Works Cited
advertisement

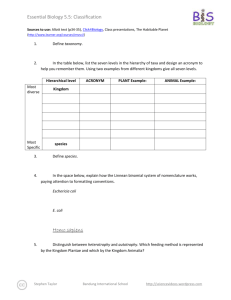
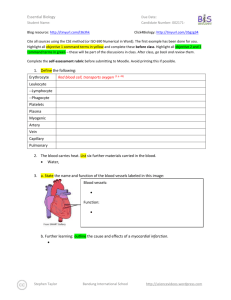
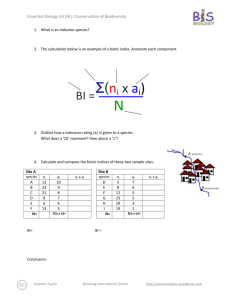
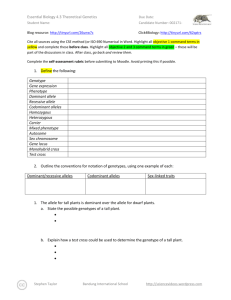
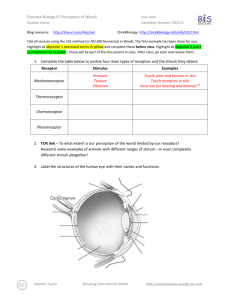
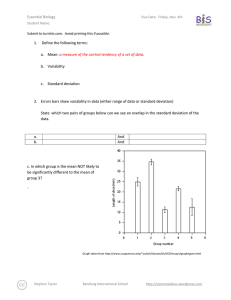
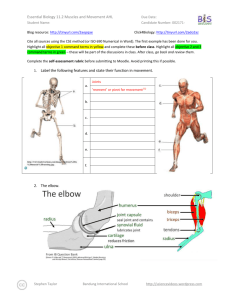
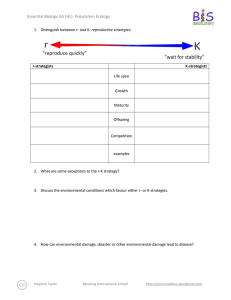
Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting. You should complete the reader ‘Evolution and Darwin’ before this Essential Biology worksheet. 1. Define evolution. Evolution is when there is a change to the population of a species to suit its environment or situation. 2. Populations tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. a. Explain how the following lead to a ‘struggle for survival’ Competition for food This leads to a struggle for survival because animals have reach their prey before the other animals, and they have to catch their prey. Competition for mates There will be a competition of attracting mates. Animals will fight over mates, and there will be less mates to choose from. They will also need to provide for their mate and offspring. Competition for space With so many animals, there will be less room to rest, and have shelter, as well as less room to reproduce. Parasitism Parasites will target the populous area, invading it. Animals will have to avoid the parasites, remove them, or simply try and tolerate them. Disease In such a highly populated area, diseases tend to appear and spread rapidly. Like parasites, animals will need to avoid, remove, or tolerate the diseases when they appear. Predation With so many animals, there will be a lot less prey. Animals will have to fight for food to Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: stay alive. To survive, prey must be able to avoid or escape their predators. b. Explain the significance of variation within a species in relation to survival. Variation between species is important in relation to survival because if a species has a trait that helps protect it from predators, for example a different colored body which will camouflage it, they stand a better chance in evading predation than other animals of their species. c. Outline how the following aspects of sexual reproduction contribute to variation within a species: Meiosis: Meiosis contributes to variation within a species by recombination and the crossing over of chromosomes. Random fertilization: Random fertilization contributes to variation within a species because each zygote formed from fertilization is unique. Mutation: Mutation contributes to variation within a species by DNA replication and viral infection. d. State which of the above is the main source of variation within genes. Random fertilization is the main source of variation within genes. e. Explain the term descent with modification. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: Descent with modification was the term used by Charles Darwin instead of the term evolution. It means that with each generation of a population that passes, there is a change, which becomes more evident each generation. f. Describe how the struggle for survival lead to natural selection. The struggle for survival led to natural selection by: the animal gets an advantageous variation selected for survival. Therefore, that animal is more likely to reproduce and pass on genes. Gene frequency then increases, and the population evolves to adjust to the environment. 3. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria is an example of evolution. a. What is Staphylococcus aureus? The common name for Staphylococcus aureus is ‘golden cluster seed’. b. Distinguish between MRSA and MSSA. The difference between MRSA and MSSA is that MRSA is resistant to many antibiotics while MSSA responds well to antibiotics. c. Use the key terms environmental change, variation, survival, reproduction to annotate this diagram, explaining how antibiotic resistance has evolved. Original population: Source of variation: Environmental change: Effect on population: Selection for: Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: Inheritance: ''........can we doubt (remembering that many more individuals are born than can possible survive) that individuals having any advantage, however slight, over others, would have the best chance of surviving and procreating their kind? On the other hand, we may feel sure that any variation in the least injurious would be rigidly destroyed. This preservation of favourable variations and the rejection of injurious variations, I call Natural Selection' Darwin C. (1859) The Origin of Species 4. Explain one other example of evolution of a species, in response to environmental change. (Galapagos finches or pepper moths) One other example of evolution of a species in response to environmental change is 5. Research Another reliable source of evidence to support the theory of evolution by natural selection is the fossil record—paleontologists have been uncovering fossilized remains of species from sedimentary rock deposits and using this information to create timelines of changes in the earth and development of species. a. Outline formation of sedimentary rock. The formation of sedimentary rock involves weathering, deposition, erosion, lithification, and compaction. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: b. Describe how the position of a fossil in sedimentary rock give a clue to its position in time. The position of a fossil in sedimentary rock gives a clue to its position in time because generally the deeper the fossil is underground, the older the fossil is. c. State some other methods used to confirm the age of fossils. Other methods used to confirm the age of fossils are the age of rocks around a fossil, mathematical calculations, the state of decay, carbon-14 and isotopes figure in calculations and tree of life relationships. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: 6. Homologous structures a. Define homologous Homologous means having the same origin of evolution but not necessarily the same function. b. One of the most obvious examples of homologous structures in animals is the pentadactyl limb. Define pentadactyl. Pentadactyl means having 5 fingers or toes on one hand or foot. c. Homologous structures has evolved through ‘adaptive radiation’. Explain this term. source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Evolution_pl.png Adaptive radiation means the development of many different forms from a group of organisms that were originally homogeneous. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: Darwin described structures such as these as having a ‘unity of type’ - although they look different, on closer inspection they share features. In this case, the bones are the same, though differently shaped. 7. Selective breeding of domesticated animals a. State the purpose of selective breeding The purpose of selective breeding is to develop livestock whose beneficial traits have components that make them easier to be inherited and can be propagated. b. Describe why selective breeding is also known as artificial selection. Selective breeding is also known as artificial selection because the animal is bred with man choosing what it will breed with, instead of letting it choose its own mate. Artificial selection, like natural selection, can work in two ways. State examples of each: c. Selection for Examples of selection for are: fast racehorses, god-natured domestic animals, and strong bulls. d. Selection against Examples of selection against are: diseased pets, lazy horses and domestic animals that have an extremely violent personalities. ToK AoK: “It’s only a theory.” Explain, using the scientific method, why evolution is described as a theory and why this represents a high level of certainty in science. What is the linguistic confusion that leads some non-scientists to question the validity of evolution as scientific truth? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.4 Evolution Student Name: Date: Works Cited 1. Allott, Andrew. IB Study Guide: Biology for the IB Diploma. s.l. : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978-019-915143-1. Self Assessment: Essential Biology Criterion Assessment Complete (2) Partially complete (1) Self Presentation & Organisation NA File names sensible, work complete and wellpresented. Sentences are complete and include vocabulary. All command terms highlighted or underlined. 1 Academic Honesty NA Sources cited using mla method, with Works Cited section complete and correct. 1 Objective 1 understanding Objective 2 understanding Objective3 understanding Logic, notation, mathematical working Further research All answers for the following command terms correct: Define Draw Label Most answers for the following command terms correct: List Measure State Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Annotate Apply Calculate Describe Distinguish Estimate Identify Outline Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Analyse Comment Compare Construct Deduce Derive Design Determine Discuss Evaluate Explain Predict Show Solve Sketch Suggest Answers are presented in a logical and concise manner. SI units used most times, with correct NA unit symbols and definitions of terms. All mathematical working shown. Evidence is apparent of research and reading beyond the textbook and presentations to find correct answers to challenging questions. If any NA questions are unanswered, this criterion scores zero. Total (max 10): Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Teacher 2 1 2 1 0 8 http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com