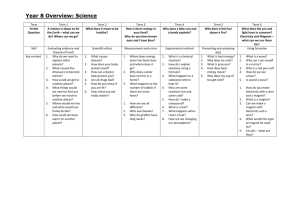
Circuits - Plantsbrook Science
advertisement
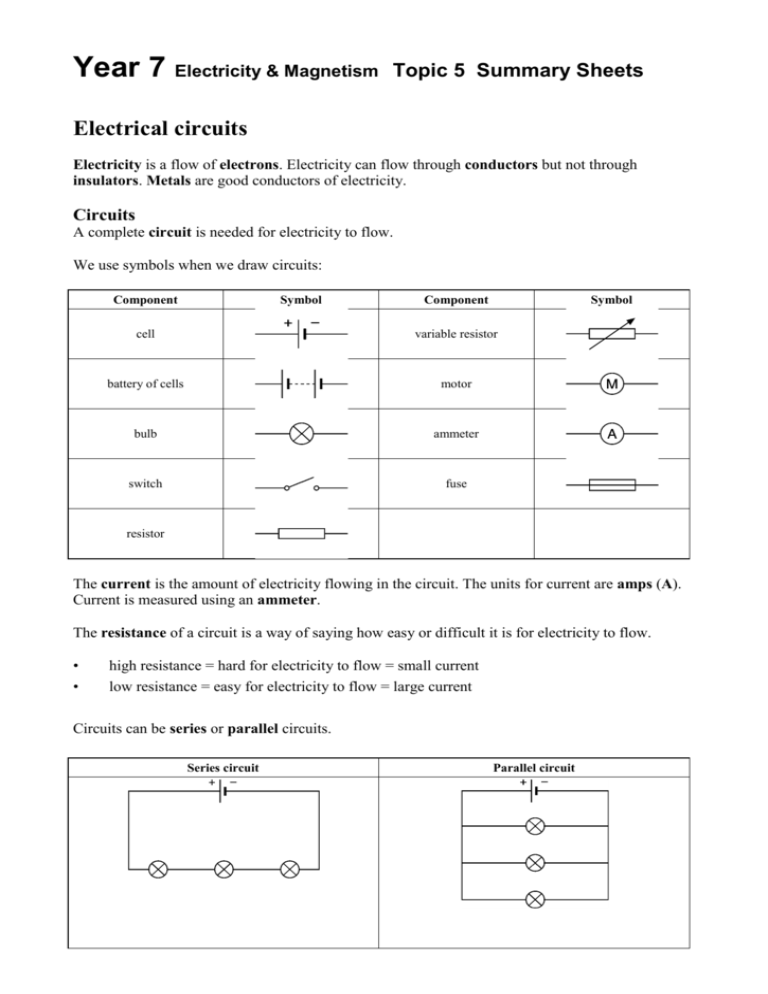
Year 7 Electricity & Magnetism Topic 5 Summary Sheets Electrical circuits Electricity is a flow of electrons. Electricity can flow through conductors but not through insulators. Metals are good conductors of electricity. Circuits A complete circuit is needed for electricity to flow. We use symbols when we draw circuits: Component Symbol Component Symbol cell variable resistor battery of cells motor bulb ammeter switch fuse resistor The current is the amount of electricity flowing in the circuit. The units for current are amps (A). Current is measured using an ammeter. The resistance of a circuit is a way of saying how easy or difficult it is for electricity to flow. • • high resistance = hard for electricity to flow = small current low resistance = easy for electricity to flow = large current Circuits can be series or parallel circuits. Series circuit Parallel circuit Series • • • • Parallel If one bulb breaks, all the others go off. • The current is the same everywhere. If you put more bulbs in they will be dimmer, because • it is harder for the electricity to get through. The resistance of the circuit is higher. • The voltage from the cell or power pack is divided between the components. • If one bulb breaks, the bulbs in the other branches stay on. The current splits up when it comes to a branch. The current in all the branches adds up to the current in the main part of a circuit. If you add more bulbs they stay bright. It is easier for the current to flow with more branches, because there are more ways for the electrons to go. The voltage is the same across all the branches of the circuit. Electricity and heat • • • When electricity flows through a wire, the wire can get hot. Hot wires are used in electric fires, irons and cookers. A fuse is a thin piece of wire that melts if too much electricity flows through it. It is used for safety. Electricity and your body Electrical signals in your body travel along nerves. If an electrical current passes through your body you may get an electric shock. This could burn you, or stop your heart or lungs working. Voltage A circuit must have a cell or power supply to provide a voltage. The voltage pushes the electrons around the circuit and gives them energy. This electrical energy is transferred to other components in the circuit, which convert it to other forms of energy. For instance, a light bulb transfers electrical energy to heat and light energy. The voltage of a cell can be measured using a voltmeter. The units for voltage are volts (V).The voltage across a component is a way of measuring how much energy the component is transferring. The voltage across all the components in a series circuit adds up to the voltage across the cell. Current The symbol for current is I Current is the flow of charged particles called electrons. It is measured in Amperes or Amps, using an Ammeter. 1 ampere is about 6 million million million electrons flowing past a point per second. Magnets and electromagnets Magnetism is a non-contact force. Magnets attract magnetic materials. Iron, nickel and cobalt are magnetic materials. Mixtures, like steel, that include a magnetic material will also be attracted to a magnet. Other metals, like aluminium, are not magnetic and will not be attracted to a magnet. Iron oxide is a compound that is a magnetic material. It is used to make video and music cassettes and computer discs. Magnetic materials can also block magnetism. You can make a magnet from a piece of iron or steel. • • • • The two ends of a bar magnet are called the north seeking pole and the south seeking pole or north pole and south pole for short. A north pole and a south pole attract each other. Two north poles or two south poles will repel each other. The space around a magnet where it has an effect is called its magnetic field. This is the shape of the magnetic field of a bar magnet. You can find the shape of the magnetic field using iron filings or using a plotting compass. The Earth has a magnetic field. A compass is a small magnet that always points north. But magnetic materials placed near a compass can change the direction that it points. Magnets can be used to sort iron and aluminium cans for recycling. Only the iron cans are attracted to the magnet. Magnets can also be used for holding fridge doors shut, and in compasses that sailors or walkers use. A wire with electricity flowing through it has a magnetic field around it. An electromagnet is a coil of wire with an electric current flowing through it. You can make an electromagnet stronger by: • • • increasing the number of coils of wire increasing the size of the current (by increasing the voltage) using an iron core. Electromagnets can be used for lifting things. They are also used in electric bells, relays and in video and music recording. Electromagnets are used to make bells work. A reed switch has two thin pieces of iron inside it. If a magnet is held near the switch, the pieces of iron are magnetised and touch each other. A reed switch can also be switched on using an electromagnet. Any switch that is worked by electricity is called a relay. Relays are used to make things safer. For example, the starter motor in a car uses a high current and needs thick wires for the current to flow through. A relay is used in a car so that the driver does not have to touch any part of the circuit that has a high current. Electricity and cells Electricity is supplied to homes and factories as mains electricity. This travels along cables connected to the National Grid. Generating electricity Fossil fuels are transported to power stations where they are burnt to release heat energy. This heats water, turning it to steam. The steam drives turbines which turn generators. The electricity generated flows along cables into the National Grid. Nuclear fuel is made from a radioactive metal called uranium. The energy in nuclear fuel did not come from the Sun. Environmental Effects of Making Electricity Acid rain The air contains small amounts of the following gases: • carbon dioxide, produced by combustion of fuels and respiration • sulphur dioxide, formed when sulphur burns in volcanoes • nitrogen oxides, produced during lightening storms. These gases dissolve in water to form acids, so rainwater is naturally acidic (pH between 5.6 and 5.9). Our rainwater has become even more acidic (pH between 3 and 5.5) due to air pollution from burning fossil fuels. This is what we call acid rain. The main sources of this pollution are power stations and cars. Both burn large amounts of fossil fuels and release more carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are the main contributors to acid rain.