Ways of Knowing Assignment
advertisement

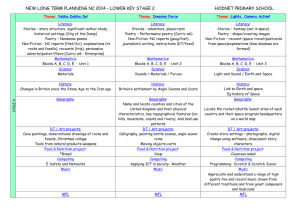
Ways of Knowing (WOKs) Assignment Objective: students are to work with a partner(S) and complete a poster which demonstrates their understanding of one way of knowing. Each poster will contain: The Way of Knowing The definition of the way of knowing Diagrams, cartoons, characters etc. to demonstrate their knowledge How a knowledge claim is understood through their way of knowing In Theory of Knowledge there are eight different ways of knowing 1. Emotion: Although many people think of emotion as an unreliable WOK which is somehow less useful than reason, it is also often the case that we know things emotionally with more certainty than by any other WOK. Are emotions universal? Can/should we control our emotions? Are emotions the enemy of, or necessary for, good reasoning? Are emotions always linked to belief? 2. Memory: Most of what we think we know, we remember. Memory is also vital to our sense of who we are. In other words, it’s one of the most important WOK. However, memory of past experience can also influence how we gain new knowledge using the other WOK. Can we know things which are beyond our personal present experience? Is eyewitness testimony a reliable source of evidence? Can our beliefs contaminate our memory? 3. Reason: Working things out logically, using reason lets us go beyond what we’ve discovered using sense perception. It’s very important WOK but has lots of different meanings depending on who you ask. A Mathematician for example might see the definition of reason in their subject very differently from a historian. What is the difference between reason and logic? How reliable is inductive reasoning? Are we predictably irrational? 4. Intuition: This is sometimes seen as the opposite to reason the idea that we know something instinctively strikes some people as illogical or unreliable. However, intuition can be extremely useful to us if we need to make very quick judgements. Why are some people considered more intuitive than others? Are there certain things that you have to know prior to being able to learn anything at all? Should you trust your intuition? 5. Faith: This is probably the most loudly argued over WOK. Religious people often believe that faith is the most certain, useful, and important WOK there is while non-religious people claim the exact opposite that faith is completely useless. However we all have faith (or trust) in things we can’t know using other WOK for instance, that the chair you’re sitting on won’t collapse under you? Should humanism or atheism be described as faith? Can theistic beliefs be considered knowledge because they are produced by a special cognitive faculty or “divine sense”? Deos faith meat a psychological need? 6. Language: Language, whether written or spoken, is vitally important way of communicating knowledge. If it wasn’t, then why would you be reading this? But some people would argue that language is even more important than this: that the process of putting our thoughts into words actually shapes what we know- in other words, that we know can be defined by our ability to put it into words. How does language shape knowledge? Does the importance of language in an area of knowledge ground it in a particular culture? How are metaphors used in the construction of knowledge? 7. Imagination: It’s difficult to define what imagination is precisely but it’s still very important way we know things. People whose imaginations works in unusual ways are often diagnosed with conditions such as autism, or synaesthesia. Imagination is also the key to being creative and solving problems. What is the role of imagination in producing knowledge about a real world? Can imagination reveal truths that reality hides? What is the role of the imagination in understanding others? 8. Sense Perception: Without the evidence of our senses we would not even know that the outside world exists. So, sense perception is an absolutely vital WOK. Covering what we can see, hear, touch, smell and taste. Although it’s vital, people disagree about whether our senses give an accurate picture of the outside world or not. How can we know if our senses are reliable? What is the role of expectations or theory in sense perception? What is the role of language in sense perception? Presentation: Each group will hand in one 11 by 17 poster and prepare a one or two slide power point to further illustrate their presentation. Criteria WOK Definition Fully Meets A/B WOK is clear and visible, the definition is easily understood. Knowledge claim example is an excellent real life example and the explanation shows a clear link to the WOK Meets C+/ CWOK is clear and visible, the definition is understood. Knowledge claim example is a good real life example and the explanation shows a somewhat clear link to the WOK Presentation Group creates an excellent PowerPoint or other type of presentation. All group members present their WOK. Ideas are presented clearly and are within the 5 to 10 minute time frame Group creates a Good PowerPoint or other type of presentation. Most group members present their WOK. Ideas are presented clearly and are within the 5 to 10 minute time frame Overall Product and Presentation The assignment is on an 11 by 17 sheet of paper. Excellent creative risk taking ideas are demonstrated. Student (s) use excellent colour, diagrams, etc. The assignment is on an 11 by 17 sheet of paper. Good creativity, some risk taking ideas are demonstrated. Student (s) use good colour, diagrams, etc. Knowledge Claim and connection to WOK Does Not Meet C-/I WOK is clear and visible, the definition is not understood. Knowledge claim example is poor. No connection to real life and the explanation does not demonstrate an understanding of the WOK Group creates a poor or adequate PowerPoint or other type of presentation. All group members are not present or do not partake in the presentation Ideas are presented clearly but do not fall within the 5 to 10 minute time frame The assignment is on an 11 by 17 sheet of paper. Little or no creativity demonstrated. Student (s) does not use colour, diagrams, etc. to demonstrate their WOK example. WOK Presentation Names: Date: Day: 1 2 WOK: : Criteria WOK Definition Fully Meets A/B WOK is clear and visible, the definition is easily understood. Knowledge claim example is an excellent real life example and the explanation shows a clear link to the WOK Meets C+/ CWOK is clear and visible, the definition is understood. Knowledge claim example is a good real life example and the explanation shows a somewhat clear link to the WOK Presentation Group creates an excellent PowerPoint or other type of presentation. All group members present their WOK. Ideas are presented clearly and are within the 5 to 10 minute time frame Group creates a Good PowerPoint or other type of presentation. Most group members present their WOK. Ideas are presented clearly and are within the 5 to 10 minute time frame Overall Product and Presentation The assignment is on an 11 by 17 sheet of paper. Excellent creative risk taking ideas are demonstrated. Student (s) use excellent colour, diagrams, etc. The assignment is on an 11 by 17 sheet of paper. Good creativity, some risk taking ideas are demonstrated. Student (s) use good colour, diagrams, etc. Knowledge Claim and connection to WOK Does Not Meet C-/I WOK is clear and visible, the definition is not understood. Knowledge claim example is poor. No connection to real life and the explanation does not demonstrate an understanding of the WOK Group creates a poor or adequate PowerPoint or other type of presentation. All group members are not present or do not partake in the presentation Ideas are presented clearly but do not fall within the 5 to 10 minute time frame The assignment is on an 11 by 17 sheet of paper. Little or no creativity demonstrated. Student (s) does not use colour, diagrams, etc. to demonstrate their WOK example. Comments: See over