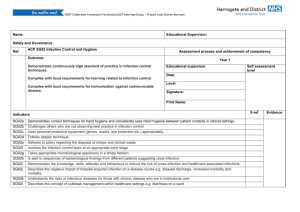
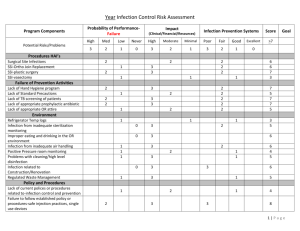
Supplemental Information The adapter protein c-Cbl
advertisement

Supplemental Information The adapter protein c-Cbl-associated protein (CAP) protects from acute CVB3-mediated myocarditis through stabilization of type I interferon production and reduced cytotoxicity Alan Valaperti, Mototsugu Nishii, Youan Liu, Howard Yang, Kotaro Naito, Peter P Liu, Urs Eriksson Supplemental Information - Materials and methods Cells and CVB3 Virus For bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMM) cultivation, bone marrow was isolated from femurs and tibiae of 5 to 8 weeks old mice and, after red blood cells lysis, cells were plated at 106/ml and cultivated for 5 days in RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS, antibiotics, and 50 ng/ml M-CSF (PeproTech) [1]. Dendritic cells were cultivated from the same crude bone marrow, but cells were plated at 2x105/ml in the same medium supplemented with 20 ng/ml GM-CSF (PeproTech) for 8 days [2]. For plasmacytoid dendritic cells, bone marrow cells were plated at 106/ml for 10 days in the same medium supplemented with 100 ng/ml Flt3L (Cedarlane) [3]. Reagents and Antibodies High molecular weight and low molecular weight (LMW) polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (polyIC), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and the imidazoquinoline R848 were purchased from Invivogen. Antibodies to MDA5, phosphorylated-IRF3 (p-IRF3), IRF3, p-Ikk/, Ikk/, p-p65, p65, MyD88, IRAK4, TRAF3, TRAF6, p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, p-p38, p38, p-JNK, JNK, p-Bad, Bad, and Poly-ubiquitin were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. Cytocrome c was purchased from BD Bioscience, FLAG antibody from Origene, CAR and Lck from Santa Cruz. Quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-Quantitative RT-PCR RNA was isolated with Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. cDNA synthesis was performed using 1 µg RNA, random primers, and Super-Script First-Strand Reverse Transcriptase (both Invitrogen). Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed with SybrGreen (Roche Diagnostic) using a LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System machine (Roche Diagnostic), with GAPDH as internal control. Gene expression was analyzed using the 2- 1 Ct method. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR was performed with the cDNA produced from 1 µg RNA, running 25 cycles and comparing genes of interest with the housekeeping gene GAPDH. Primers used for quantitative RT-PCR: ifn- - TGAGTGAGCTGACCCAGCAGA; GCTGGTGGAGGTCATCATTG ifn- - CAGCTCCAAGAAAGGACGAAC; GGCAGTGTAACTCTTCTGCAT ifn- - AACTCAAGTGGCATAGATGTGGAA; CTGGCTCTGCAGGATTTTCAT il-1 - TTGGGCCTCAAAGGAAAGAAT; TGGGTATTGCTTGGGATCCA il-6 - GCTAAGGACCAAGACCATCCAAT; GGCATAACGCACTAGGTTTGC il-12p40 - GCCAGTACACCTGCCACAAA; TTAAAATTTCAGTGGACCAAATTCC tnf- - GCCAACGGCATGGATCTC; GCAGCCTTGTCCCTTGAAGAG ccl5 - TGCCTCGTGCCCACGTCAAG; TGGCACACACTTGGCGGTTCC il-10 - GCCAAGCCTTATCGGAAATG; GGGAATTCAAATGCTCCTTGAT il-17a - ACCGCAATGAAGACCCTGAT; TCCCTCCGCATTGACACA il-17f - CTGTTGATGTTGGGACTTGCC; TCACAGTGTTATCCTCCAGG il-23p40 - CGGAATCTCTGCATGCTAGCC; ACACTGGATACGGGGCACATT Tbet - CAACAACCCCTTTGCCAAAG; TCCCCCAAGCAGTTGACAGT RORt - TTTGGAACTGGCTTTCCATC; AAGATCTGCAGCTTTTCCACA Eomes - CGGGACAACTACGATTCCATGT; GGGCTTGAGGCAAAGTGTTG irf3 - AGCCCTGAACCGGAAAGAAG; CCCAGATGTACGAAGTCCCG irf7 - CTGGAGCCATGGGTATGCA; AAGCACAAGCCGAGACTGCT perforin - AAACATGCGCGCCTCCGTGG; AGGCGAAAACTGTACATGCGACACT granzyme - CTTGACGCTGGGACCTAGGCG; CCGATGATCTCCCCTGCCTTTGT gapdh - ACTCCACTCACGGCAAATTCA; GGTCTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG 2 Flow Cytometry Analysis Cell suspensions, as well as in vitro-cultivated cells, were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated mouse-specific mAb against CD8, CD11c, CD11b, CD45, CD45.1, CD45.2, CD45R, CD49b, CD69, Ly6G, PDCA-1, (all BD Biosciences), and F4/80 (BioLegend). Anti-mouse perforinFITC antibody, clone eBioOMAK-D, and anti-mouse Granzyme B-FITC antibody, clone NGZB, were purchased from eBiosciences. Western Blot Analysis, and Co-Immunoprecipitation In vitro cultivated cells were harvested and washed twice with cold PBS. Heart tissue was homogenized in 1x Cells Lysis Buffer (Cell Signaling Technology) supplemented with protease inhibitors (Complete, Roche Diagnostic) using small stainless steel beads in a TissueLyser machine (Qiagen). After removing beads, homogenized organs were sonicated, centrifuged, and supernatant collected for protein assays. Sonication, centrifugation and supernatant collection was also performed for in vitro cultivated cells when used as whole cell lysates. Cell lysates were separated in a NuPAGE electrophoresis system (Invitrogen) using NuPAGE Novex Bis-Tris gel (Invitrogen) and then transferred on a PVDF membrane (Roche Diagnostics), subsequently immunoblotted with specific antibody to indicated protein. Bands were visualized with horseradish peroxidase-coupled secondary antibody activated with an ECL chemiluminescent substrate (Luminata Crescendo, Millipore). Bands were scanned using a densitometer (GS-700, BioRad). For immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged CAP protein, an anti-DDK Tag (L5) affinity gel was used according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Biolegend). For immunoprecipitation of MDA5 and MyD88 (Cell Signaling), antibodies were coupled to Dynabeads Protein G (Life Technologies) and immunoprecipitated following the manufacturer’s protocol. 3 Supplemental Information - Fig. S1 4 Fig. S1 Worsened viral myocarditis after CVB3 challenge in the absence of CAP. a Heart function is impaired after CVB3 challenge in the absence of CAP. Echocardiography performed before viral infection (Day 0) and after CVB3 infection (Day 7). b Statistical analysis of the percentage of heart-infiltrating cells four days after CVB3 infection. Hearts were first carefully perfused with PBS and after digestion with Liberase, total heart lysates were triple stained. Heart-infiltrating cell were first gated on CD45high cells and then represented as indicated. c Statistical analysis of the percentage of heart-infiltrating cells four days after CVB3 infection. Hearts were first carefully perfused with PBS and after digestion with Liberase, total heart lysates were triple stained. Heart-infiltrating cell were first gated on CD3+ cells and then represented as indicated. Data are representative for one out of two independent experiments (n = 5 each group) (mean, s.d.). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). 5 Supplemental Information - Fig. S2 6 Fig. S2 CAP+/+ and CAP-/- splenocytes before and after CVB3 infection. a, b Comparable baseline levels of splenic leukocytes in CAP+/+ and CAP-/- mice before infection. Splenic sub-populations analyzed before infection. T cells and NK cells (a) and different groups of monocytes/macrophages and granulocytes (b) were measured by flow cytometry. c Statistical analysis of the percentage of splenocytes four days after CVB3 infection. T cells were first gated on CD3+ cells and then double stained and the represented as indicated. Data are representative for one out of two independent experiments (n = 5 each group) (mean, s.d.). * P < 0.05, (Student’s t-test). d CAR and Lck were measured in total heart tissue before (Day 0) and after (Day 4) CVB3 infection by western blot. Densitometry evaluation is shown below, comparing CAR or Lck with GAPDH, which was used as internal loading control. 7 Supplemental Information - Fig. S3 Fig. S3 Expression of co-stimulatory surface molecules is independent of CAP. a, b Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells were stimulated for 8h with 1 µg/ml LPS (a) or 10 ng/ml PolyIC (b). Surface staining was performed by flow cytometry to evaluate costimulatory markers. 8 Supplemental Information - Fig. S4 Fig. S4 CAP inhibits IL-17A-producing CD4+ Th cells but not IFN--producing CD4+ Th cells, while limiting the expression of Tbet, ROR, and Eomes. a Intracellular flow cytometry analysis of splenocytes suspensions stimulated in vitro with soluble CD3/CD28 antibodies for 48h. IL-17A and IFN- production was detected in CD3+CD4+ T cells, cytotoxic CD3+CD8+ T cells, and cytotoxic CD3-CD49b+ NK cells. b Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of splenic RNA expression of transcription factors Tbet and ROR 4 days after CVB3 infection in vivo. Data are representative for two independent experiments (n = 5 each group) (mean, s.d.). * P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). c Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of splenic RNA expression of the transcription factor Eomes 4 days after CVB3 infection in vivo. Data are representative for two independent experiments (n = 5 each group) (mean, s.d.). * P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). 9 Supplemental Information - Fig. S5 Fig. S5 PI3K and Akt phosphorylation are CAP-independent after CVB3 infection. a, b Total splenocytes (a) and heart tissue (b) collected from uninfected (D0) or CVB3infected (D4) mice were blotted with p-PI3K, PI3K, and p-Akt antibodies. GAPDH and Actin were used as internal loading control. 10 Supplemental Information - References 1. Valaperti A, Marty RR, Kania G, et al. (2008) CD11b+ monocytes abrogate Th17 CD4+ T cell-mediated experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 180:2686–2695. 2. Eriksson U, Ricci R, Hunziker L, et al. (2003) Dendritic cell-induced autoimmune heart failure requires cooperation between adaptive and innate immunity. Nat Med 9:1484–1490. doi: 10.1038/nm960 3. Gilliet M, Boonstra A, Paturel C, et al. (2002) The development of murine plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors is differentially regulated by FLT3-ligand and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med 195:953–958. 11