View
advertisement
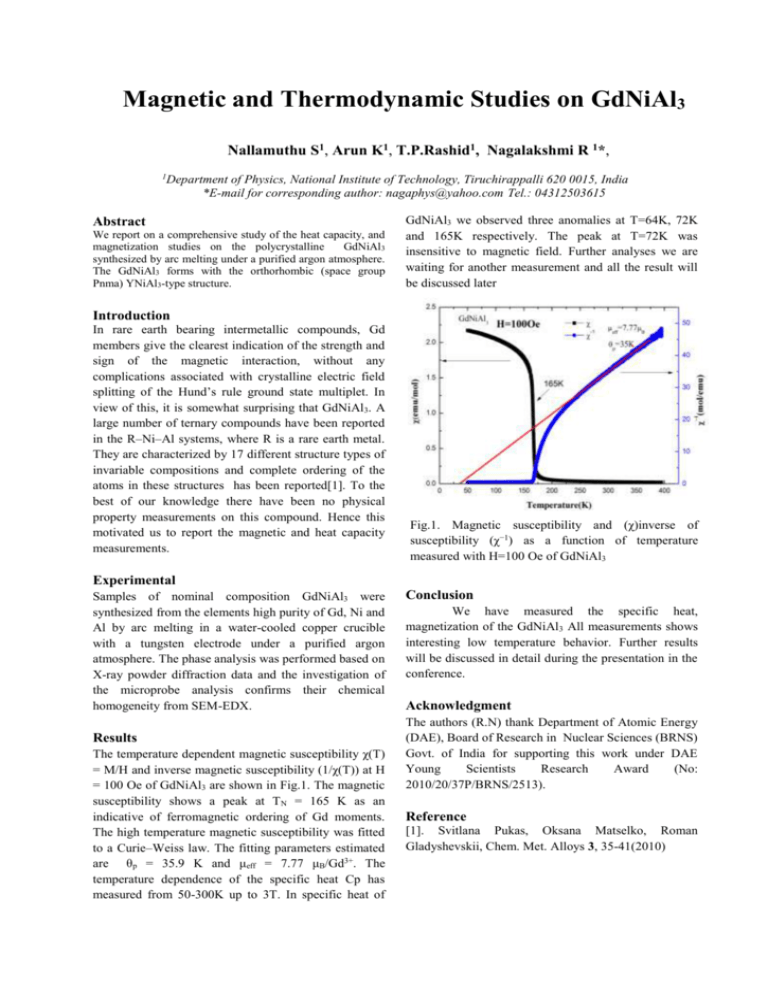
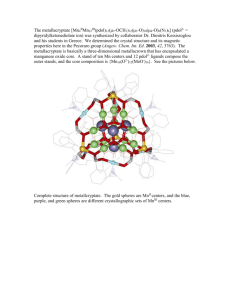
Magnetic and Thermodynamic Studies on GdNiAl3 Nallamuthu S1, Arun K1, T.P.Rashid1, Nagalakshmi R 1*, 1 Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli 620 0015, India *E-mail for corresponding author: nagaphys@yahoo.com Tel.: 04312503615 Abstract We report on a comprehensive study of the heat capacity, and magnetization studies on the polycrystalline GdNiAl3 synthesized by arc melting under a purified argon atmosphere. The GdNiAl3 forms with the orthorhombic (space group Pnma) YNiAl3-type structure. GdNiAl3 we observed three anomalies at T=64K, 72K and 165K respectively. The peak at T=72K was insensitive to magnetic field. Further analyses we are waiting for another measurement and all the result will be discussed later Introduction In rare earth bearing intermetallic compounds, Gd members give the clearest indication of the strength and sign of the magnetic interaction, without any complications associated with crystalline electric field splitting of the Hund’s rule ground state multiplet. In view of this, it is somewhat surprising that GdNiAl3. A large number of ternary compounds have been reported in the R–Ni–Al systems, where R is a rare earth metal. They are characterized by 17 different structure types of invariable compositions and complete ordering of the atoms in these structures has been reported[1]. To the best of our knowledge there have been no physical property measurements on this compound. Hence this motivated us to report the magnetic and heat capacity measurements. Fig.1. Magnetic susceptibility and (χ)inverse of susceptibility (χ−1) as a function of temperature measured with H=100 Oe of GdNiAl3 Experimental Samples of nominal composition GdNiAl3 were synthesized from the elements high purity of Gd, Ni and Al by arc melting in a water-cooled copper crucible with a tungsten electrode under a purified argon atmosphere. The phase analysis was performed based on X-ray powder diffraction data and the investigation of the microprobe analysis confirms their chemical homogeneity from SEM-EDX. Results The temperature dependent magnetic susceptibility χ(T) = M/H and inverse magnetic susceptibility (1/χ(T)) at H = 100 Oe of GdNiAl3 are shown in Fig.1. The magnetic susceptibility shows a peak at T N = 165 K as an indicative of ferromagnetic ordering of Gd moments. The high temperature magnetic susceptibility was fitted to a Curie–Weiss law. The fitting parameters estimated are θp = 35.9 K and μeff = 7.77 μB/Gd3+. The temperature dependence of the specific heat Cp has measured from 50-300K up to 3T. In specific heat of Conclusion We have measured the specific heat, magnetization of the GdNiAl3 All measurements shows interesting low temperature behavior. Further results will be discussed in detail during the presentation in the conference. Acknowledgment The authors (R.N) thank Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences (BRNS) Govt. of India for supporting this work under DAE Young Scientists Research Award (No: 2010/20/37P/BRNS/2513). Reference [1]. Svitlana Pukas, Oksana Matselko, Roman Gladyshevskii, Chem. Met. Alloys 3, 35-41(2010)