Flexibility LAB
advertisement

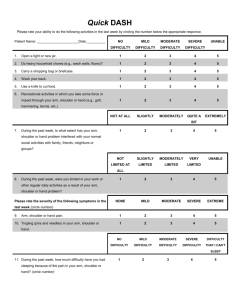
Name: _____________________________________ Period: _______ Body Proportions, Range of Motion & Flexibility LAB Station I - Body Proportions Problem: How does a person’s arm span relate to his or her height? Hypothesis (use proper form; If…then...): _____________________________________________________________________________________ Materials: Meter stick Subjects Method: Your measurements Class avg. in cm in cm Arm span Height 1. Measure arm span; record in table and on Instructor’s class data sheet. 2. Measure height; record in table and on Instructor’s class data sheet. (Use tape measures around classroom entry doorway) 3. Analyze data Conclusions (How does a person’s arm span relate to his or her height?): _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Station II - Limber Gauge Materials: Partner Metric ruler Chalk Method: 1. Get a partner to help you. 2. Reach as far as you can across the length of your desk/table and have your partner you’re your reach distance with a chalk mark, measure the distance and record it in the table and on class data sheet. 3. Now stretch your arm before you reach. Repeat step 2. Reach before stretching in cm Reach after stretching in cm Your reach Total – female Total – male Total – all Average – female Average – male Average – all (Divide total all by total number of students) Describe the stretch that you used. 1 _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Analysis Questions Station II – Limber Gauge 1. Who was more flexible before stretching (circle one)? 2. Who was more flexible after stretching (circle one)? 3. Was your stretch effective? Support your answer. males or females males or females ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Station III – Flexibility Tests Directions: To test flexibility of all joints is impractical. These tests are for joints used frequently. Follow the instructions carefully. Determine your flexibility using Chart 1. TEST ONE: Modified Sit-and-Reach (Flexibility Test of Hamstrings) Materials: Partner Wall and table Metric ruler Method: 1. Remove shoes and sit on floor near a wall. Place your head, back, and hips against the wall with a 90-degree angle at the hips. Next have your partner move the table top (table is on its side) so that you can place the sole of the foot of the extended leg flat against the table top, your other leg will be slightly bent at the knee (see the picture below). Record which leg in flat; right or left here….__________________________ 2. Place one hand over the other and slowly reach forward as far as you can with arms fully extended. Keep back and head in contact with the wall. Your partner will use a metric ruler to measure the distance from the tip of your fingers to the table top and record it in the Table below. (If you cannot reach the table, measure distance away from table) 3. Repeat Step 2 two more times, but this time you can move your head away from the wall. If you can reach the table enter zero here. 4. Average the scores of all three trials. 2 TEST 1~ TRIAL DISTANCE FROM TABLE TOP IN CM 1 2 3 AVERAGE TEST TWO: Shoulder Flexibility (“Zipper” Test) DISTANCE Materials: Partner Metric ruler Method: 1. Raise your arm, bend your right elbow, and reach down across your back as far as possible. 2. At the same time, extend your left arm down and behind your back, and try to cross your fingers over those of your right hand as shown in the picture below. 3. Measure the distance to the nearest cm and record it in the Table below. If your fingers overlap, score as a plus. If they fail to meet, score as a minus; use a zero if your fingertips just touch. 4. Repeat with arms crossed in opposite direction (left hand over shoulder). Most people will find that they are more flexible on one side than the other. TEST 2~ RIGHT HAND OVER SHOULDER IN CM LEFT HAND OVER SHOULDER IN CM TEST THREE: Hamstring and Hip Flexor Flexibility Materials: Partner Meter stick Wall Goniometer Method: 1. Lie on your back on the floor (on a mat) beside a wall. 3 2. 3. 4. 5. Slowly lift one leg off the floor. Keep the other leg flat on the floor. Keep both legs straight. Continue to lift the leg until either leg begins to bend or the lower leg begins to lift off the floor. Have your partner place a meter stick against the wall and underneath the lifted leg, keep the meter stick against the wall and slowly lower your leg (see picture on next page). 6. Use a goniometer, measure the angle created by the floor and the yardstick, record the angle measurement in the Table provided on the next page. The greater the angle, the better your score. 7. Repeat with your other leg. TEST 3~ RIGHT LEG ANGLE MEASUREMENT LEFT LEG ANGLE MEASUREMENT TEST FOUR: Trunk Rotation Materials: Partner 2 Meter sticks Wall Masking tape Method: 1. Tape two meter sticks to the wall at shoulder height, one right side up (when facing wall leftside) and the other upside down (when facing wall right-side). Tape a line on the floor, which is perpendicular to the wall and even with the 40 cm mark on the upside down meter stick. 2. Stand with your left shoulder an arm’s length (fist closed) away from the wall. Toes should be on the 40 cm line. (you must stand away from the wall. 3. Drop the left arm and raise the right arm to the side, palm down, fist closed (see picture). 4. Without moving your feet, rotate the trunk to the right as far as possible, reaching along the meter stick, and hold it for 2 seconds. Do not move your feet or bend your trunk. Your knees may bend slightly. 5. Your partner will read the distance reached to the nearest cm. on the upright meter stick and record your score in the Table provided. Repeat this one more time and average your two scores. 6. Next, perform the test facing the opposite direction. Rotate to the left. For this test, you will use the second meter stick (upside down) so that, the greater the rotation, the higher the score. TEST 4~ 4 TRIALS LEFT RIGHT SHOULDER SHOULDER IN CM IN CM 1 2 AVERAGE CHART 1~ Flexibility Rating Scale for Tests 1-4 Summarize your data from each test in the chart below…use the correct gender chart. Men Classification Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4 Right hand over Left hand over Right leg angle Left leg angle Left shoulder Right shoulder High performance Fingertips touch table (0 cm avg) 12+ 10+ 111+ 111+ 51+ 51+ Good fitness zone 1-5 cm away 3-11 3-9 80110 80110 40-50 40-50 Marginal zone 6-12 cm away 0-2 0-2 60-79 60-79 34-39 34-39 Low zone > 13 cm away <0 <0 <60 <60 <34 <34 Women Classification Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4 Right hand over Left hand over Right leg angle Left leg angle Left shoulder Right shoulder High performance Fingertips touch table (0 cm avg) 13+ 11+ 111+ 111+ 52+ 52+ Good fitness zone 1-3 cm away 5-12 5-10 80110 80110 43-51 43-51 Marginal zone 6-12 cm away 0-4 0-4 60-79 60-79 37-42 37-42 Low zone > 11 cm away <0 <0 <60 <60 <37 <37 5 EVALUATING YOUR FLEXIBILITY Compare your scores for each flexibility test to Chart 1 above to determine your ratings on the selfassessments below; then place an X over the circle for your appropriate rating. Self-Assessment: Test One: Modified Sit-and-Reach Refer back to your data and enter your rating for the leg that was flat… Test Two: Shoulder Flexibility (“Zipper” Test) Test Three: Hamstring and Hip Flexor Flexibility Test Four: Trunk Rotation 6 Self-Evaluation…. Analysis Questions Station III Flexibility Tests On a separate sheet of paper (if used staple to the back of this lab) or below, discuss your current flexibility and your flexibility needs for the future. Include comments about your current state of flexibility, need for improvement in specific areas, and special flexibility needs for sports or other special activities. Describe some activities that might help increase your flexibility. 7