Unit 2 Objectives and Guided Reading
advertisement

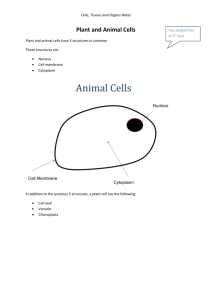
Unit 2 Objectives – Organization of the Body Students will be able to: 1. Describe the hierarchy of human structures 2. Describe the makeup of the human physiological environment and factors that affect it 3. Describe the components of each level of organization and how they maintain the overall homeostasis in the body a. Describe the basic structures found within a cell b. Describe the basic cellular processes/functions c. Describe the different types of human tissues d. Describe the different types of organs and systems 4. Use the terminology associated with cell structure and function 5. Understand the cellular basis of aging and pathology Guided Reading Questions: Chapter 3 Answer the following questions as you read each section. Be ready to discuss your answers in class the following day. Be sure to define all terms as you go! Hierarchy of Human Structure 1. List the levels of organization, starting with molecules. 2. Why does the author use the word “hierarchy” to describe the levels of organization? 3. What are stem cells? How do they relate to the concept of differentiation? The Human Physiological Environment (Water) 1. If humans live on land, why does the author say that the human physiological environment is “aqueous”? 2. What kinds of conditions determine the body’s aqueous environment? 3. What does it mean when people say that something acts as a “solvent”? Tissues 1. What is the fate of the embryological germ layers? 2. What are the four types of tissue found in humans? 3. What are the major characteristics/functions of the four types of tissue? (Recommend you make a chart) Organs and Systems 1. What is the relationship between tissues and organs/systems? 2. What are the various organ systems found in humans? Wellness and Illness over the Life Span 1. What does this statement mean? “Cell pathology causes hierarchy dysfunctions of the body”? 2. What is the purpose of a biopsy? 3. Make a chart describing the major types of cell pathology. 4. What is “molecular decay”? 5. What does “telomere shortening” cause for a cell?



![Abraham Maslow [Autosaved]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/025194284_1-d4cda09130dfc06314210c770d18f8c4-300x300.png)