Title: Quantitative Analysis of Left Ventricular Deformation through
advertisement

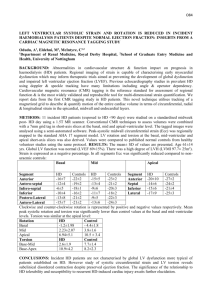
Title: Quantitative Analysis of Left Ventricular Deformation through Radial Tagging Authors (corresponding author): Razieh Kaveh, MS*1, Maryam Haftehkhanaki, MS1, Abbas Nasiraei Moghaddam, PHD1,2, Zahra Alizadeh Sani, MD3, Zahra Ojaghi Haghighi, MD4, J Paul Finn2 Affiliation: 1 Biomedical Engineering, Amirkabir University (Tehran Polytechnic), Tehran, Iran. 2 Radiological Science, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, CA, USA. 3 Shaheed Rajaei Cardiovascular, Medical and Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. 4 Echocardiography Research Center, Shaheed Rajaei Cardiovascular, Medical and Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Degree: RK=Master Student in Biomedical Engineering, MH=Master of Science in Biomedical Engineering, AN=Assistant Professor of Biomedical Engineering, ZA= Assistant Professor of Cardiology, ZO= Assistant Professor of Cardiology, PF=Professor of Radiological Science Introduction: Assessment of myocardial deformation patterns plays crucial role in evaluating cardiac function. Left ventricular (LV) strain and torsion are two determinants of myocardial deformation that can be measured using variety of cardiac imaging techniques among which tagged magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is considered as the gold standard due to its high resolution and in vivo nature. LV tagging in dense radial pattern [1], highlighting the LV circumferential shortening and LV rotational motion, facilitates computation of these parameters (Fig.1). In this study, we quantify myocardial deformation patterns by computing LV circumferential strain and torsion thorough radially tagged images in a group of healthy subjects. Furthermore, we make a comparison in one case between parameters extracted from speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) and tagged MRI. Figure 1. Radially tagged LV at diastolic (left) and systolic (right) frames. Methods and materials: *Corresponding Author Short axis radially tagged images were acquired at apical, mid, and basal levels in 10 healthy subjects. Images were acquired either at 1.5T or 3T. For comparison purpose, conventional grid tagging and echocardiographic speckle tracking were also performed in one of our subjects. Radially tagged images were processed as described in [1] and [2] to calculate circumferential strain and normalized torsion. Circumferential strain was also assessed by employing HARP method on images with grid tagging. Findings: Mean global circumferential strain and torsion measured in 10 healthy subjects (Fig.2) are consistent with those reported in the literature, which points to the reliability of our method. Measured global circumferential strains through grid tagging, radial tagging and speckle tracking (Fig.3) indicate general agreement. Figure 2. Mean±standard deviation of strain (left) and normalized torsion (right) in 10 healthy subjects obtained from radially tagged images. Figure 3. Comparison of Strain extracted from tagged MRI and STE in a healthy case. References: [1] N. Moghaddam, Abbas; Finn, J Paul. “Accelerated Circumferential Strain Quantification of the Left Ventricle Using CIRCOME: Simulation and Factor Analysis”. SPIE Vol. 6916 691604-1 2008 [2] Kaveh, Razieh; N. Moghaddam, Abbas; N Khan, Sarah; Finn, J Paul. “Twist measurement of the left ventricle through radial tagging”. JCMR 2013 15(Suppl 1):E48 Key words: Strain, Twist, Radial Tagging, MRI E-mail: razieh_kaveh@yahoo.com Postal address: Amirkabir University, Hafez Ave, Tehran, Iran, 15875-4413. Mobile Phone: 09126354428