Ion test past paper questions
advertisement
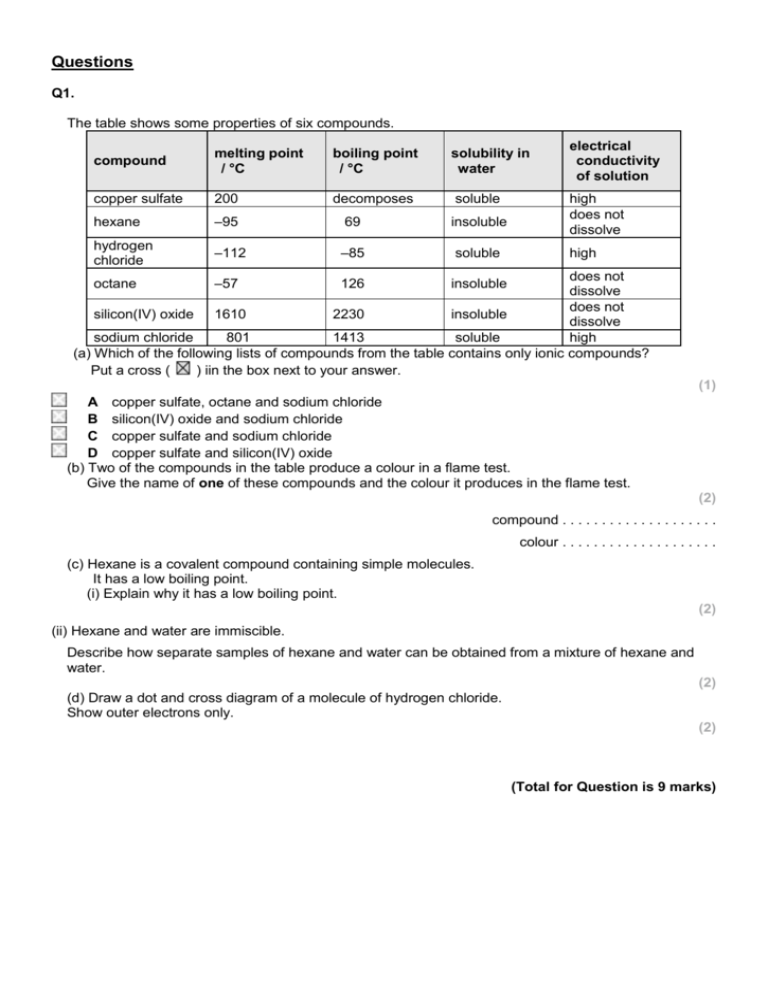
Questions Q1. The table shows some properties of six compounds. compound melting point / °C boiling point / °C solubility in water copper sulfate 200 decomposes soluble hexane –95 69 insoluble hydrogen chloride –112 –85 soluble electrical conductivity of solution high does not dissolve high does not dissolve does not silicon(IV) oxide 1610 2230 insoluble dissolve sodium chloride 801 1413 soluble high (a) Which of the following lists of compounds from the table contains only ionic compounds? Put a cross ( ) iin the box next to your answer. octane –57 126 insoluble (1) A copper sulfate, octane and sodium chloride B silicon(IV) oxide and sodium chloride C copper sulfate and sodium chloride D copper sulfate and silicon(IV) oxide (b) Two of the compounds in the table produce a colour in a flame test. Give the name of one of these compounds and the colour it produces in the flame test. (2) compound . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . colour . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (c) Hexane is a covalent compound containing simple molecules. It has a low boiling point. (i) Explain why it has a low boiling point. (2) (ii) Hexane and water are immiscible. Describe how separate samples of hexane and water can be obtained from a mixture of hexane and water. (2) (d) Draw a dot and cross diagram of a molecule of hydrogen chloride. Show outer electrons only. (2) (Total for Question is 9 marks) Q2. Salts and analysis (a) Which of the following pairs of substances contains one substance that is soluble in water and one that is insoluble in water? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) A B C D aluminium nitrate and lead sulfate ammonium chloride and copper sulfate copper hydroxide and lead sulfate sodium hydroxide and potassium nitrate (b) Barium chloride is an ionic compound and has a high melting point. Explain why barium chloride has a high melting point. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (c) Barium chloride solution is used to test for the presence of sulfate ions in a solution. When sulfate ions are present, insoluble barium sulfate is formed. (i) Describe the appearance of barium sulfate. (1) ............................................................................................................................................. (ii) Complete the balanced equation for the reaction between barium chloride and potassium sulfate. (2) BaCl2 + K2SO4 → ................................................................................................ (d) Compound X is a metal carbonate. (i) A flame test was carried out on compound X. A lilac flame was seen. Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) The formula of the metal ion in compound X is A Ca2+ B Cu2+ C K+ D Na+ (ii) Lead carbonate is an insoluble salt. Describe how a pure, dry sample of solid lead carbonate can be obtained from sodium carbonate solution and lead nitrate solution. (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (Total for question = 10 marks) Q3. Sodium carbonate and copper chloride are both ionic solids. They are both soluble in water. (a) Which row of the table shows the most likely melting points of these two salts? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) melting point / °C %%% sodium carbonate copper chloride %%% 17 498 A 851 9 B 851 498 C 9 17 D 2+ (b) Copper chloride contains copper ions, Cu , and chloride ions, Cl–. Give the formula of copper chloride. (1) .............................................................................................................................................. (c) Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. If a flame test is carried out on copper chloride, the colour in the flame is (1) A red-brown B yellow C lilac D green-blue (d) Describe how this apparatus can be used to show that sodium carbonate reacts with dilute acid to form carbon dioxide. (3) .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. (e) Copper carbonate is an insoluble salt. Describe how you would use sodium carbonate and copper chloride to produce a pure, dry sample of copper carbonate. (3) .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. (Total for Question is 9 marks) Mark Scheme Q1. Answer (a) (b) (c)(i) (c)(ii) C : copper sulfate and sodium chloride copper sulfate (1) blue-green (1) or sodium chloride (1) yellow (1) colour mark consequential on correct metal (compound) An explanation linking weak intermolecular forces /weak forces between molecules (1) little heat / energy needed to separate (molecules) (1) A description linking use separating funnel (1) run off lower layer / liquid / OWTTE (1) (d) shared pair in molecule (1) rest of molecule consequent on first mark (1) Acceptable answers Mark (1) allow blue or green or greenblue reject orange and yellow-orange (2) bonds / attractions in place of forces intermolecular forces between atoms / bonds loses 1st marking point any answer in terms of covalent or ionic bonding scores zero alternative description of separating funnel eg funnel with a tap at the bottom suitable labelled diagram burette allow layers / liquids to separate ignore fractional distillation Allow a diagram without labels for 2 marks any symbols shown must be correct for the 2nd mark allow any combination of dots and crosses for electrons wrong compound = zero marks (2) (2) (2) Q2. Q3. Answer (a) (b) C CuCl2 (c) (d) D A description including the following put/mix/react (sodium) carbonate and acid in (conical) flask (1) put limewater in test tube(1) (carbon dioxide produced) turns lime water milky/cloudy/white precipitate (1) A description including three of the following make solutions/dissolve/ mix/react solutions (1) precipitate (of copper carbonate) (1) filter (1) wash (with water) (1) leave to dry/dry in oven/dry between filter paper (1) (e) Acceptable answers ensure that 2 is subscript at most half the size of Cl and cases are correct ignore correct charges reject an overall charge 2 max if reactants and limewater are in the wrong vessels with the correct test marks can be awarded for the first two marking points by labelling the diagram "reactants" for sodium carbonate and acid max 2 marks if clear error in process, e.g. heat/add acid/evaporate ignore colours of precipitate accepts forms a solid for precipitate Mark (1) (1) (1) (3) (3)








