01_Chemical Reactions Text Notes
advertisement

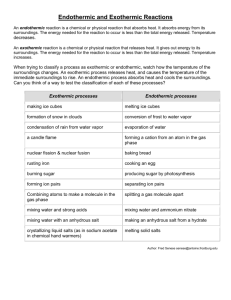
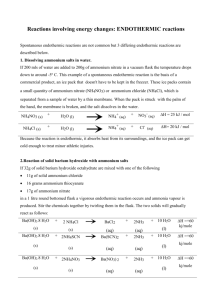
Chemical Reactions Week 1 Day 1 Monday Chemical Reactions Text Notes and Demos DSJ 4-6-15: Is adding blue food coloring to a liquid a chemical or a physical change? Justify your reasoning. DIRECTIONS: IP 151 Title: Chemical Reactions Notes Notes are on IP 151 Pg. 271 Reactions Pg. 272 Physical changes Chemical Changes Evidence Pg. 273 Pg. 274 243 Pg. 288 Energy and reactions Pg. 289- Exothermic 291 reactions Pg. 291- Endothermic 292 reactions What happens to atoms to make chemical reactions? What are physical changes, give examples. Terms: Reactants, Products Explain what evidence we have for chemical reactions. Please include the main idea from p. 243 Describe Bond Energy Explain exothermic reactions. How do they feel, what do they do, how would you recognize them? Explain endothermic reactions. How do they feel, what do they do, how would you recognize them? DEMOS: Exothermic Reaction (Hot Snapz) Endothermic (Ammonium Thiocyanate and Barium Hydroxide) HOMEWORK: OP 151 - Draw a 2 square. Summarize endothermic and exothermic reactions. (See Page 292 in science textbook) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MyAzjSdc3Fc&noredirect=1 for Endothermic Reaction Notes are on IP 151 Pg. 271 Reactions Pg. 272 Physical changes Pg. 273 Chemical Changes Pg. 274 Evidence 243 Pg. 288 Energy and reactions What happens to atoms to make chemical reactions? Bonds between atoms are broken or new bonds are formed. The new arrangement of atoms is a completely different substance What are physical changes, give examples. Changing from one state of matter to another is a physical change, such as water going from a solid state (ice) to a liquid state (water) Terms: Reactants, Products Reactants are the substances present at the beginning of any reaction. They are listed to the left of the yields sign (arrow). Products are the new substances that are formed as a result of the reaction. They are listed to the right of the yields sign Reactants Products CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O Explain what evidence we have for chemical reactions. Please include the main idea from p. 243 Evidence is what we are able to see 1. A new substance is formed that is completely different from the beginning substance 2. A change in color 3. A Precipitate is formed (this is a solid formed, may appear as cloudiness 4. A gas is formed 5. A change in temperature (not from heating Describe Bond Energy The energy that is formed when breaking or forming new chemical bonds is called bond energy Pg. 289- Exothermic 291 reactions Explain exothermic reactions. How do they feel, what do they do, how would you recognize them? If energy is released when a new product is formed this is called exothermic reactions. Exothermic reactions will feel hot to the touch, may look like burning or explosions In an equation energy is on the product side of the equation Pg. 291- Endothermic Explain endothermic reactions. How do they feel, 292 reactions what do they do, how would you recognize them? If energy is absorbed during a reaction this is called endothermic reactions. Endothermic reactions will feel cold to the touch as they absorb the energy from your hand. In an equation energy is on the reactant side of the equation Barium hydroxide –ammonium thiocyanate reaction seriously endothermic! Also a great one for observations. Copy entire equation (both reactant and product side) Can you identify each element in the equation? Look at your periodic table!! REACTANTS Ba(OH)2.8H2O (s) + 2 NH4SCN (s) + energy PRODUCTS --> Ba(SCN)2 (s) + 10 H2O (l) + 2 NH3 (g) To use this reaction as a demonstration: 32g barium hydroxide octahydrate 17g ammonium thiocyanate (or could use ammonium nitrate or chloride) 250 ml beaker stirring rod wood block or piece or card thermometer-digital is good some wet litmus paper if you want to show gas is basic ammonium Method: Smear some water over a wood block or piece of card or lab mat Pour the barium hydroxide and ammonium thiocyanate into the beaker and stir. The smell of ammonia should become evident within seconds. If you hold a piece of wet litmus paper over the reaction mixture in the flask, you can see that the gas produced by the reaction is basic. Liquid will be produced, so the mixture will turn slushy as the reaction proceeds. If you set the flask on a damp block of wood or piece of cardboard while performing the reaction you can freeze the bottom of the flask to the wood or paper. You can touch the outside of the beaker, but don't hold it in your hand – better to have the digital thermometer giving the dramatic fall in temperature. When you are finished, the contents of the flask can be washed down the sink with plenty of water. Avoid skin contact. If you get any solution on your skin, rinse it off straight away with water. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yTzcoyzPQE0 is a nice video of this.