Soil Analysis Lab Worksheet
advertisement

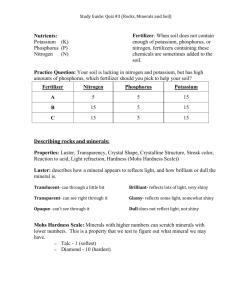
Soil Analysis Lab Your Name(s):___________________________ PURPOSE: In your own words: 1) Why is soil important? 2) How does soil form? STEP 1: Collecting Soil Materials: Procedure: Where did you collect your soil sample? What kind of plants (if any) were growing nearby? DATE:______ STEP 2: Soil Color, Organic Materials and Texture COLOR: Dark brown or black soils are usually rich in plant nutrients. Grey soils often contain clay or can indicate waterlogged soils. Light brown or white can contain lots of sand particles. Red or orange soils often contain iron. Describe the color of your soil. ORGANIC MATERIALS: Twigs, leaves and roots in the soil indicate decomposing organic materials, very important part of healthy soil. As the organic material breaks down, nutrients are released into the soil. Organic material also acts like a sponge to hold in water and nutrients. Manure, compost, peat moss and fallen leaves left on a field can add organic material to the soil. Describe any organic material you can see in your soil (use magnifying lense). SOIL TEXTURE: Soil contains small particles of weathered, broken down, rock. The size of this mixture effects the movement of water and air through the soil. The three kinds of particle are sand, silt and clay. Sand particles are larger, and then silt, and then clay is the smallest. Procedure: wet your clean index finger, rub a little bit of soil between your index finger and thumb. Sand particles should feel grainy and gritty. Silt particles feel smooth, silky or like flour. Clay particles will feel sticky. Soil almost always contains a mixture of sand, silt and clay. How does your soil sample feel? Did it feel grainy or gritty? Did it feel smooth or silky, like flour? Did it feel sticky when moist? Where do you think your soil sample fits on the triangle to the right? How can a farmer improve the organic material in his/her soil? STEP 3: Soil pH MATERIALS: 1) Soil samples, 2) plastic spoons, 3) distilled water, 4) plastic test bags, 5) one soil pH TesTab , 6) Color Chart Poster WHAT IS pH? pH is a measure of how acid or basic a substance is. The range goes from 0 to 14. pH less than 7 is an acid. For instance vingar has a pH of about 3.5 pH greater than 7 is basic. Ammonia is basic with a PH of about 10 pH of 7 is neutral. Distilled water has a pH of 7 The pH of soil impacts how well the nutrients in the soil will be available to plants. When the pH is too high or low, nutrients in the soil will be unavailable for plants. Most plants prefer neutral or slightly acid soils in a range of 6.0 to 6.8. If soils are too acid, powdered lime can be added to raise the pH. (Home Depot sells it) PROCEDURE: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Fill the plastic test bag to line C with distilled water. (about 10 ml of water) Use the plastic spoon to add about ½ of a teaspoon of soil. Add 1 soil pH TesTab Roll top of bag down 3-4 times and fold yellow tabs back to seal tightly Shake for 15 seconds (do not squeeze or pinch bag, just shake) Let bag stand for 1 minute for soil to settle Compare color of liquid to the Color Chart Poster and record pH below and answer question Pour liquid into waste bucket and rinse out, dry out test bag for future use What is your soil sample pH result? You want to plant broccoli, which likes a pH between 6.0 and 7.0, is your soil too acidic, basic or about right? Should you add “lime” to your soil to help broccoli? Why? STEP 4: EXTRACTION OF SOIL NUTRIENTS Materials: 1) Soil Samples, 2) Distilled Water, 3) 2 Floc-Ex Tablets, 3) Plastic Tubes What are soil nutrients? Soil nutrients are things like nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium that plants need to survive. Plants absorb these nutrients through their roots in the soil after the nutrients have been dissolved into solutions. Each nutrient has a specific role in producing healthy plants. When soil nutrients are used up by plants they must be replaced by adding manure, compost or fertilizer. Without fertilizers most farmland would be quickly drained of nutrients and food shortages would occur. It is estimated the world would need 30% more farmland without the usage of fertilizers. What is extraction? Separates the nutrients from the soil so we can measure them. The extraction will be used for the next 3 tests. Procedure: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Fill the larger round extraction tube with 30 ml of distilled water Add 2 Floc-Ex Tablets. Cap Tube and shake until tablets are disintegrated. Remove the cap and add one large heaping teaspoon of soil. Cap the tube and shake for one minute. Let the tube stand until the soil settles to the bottom. The clear solution above the soil will be used for the next 3 tests (nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium) Questions: 1) What are 3 nutrients found in soils that are needed for plants to be healthy? 2) Why do farmers often apply fertilizer to their land? STEP 5: NITROGEN Materials: 1) Pipet, 2) Extraction Solution, 3) Smaller Plastic Tube, 4) One Nitrate WR Tablet, 5) Color Chart What is nitrogen? Nitrogen makes up 78% of the air we breathe in. However, that nitrogen is often unavailable to plants. There are certain plants and bacteria in the soil that “fix” nitrogen and transfer it from the air to the soil where it can be used by plants. Why do plants need nitrogen? Plants use nitrogen to make chlorophyll, the green color in the leaves that allow them to transfer the suns energy to food through photosynthesis. Nitrogen is critical to the growth of plants and to healthy green leaves. Nitrogen is the most common nutrient found in plants. Decomposing organic matter, like manure, compost and fertilizers are a vital source of nitrogen for most plants. Broccoli needs high amount of nitrogen for growth. Procedure: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Use the pipet to transfer the clear extraction solution above the soil. Fill the small plastic tube almost to the top with the soil extraction solution. Add one Nitrate WR TestTab. Cap and mix until tablet disintegrates. Wait 5 minutes. Compare the color to the Nitrogen Color Chart. Dump contents of small tube in waste bucket and clean out with water Questions: What is the nitrogen level in your soil sample? (low, medium, or high) Will you need to add nitrogen fertilizer for your broccoli? Why? What are some ways farmers increase nitrogen in their soils? What part of plants is critical for nitrogen? STEP 6: Phosphorous Materials: 1) Pipet, 2) Soil Extraction Solution, 3) Smaller Plastic Tube, 4) One Phosphorus Tablet, 5) Color Chart, 6) Distilled water What is phosphorus? Phosphorus is critical to root development and growth. It helps the plant grow strong and produce flowers and fruit. Most of the phosphorus in the soil comes from weathered rock minerals. Broccoli needs high amounts of phosphorous. Procedure: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Use the pipet to transfer 25-30 drops of the clear soil extract solution into the small plastic tube Fill the tube the rest of the way to the top with distilled water Add one Phosphorous Tablet, cap and mix until tablet disintegrates Wait 5 minutes for color to develop Compare blue color with Color Chart and Record Dump out contents of small tube and rinse with clean water Questions: 1) What is the phosphorus level in your soil? 2) Is the phosphorus level adequate for broccoli? 3) What part of the plant is phosphorus critical for? STEP 7: Potassium Materials: 1) Pipet, 2) Soil Extraction Solution, 3) Smaller Plastic Tube, 4) One Potassium Tablet, 5) Color Chart, What is potassium? Potassium is critical to new cell growth within plants. It also helps the plant deal with disease and survive cold or dry conditions. The whole plant needs potassium. Without enough potassium, the pant will have slow growth, small size and may have browning of the leaves. Procedure: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Use the pipet to transfer the clear soil extraction solution from the big to small plastic tube Fill the small tube almost to the top with the clear soil extraction solution Add one Potassium Tablet Cap and shake small tube until tablet disintegrates Compare the cloudiness of the solution to the Color Chart by holding the tube over the black boxes in the left column and compare it to the shaded boxes in the right column 6) Dump out waste and clean up all materials Questions: 1) What is the level of potassium found in your soil sample? 2) If broccoli needs high amounts, will you need to add potassium to your soil? RESULTS/CONCLUSION Name Soil Sample Location Texture Result pH result Nitrogen Phosphorus ** Share your data with the class using the SMART Board ** 1) Is your soil good for growing broccoli? Why or Why not? 2) Why is the pH of soil important to plants? 3) For nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus, briefly describe why each is important to plants. Potassium