Grade 3 Unit 3 Math - Pendleton County Schools
advertisement
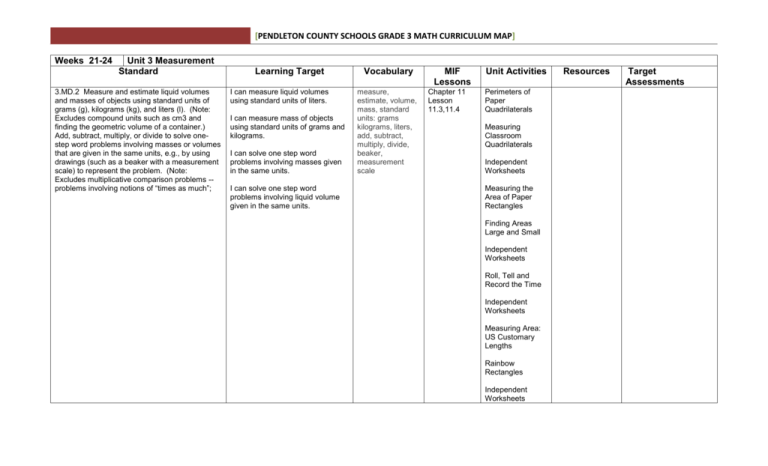
[PENDLETON COUNTY SCHOOLS GRADE 3 MATH CURRICULUM MAP] Weeks 21-24 Unit 3 Measurement Standard 3.MD.2 Measure and estimate liquid volumes and masses of objects using standard units of grams (g), kilograms (kg), and liters (l). (Note: Excludes compound units such as cm3 and finding the geometric volume of a container.) Add, subtract, multiply, or divide to solve onestep word problems involving masses or volumes that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as a beaker with a measurement scale) to represent the problem. (Note: Excludes multiplicative comparison problems -problems involving notions of “times as much”; Learning Target I can measure liquid volumes using standard units of liters. I can measure mass of objects using standard units of grams and kilograms. I can solve one step word problems involving masses given in the same units. I can solve one step word problems involving liquid volume given in the same units. Vocabulary measure, estimate, volume, mass, standard units: grams kilograms, liters, add, subtract, multiply, divide, beaker, measurement scale MIF Lessons Chapter 11 Lesson 11.3,11.4 Unit Activities Perimeters of Paper Quadrilaterals Measuring Classroom Quadrilaterals Independent Worksheets Measuring the Area of Paper Rectangles Finding Areas Large and Small Independent Worksheets Roll, Tell and Record the Time Independent Worksheets Measuring Area: US Customary Lengths Rainbow Rectangles Independent Worksheets Resources Target Assessments [PENDLETON COUNTY SCHOOLS GRADE 3 MATH CURRICULUM MAP] Metric Rectangles Ladybug Dream House Independent Worksheets 3.MD.1 Tell and write time to the nearest minute and measure time intervals in minutes. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of time intervals in minutes. e.g. by representing the problem on a number line diagram. I can measure time intervals in minutes. I can solve and explain word problems involving addition of time intervals in minutes. tell time, write time, minute, time intervals, addition, subtraction, represent, number line diagram, solve Chapter 16 Lesson 16.1, 16.2, 16.3, 16.4, 16.5 recognize, attribute, plane figure, concepts of area measurement, unit square, square units, area Chapter 19 Lesson 19.1, 19.2, 19.3 I can solve and explain word problems involving subtraction of time intervals in minutes. 3.MD.5 Recognize area as an attribute of plane figures and understand concepts of area measurement. a. A square with side length 1 unit, called “a unit square,” is said to have “one square unit” of area, and can be used to measure area. b. A plane figure which can be covered without gaps or overlaps by n unit squares is said to have an area of n square units. 3.MD.7 Relate area to the operations of multiplication and addition. a. Find the area of a rectangle with wholenumber side lengths by tiling it, and show that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths. I can solve word problems involving addition/subtraction of time intervals in minutes by representing the problem on a number line diagram. I can cover the area of a plane figure with unit squares without gaps or overlays. I can relate the number (n) of unit squares to the area of a plane figure. A. I can compare the area found by tiling a rectangle to the area found by multiplying the side lengths. B. I can solve real world and area, rectangle, whole-number, side, tiling, multiply, side lengths Time Ruler [PENDLETON COUNTY SCHOOLS GRADE 3 MATH CURRICULUM MAP] b. Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole-number side lengths in the context of solving real world and mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning. c. Use tiling to show in a concrete case that the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths a and b + c is the sum of a × b and a × c. Use area models to represent the distributive property in mathematical reasoning. d. Recognize area as additive. Find areas of rectilinear figures by decomposing them into nonoverlapping rectangles and adding the areas of the non-overlapping parts, applying this technique to solve real world problems. mathematical area problems by multiplying side lengths of rectangles. I can represent whole-number products in multiplication problems by using rectangular arrays. C. I can use tiling to show the area of a rectangle with whole number sides. I can use area models to represent the distributive property in mathematical reasoning. D. I can decompose rectilinear figures into non-overlapping rectangles. I can determine the technique of decomposing rectilinear figures to find the area of each rectangle to solve real world problems. 3.MD.8 Solve real world and mathematical problems involving perimeters of polygons, including finding the perimeter given the side lengths, finding an unknown side length, and exhibiting rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas or with the same area and different perimeter I can determine the area of each rectangle by using the technique of decomposing regular figures. I can design, create, draw, model, exhibit etc. rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas. I can design rectangles with the same area and different perimeters. I can exhibit rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas or with the same area and different multiply, side lengths, area, whole-number, context, realworld, product, mathematical reasoning tiling, concrete case, area of rectangles, wholenumber, length, area models, distributive property, mathematical reasoning recognize, area, additive, rectilinear figures, decompose, nonoverlapping, parts, technique real-world, perimeter, polygons, side length, area Chapter 19 Lesson 19.5 [PENDLETON COUNTY SCHOOLS GRADE 3 MATH CURRICULUM MAP] perimeters. (design, create, draw, model etc.) Demonstrate, explore, investigate rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas or the same area and different perimeters. I can determine the perimeter when given the length of sides. I can determine the perimeter when there is an unknown side length.