Supplemental File S7. Predisposition to Cancer
advertisement
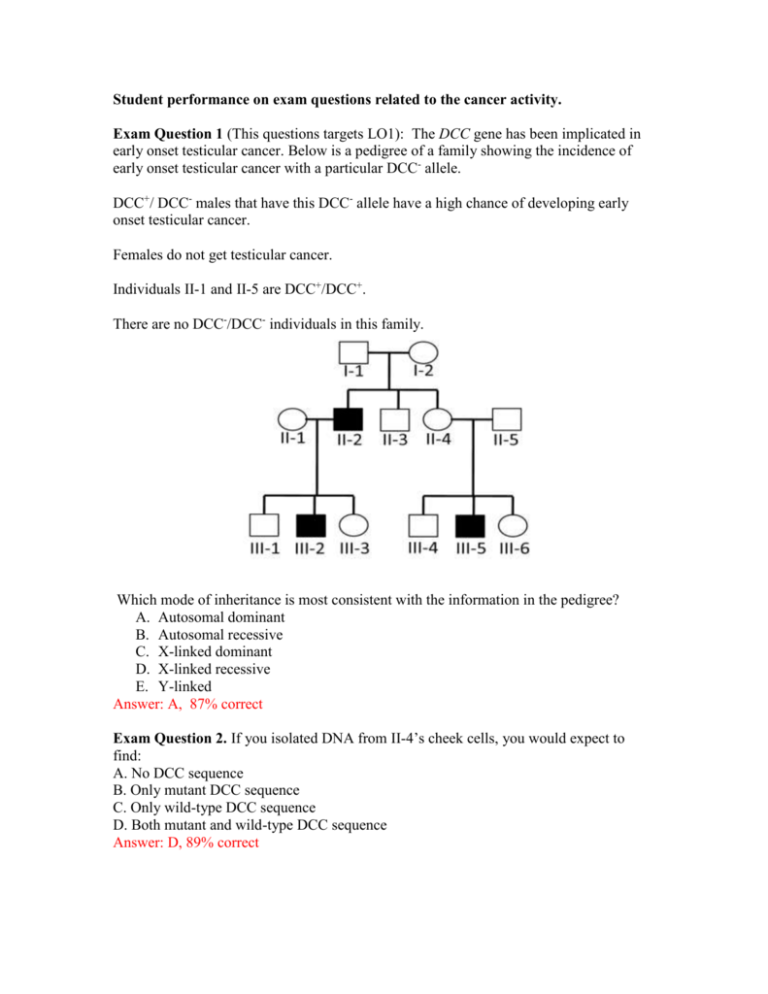
Student performance on exam questions related to the cancer activity. Exam Question 1 (This questions targets LO1): The DCC gene has been implicated in early onset testicular cancer. Below is a pedigree of a family showing the incidence of early onset testicular cancer with a particular DCC- allele. DCC+/ DCC- males that have this DCC- allele have a high chance of developing early onset testicular cancer. Females do not get testicular cancer. Individuals II-1 and II-5 are DCC+/DCC+. There are no DCC-/DCC- individuals in this family. Which mode of inheritance is most consistent with the information in the pedigree? A. Autosomal dominant B. Autosomal recessive C. X-linked dominant D. X-linked recessive E. Y-linked Answer: A, 87% correct Exam Question 2. If you isolated DNA from II-4’s cheek cells, you would expect to find: A. No DCC sequence B. Only mutant DCC sequence C. Only wild-type DCC sequence D. Both mutant and wild-type DCC sequence Answer: D, 89% correct Exam Question 3 (This questions targets LO2): III-3 has a son with Mohammed who does not have early onset testicular cancer and no family history of the disease. What is the chance their son will develop early onset testicular cancer if the disease is fully penetrant? A. 0% B. 25% C. 50% D. 66.7% E. 100% Answer: B, 68% correct Exam Question 4 (This questions targets LO3): Mutations in p53 are associated with an aggressive form of breast cancer. Normally the p53 protein stops the cell cycle if DNA is damaged. Mutations in the p53 gene prevent the production of the p53 protein. Without a functional p53 protein, cells continue to divide even when there is DNA damage. The p53 gene is a: A. Tumor suppressor gene B. Proto-oncogene Answer: A, 87% correct