Answers
advertisement

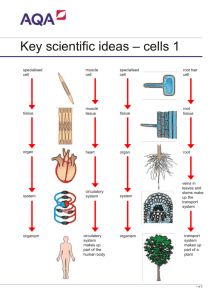
Year 8 Cell and Organisation - Revision 2014 Name: Mr. Hung Form: _________ Words: function, respiratory, multicellular, cells, level, circulatory, tissues, nervous system 1. The Human Body is very complex. The Human Body, as a multicellular organism, is composed of several level of organization that include cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. 2. Each smaller level combines together to make the next level. 3. Cells are the building blocks of all living things. 4. A tissue is a group of similar cells that perform the same function . 5. Organs are groups of different tissues with a specific function. 6. Finally, organ systems are groups of organs that work together to perform a specific job. Give 3 systems in our body: respiratory, circulatory and nervous systems. 7. The Human Body is made up of many systems that work together to perform complex tasks on a daily basis. 8. Arrange the 6 different levels of organisation of human body: tissue, cell, organ, organism, organelle, organ system organelle cell tissue organ organ system organism 9. Match the following organelles with their role in a cell. Choice Cell Wall Function Stores water in plants The correct structure: Cell Membrane Jelly-like substance where chemical reactions happen Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Structures found in living cells Nucleus Gives energy to a cell Organelles Mitochondrion Vacuole A skin that lets substances into and out of a cell Cell membrane Mitochondria Barrier of a plant cell Cell wall Chloroplasts Control centre of cell, where cell division starts (mitosis) Nucleus Organelles Makes own food using Photosynthesis Chloroplast Vacuole 10. Why are cells important? (Check the Internet for answers if needed) They are the basic building blocks or units of multicellular organisms; Cells can be specialised to perform different functions; Different cells can be organised to tissues, organs and systems. 11. 12. Give three differences between an animal cell and a plant cell. A plant cell has extra structures: large vacuole, cell wall and chloroplasts which are not found in an animal cell. 13. What is the difference between a unicellular and multicellular organism? A unicellular organism is made of one cell but a multicellular organism is made up millions to trillions of cells. A multicellular organism is usually larger however a unicellular can’t be seen unless using a microscope. 14. Label the microscope Eyepiece Coarse Focus Adjustment Fine Focus Adjustment Arm Stage Base Mirror Body tube Nose piece Objective Stage clip Diaphragm Mirror 15. What do the following parts of a microscope do? Stage - to place the microscopic slide Diaphragm- to adjust different amount of light from below Objective Lenses- to magnify the image to different degrees Mirror- to reflect light upward to the microscopic slide 16. When you see an image under a microscope what happens to the image: (Draw the image of a letter “F”) a. It stays the same b. It becomes a mirror image c. It looks upside down – left to right d. It is a mirror image and is also upside down 17. Fill in the magnification of a microscope: eyepiece Objective lens X 10 X 10 X 10 X5 X 10 X 80 18. magnification 100X 50X 800X Give 2 differences between Light Microscope (LM)and Dissecting Microscope (DM) A LM consists of one eyepiece compared to 2 in a DM A LM has light shining upward compared to downward in DM A LM has a higher magnification than that of a DM A LM gives a 2 dimensional image but it is a 3 dimensional image in a DM A LM requires the use of microscopic slide to prepare the sample and the sample must be very thin and transparent; but the sample can be bigger or thicker and need not to be transparent when viewing under the DM. 19. What are the steps to preparing an onion cell? (1) Peel off the skin (epidermis) from an onion leaf (2) Place the sample to a microscopic slide (3) Add a drop of water / dye to the sample (4) Cover the slide with a coverslip 20. Our body is made up of many specialised cells, what do the following cells do in our body: Red blood cell – for transporting oxygen from lungs to other cells Fat cells – for storage of fat Nerve cells – for passing nerve messages for action Muscle cells – for contraction and relaxation to move. 21. Which is the only cell in our body that doesn’t have a nucleus? RED BLOOD CELLS 22. What is a tissue? Give 3 examples A group of similar cells that perform a particular function. Blood, fat, nerve, muscle 23. Why are tendons and ligaments in our body called connective tissue? Tendons are connective tissues that join muscles to bones Ligaments are connective tissues that join bones to bones 24. What is an organ made up of? a. The building block of all living things b. At least two different types of tissues c. d. Two or more different organs that work together A group of cells that do the same thing in the body 25. What is mitosis? It is a cell division in which the daughter cells have exactly the same genetic materials as their parent cells. 26. What structure/chemical makes the mitosis possible? Chromosomes and DNA 27. Arrange different stages of mitosis in the correct sequence. CBEAD