Introduction to bioinformatics
advertisement
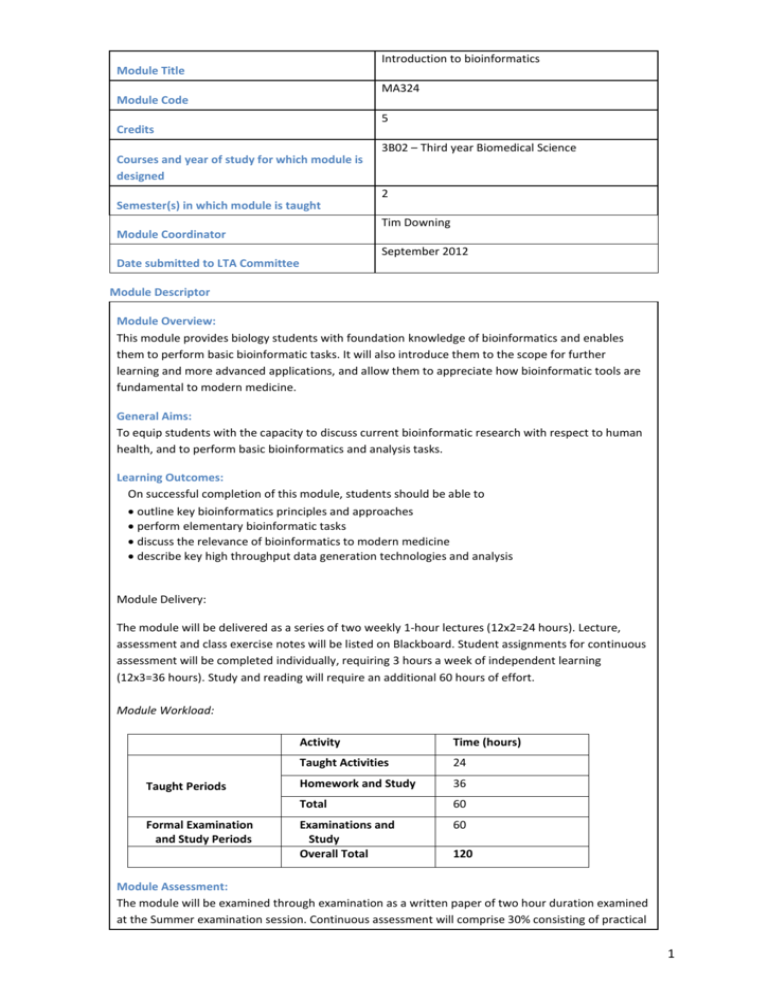
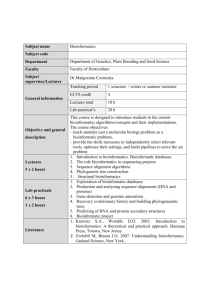
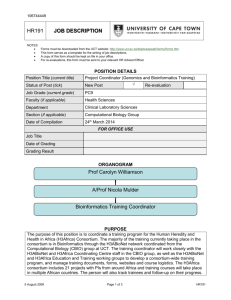
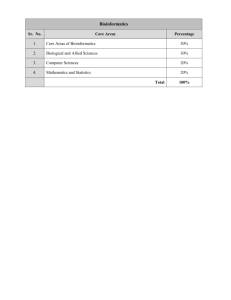
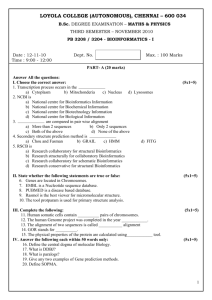
Introduction to bioinformatics Module Title MA324 Module Code 5 Credits 3B02 – Third year Biomedical Science Courses and year of study for which module is designed 2 Semester(s) in which module is taught Tim Downing Module Coordinator September 2012 Date submitted to LTA Committee Module Descriptor Module Overview: This module provides biology students with foundation knowledge of bioinformatics and enables them to perform basic bioinformatic tasks. It will also introduce them to the scope for further learning and more advanced applications, and allow them to appreciate how bioinformatic tools are fundamental to modern medicine. General Aims: To equip students with the capacity to discuss current bioinformatic research with respect to human health, and to perform basic bioinformatics and analysis tasks. Learning Outcomes: On successful completion of this module, students should be able to outline key bioinformatics principles and approaches perform elementary bioinformatic tasks discuss the relevance of bioinformatics to modern medicine describe key high throughput data generation technologies and analysis Module Delivery: The module will be delivered as a series of two weekly 1-hour lectures (12x2=24 hours). Lecture, assessment and class exercise notes will be listed on Blackboard. Student assignments for continuous assessment will be completed individually, requiring 3 hours a week of independent learning (12x3=36 hours). Study and reading will require an additional 60 hours of effort. Module Workload: Taught Periods Formal Examination and Study Periods Activity Time (hours) Taught Activities 24 Homework and Study 36 Total 60 Examinations and Study Overall Total 60 120 Module Assessment: The module will be examined through examination as a written paper of two hour duration examined at the Summer examination session. Continuous assessment will comprise 30% consisting of practical 1 reports 6%, class test (10%) and assignments (14%). Overall scheme: 1. Biological databases and online resources 2. Genome browsers/accessing genomic data 3. Sequence homology and evolution 4. Algorithms for sequence alignment: BLAST 5. Phylogenetics 6. Comparative genomics 7. Introduction to microarrays & gene expression analysis 8. Overview of next-generation sequencing applications 9. Bioinformatics of post-transcriptional regulation 10. Analysis of high-throughput genotype data (phasing and inference of population structure) 11. Concepts in genome-wide association studies & personal genomics 12. Overview of systems biology 2