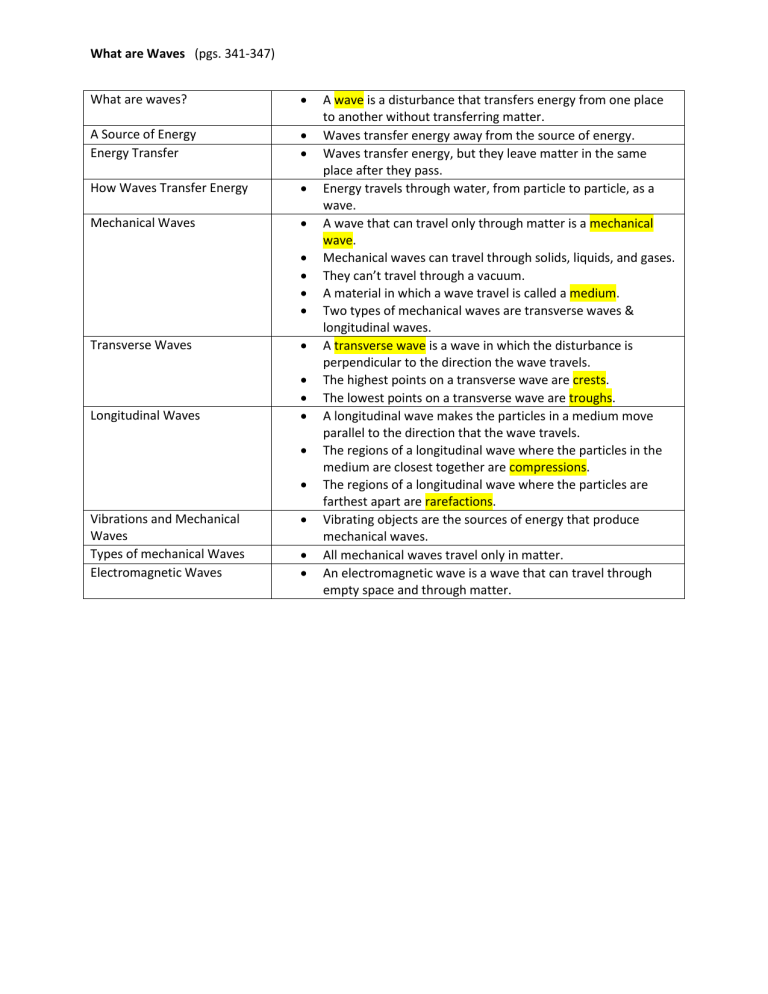
What are Waves (pgs. 341-347) What are waves? A wave is a
What are Waves (pgs. 341-347)
What are waves?
A Source of Energy
Energy Transfer
How Waves Transfer Energy
Mechanical Waves
Transverse Waves
Longitudinal Waves
Vibrations and Mechanical
Waves
Types of mechanical Waves
Electromagnetic Waves
A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another without transferring matter.
Waves transfer energy away from the source of energy.
Waves transfer energy, but they leave matter in the same place after they pass.
Energy travels through water, from particle to particle, as a wave.
A wave that can travel only through matter is a mechanical wave.
Mechanical waves can travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
They can’t travel through a vacuum.
A material in which a wave travel is called a medium.
Two types of mechanical waves are transverse waves & longitudinal waves.
A transverse wave is a wave in which the disturbance is perpendicular to the direction the wave travels.
The highest points on a transverse wave are crests.
The lowest points on a transverse wave are troughs.
A longitudinal wave makes the particles in a medium move parallel to the direction that the wave travels.
The regions of a longitudinal wave where the particles in the medium are closest together are compressions.
The regions of a longitudinal wave where the particles are farthest apart are rarefactions.
Vibrating objects are the sources of energy that produce mechanical waves.
All mechanical waves travel only in matter.
An electromagnetic wave is a wave that can travel through empty space and through matter.







