CURRICULUM SUMMARY –Spring Term (January – March) 2016
advertisement
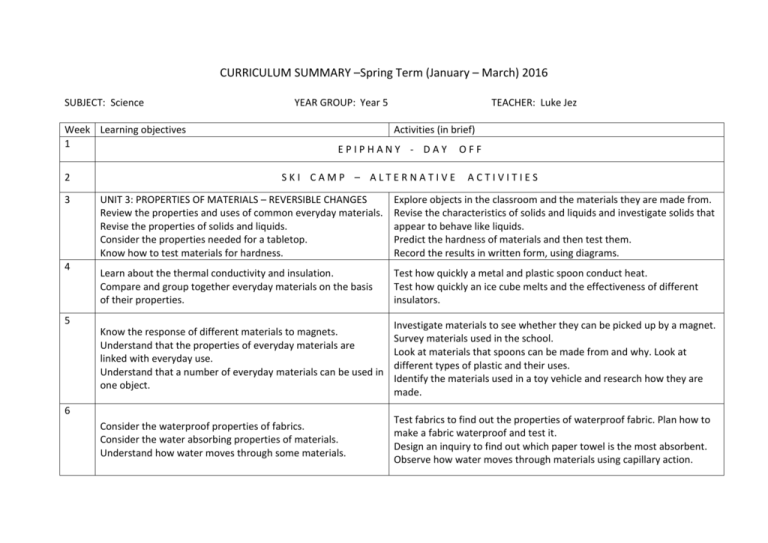
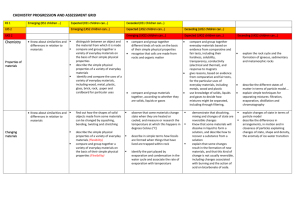
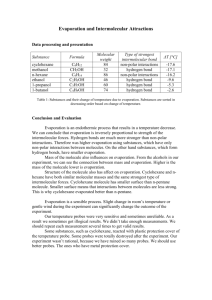
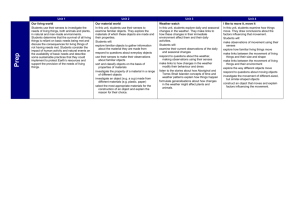
CURRICULUM SUMMARY –Spring Term (January – March) 2016 SUBJECT: Science Week Learning objectives 1 2 3 4 YEAR GROUP: Year 5 TEACHER: Luke Jez Activities (in brief) EPIPHANY - DAY SKI CAMP – ALTERNATIVE OFF ACTIVITIES UNIT 3: PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS – REVERSIBLE CHANGES Review the properties and uses of common everyday materials. Revise the properties of solids and liquids. Consider the properties needed for a tabletop. Know how to test materials for hardness. Explore objects in the classroom and the materials they are made from. Revise the characteristics of solids and liquids and investigate solids that appear to behave like liquids. Predict the hardness of materials and then test them. Record the results in written form, using diagrams. Learn about the thermal conductivity and insulation. Compare and group together everyday materials on the basis of their properties. Test how quickly a metal and plastic spoon conduct heat. Test how quickly an ice cube melts and the effectiveness of different insulators. Know the response of different materials to magnets. Understand that the properties of everyday materials are linked with everyday use. Understand that a number of everyday materials can be used in one object. Investigate materials to see whether they can be picked up by a magnet. Survey materials used in the school. Look at materials that spoons can be made from and why. Look at different types of plastic and their uses. Identify the materials used in a toy vehicle and research how they are made. Consider the waterproof properties of fabrics. Consider the water absorbing properties of materials. Understand how water moves through some materials. Test fabrics to find out the properties of waterproof fabric. Plan how to make a fabric waterproof and test it. Design an inquiry to find out which paper towel is the most absorbent. Observe how water moves through materials using capillary action. 5 6 7 HALF–TERM 8 9 BREAK Learn about porous materials and that soil has air in it. Understand how a sieve works. Know that a sieve can be used to separate materials. Investigate and compare the amount of air in different substances. Use a sieve to separate pebbles from a mixture. Devise, make and use a sieve to separate aquarium gravel from sand. Know how particles of different sizes can form different layers of sediment, and that this process can be used to separate materials. Understand that when some mixtures mix with water, some of their components may dissolve. Identify substances which are soluble and insoluble in water. Investigate the use of sedimentation in soil analysis, and compare this to using sieves to try to separate the components of a soil. Explore sedimentation as a way of separating all the components in soil. Mix substances with water and identify those that dissolve and those that do not. Know that evaporation can be used as a means of recovering a dissolved solid. Learn how mixing, dissolving, filtering and evaporation can be used in separating materials. Explain how evaporation could be used to recover dissolved substances. Investigate the use of evaporation in the formation of crystals of Epsom salts. Devise and carry out an investigation to see if filtering and evaporation can be used to separate sand and salt. Demonstrate knowledge of reversible changes. Review learning from the chapter to produce a detective manual based on new knowledge. 10 11