycle for growth and asexual reproduction 10 The stages of mitosis To describe the stages of mitosis and how to prepare and stain a root tip squash in order to observe them practically 11 Totipotency 12 Stem cell research To describe how totipotency can be demonstrated practically using plant tissue culture techniques To explain what is meant by the terms stem cell, pluripotency and totipotency, and discuss the way society uses scientific knowledge to make To describe the process of fertilization in mammals and flowering plants and explain the importance of fertilization and sexual reproduction. To explain the role of meiosis in the production of gametes and genetic variation through recombination of alleles and genes including independent assortment and crossing over To describe the process of fertilization in mammals and flowering plants and explain the importance of fertilization and sexual reproduction. Resources / References / Visits Interactive Introductory presentation GCSE review and GCSE review test (Interactive) Textbook pages 100-101 A3.01L Interactive activity: Cell structure and function Textbook pages 102-104 (Checkpoint question 3.1) A3.02L Interactive activity: Protein transport within the cell Textbook pages 105 A3.04L Practical: Fertilisation in a marine worm A3.03L Interactive: Gametes and fertilisation Textbook pages 106-107 (Checkpoint question 3.2) A3.05L Chromosome assortment Textbook pages 108- 111 (Checkpoint question 3.3) A3.06L Practical: Observing pollen tube growth Textbook pages 112- 113 A3.07L Mitosis flick book A3.08L Interactive: The cell cycle Textbook pages114- 115 A3.09L CORE PRACTICAL Observing mitosis A3.10L Interactive activity: Mitosis cell count in an onion root tip Textbook pages 116-119 (Checkpoint question 3.4) A3.11L CORE PRACTICAL Plant tissue culture Textbook pages 120- 121 (Checkpoint question 3.5) A3.12L Ethical concerns about stem cell research Textbook pages 122-124 Subject and Unit: AS Biology Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment Topic 3: Voice of the genome Key Assessment: End of topic test 13 The role of the nucleus in the control of development 14 Differential gene expression 15 Cellular organization 16 Differential gene expression 17 How phenotype is a result of genotype and environment 18 How phenotype is a result of genotype and environment 19 How phenotype is a result of genotype and environment Peer Activity 3.19 Using checklist of learning outcomes decisions about the use of stem cells in medical therapies To explain how cells become specialized through differential gene expression, producing active mRNA leading to synthesis of proteins which in turn control cell processes or determine cell structure in animals and plants To explain how cells become specialized through differential gene expression, producing active mRNA leading to synthesis of proteins which in turn control cell processes or determine cell structure in animals and plants To describe how the cells of multicellular organisms can be organized into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into organ systems. To explain how cells become specialized through differential gene expression, producing active mRNA leading to synthesis of proteins which in turn control cell processes or determine cell structure in animals and plants To explain how cells become specialized through differential gene expression, producing active mRNA leading to synthesis of proteins which in turn control cell processes or determine cell structure in animals and plants To explain how some phenotypes are affected by alleles at many loci as well as the environment and how this can give rise to phenotypes that show continuous variation To explain how phenotype is the result of an interaction between genotype and the environment, but the data on the relative contributions of genes and environment is often difficult to interpret To explain how phenotype is the result of an interaction between genotype and the environment, but the data on the relative contributions of genes and environment is often difficult to interpret A3.13 Interactive activity: Acetabularia experiments Textbook pages 125- 127 A3.14 Practical: Incuction of beta galactosidase Textbook pages 128-129 Textbook pages 130- 133 (Checkpoint question 3.6) A3.15L Modelling flowers A3.16L Polygenic inheritance Textbook pages 134- 136 A3.17L Practical and Interactive activity: Are we still getting taller? Textbook pages 137 A3.18L Genes or the environment Textbook pages 138-141 Subject and Unit: AS Biology Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment Topic 3: Voice of the genome Key Assessment: End of topic test Learning Tasks students review their learning during the topic Directed independent study Write up of class practical’s Homework P102- 141 Textbook questions