File
advertisement
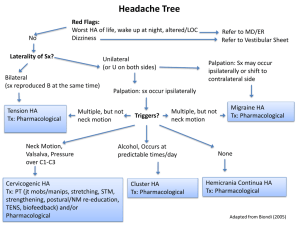
1 Differentials for Headaches New or different HA 50+ HA develops within minutes (thunderclap headache), inability to move a limb or abnormalities on neurological examination, mental confusion, being woken by HA, HA that worsens with changing posture. HA worsened by exertion /Valsalva manoeuvre visual loss or visual abnormalities, jaw claudication, neck stiffness, fever, and HA in people with HIV, cancer or risk factors for thrombosis. What are primary and secondary HA and Primary HA are not caused by other disease. Examples are what causes them? migraine and tension type). Secondary HA caused by some other underlying condition. Cervicogenic HA AKA: occipital neuralgia. Causes: can be caused by compression (causing irritation or injury) of the greater occipital nerve by over-tight neck mms, osteophytic growth as the nerve leaves the spine, trauma or tumour. Also diabetes, blood vessel inflammation (vasculitis), and prolonged neck flexion. Symptoms: gradual onset of post head, above eye, temporal pain. Usually unilat. Who? 20-60 yrs. Osteopathy? Some evidence osteopathic ttt such as HVT, ST and MET is effective. Examinations-MT: observe for altered neck posture, decreased ROM in Csp, trigger points in s.occipitals, neck and shoulder mms. Nerve blocks can confirm diagnosis but MRI shows nothing. Migraine: cause, symptoms, most likely Primary HA people to be effected? Causes: Vascular origin, facilitated segment in the brain stem. Trigeminal nerve involved. Symptoms: prodrome up to 2 days before, aura (visual, sensory, physical) just before. One sided, throbbing Can become less sever but more frequent with age. Who? male: female 1:3. 12% population. Osteopathy? Some small studies suggest manipulation can decrease pain intensity and frequency of migraine. What are the red flags for HA? Tension type HA. Primary HA, most common HA. Causes: associated with stress, mms contraction. Symptoms: pain on both sides of the head, forehead, temples or the back on head and/or neck. Who? 40% population. More common in females. 30-39 age group most affected. Osteopathy? Systematic review showed manipulation to be affective. Cluster HA. Primary HA Causes: mechanism unknown, possible due to ANS affecting trigeminal nerve, cold weather/alchohol can trigger. 2 Symptoms: most severe pain humans report. Upto 3 x day. ipsilateral lacrimation, rhinorrhea, ptosis Who? Men more than women. 4:1, 0.1% of population. Osteopathy? Do not seem to be musculo-skeletal-no evidence easily available on pubmed…some anecdotal evidence. Sinus HA Hypertension HA Worse am CA headache Bleeds cause HA? Whiplash HA Secondary HA; hard to distinguish from migraine. Migraines usually not accompanied by yellow snot! Important to get right as meds are effective for each type if diagnosed correctly. Causes: different opinions…some say rarely due to sinusitis; others that the infection causes the pain. Symptoms: dull, deep, throbbing pain anteriorly. Face TTP, worse for sudden mmts and leaning forward. Worse am as drainage worse. Who? Osteopathy? Maryland medical system says: Stretches for the head and neck/ Relaxation techniques help prevent sinusitis. Drinking more fluids and using a humidifier Secondary HA Causes: best evidence suggests high BP doesn’t cause HA unless in case of hypertensive crisis (systolic/top number higher than 180 OR diastolic/bottom number higher than 110) (heart.org) Symptoms: generalized or "hairband" type pain. They are most severe in the morning and diminish throughout the day Who? Hypertension is more common in men but women have a higher incidence of headaches Osteopathy? If we can reduce BP through relaxation advise, reducing stress, lifestyle advise. Causes: Symptoms: progressively worse over time worse am, pain may wake you up. Accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Headache pain that is relieved by vomiting is a typical symptom of brain tumour. Straining/ Leaning forward agg. pain. Not relieved by painkillers. Who? 2 peaks incidence; childhood, then larger peak in 70. Osteopathy? No The headache attributed to Sub-arachnoid Haemorrhage often unilateral, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, disorders of consciousness and nuchal rigidity ((neck stiffness), and less frequently by fever and cardiac dysrythmia Headache attributed to intracerebral haemorrhage Headache is more frequent and more severe in haemorrhagic than in ischaemic stroke. It is usually overshadowed by focal deficits or coma, but it can be the prominent early feature of cerebellar haemorrhage which may require emergency surgical decompression. Osteopathy? No Causes: C3 facet and its nerve most vulnerable to whiplash injury. Symptoms: Pain from the C2–3 facet is referred to the occipital region but is also referred to the frontotemporal and periorbital regions. Osteopathy? The majority of cervicogenic headaches occurring after whiplash resolve 1 yr. treat as cervicogenic HA, evidence for myofascial release etc 3 Meningitis HA Glaucoma HA Causes: Inflammation of meninges caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms. Symptoms: severe headache and neck stiffness, pain on passive neck flexion. Fever, photophobia and altered mental status. Who? Babies, uni students and adults 55+. Osteopathy? Obviously not. Examinations- Koernig sign (below pic) and Brudinski’s (Flexing the patient’s neck causes flexion of the patient’s hips and knees.) Causes: Fluid in the eye does not drain properly, or there is over-production of fluid, which causes increased pressure within the eye Symptoms: HA in or around the eyes or the forehead, and vary in intensity from mild to severe. Nausea and vomiting also can accompany the headache. Chronic-slowly develops-peripheral vision affected. Acute: intense pain, redness of the eye, HA, tender eye Who? 60+, Hypertension, injury to the eye can cause acute angle glaucoma. Encephalitis HA Causes: Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. Symptoms:HA, fever, confusion, drowsiness. Neck stiffness. 4 TMJ HA Briefly list other HA and how to recognise them. Causes: Dental problems, Trauma Hormonal changes, Fatigue, Clenching and grinding, Poor posture. Symptoms: ‘vice-like grip’. achy, throbbing headache HA in temples, back of the head/ shoulders. Clenching and grinding of the teeth, both of which may be TMJ symptoms, produce mms pain which can cause HA. Displaced disc in the TMJ may cause pain in the joint referred into the temples, forehead or neck. Worse am or pm depending on when teeth grinding occurs. Who? Osteopathy? Seems to be treated will good results-SF masseter, Temporalis, gapping TMJ joint. Questions: Do you hear popping, clicking or cracking sounds when you chew? Do you hear a grating sound (like crumpling of newspaper) when you chew? Thunderclap HA-Severe and sudden-onset. It is defined as a severe headache that takes seconds to minutes to reach maximum intensity. It can be indicative of a number of medical most importantly subarachnoid hemorrhage problems Carbon monoxide exposure-frontal HA all the time, present in winter. Caffeine withdraw-starts behind the eyes and then moves up the front of the head. Acute caffeine abstinence increased brain blood flow. Coital cephalalgia “sexual headaches" occurs at the base of the skull, extremely severe and sharp pain behind the eyes. Usually men early 20’s, or 35-40 , 1% population. Temporal arteritis: HA is persistent but often worse at night and sometimes severe, in a patient over 50 who does not feel entirely well. It may be accompanied by marked scalp tenderness.