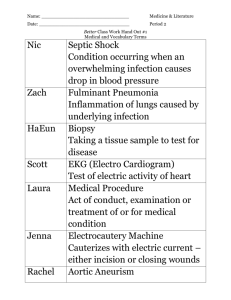
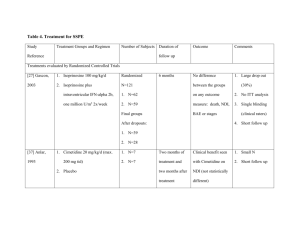
表一、海生所103學年專題討論(二) 摘要表 IMB 103 Seminar (II
advertisement

表一、海生所 103 學年專題討論(二) 摘要表 IMB 103 Seminar (II) Abstract form 報告日期/Date:2015 年/year11 月/month25 日/day 班別/學生姓名: Class/Name:碩二/蔡季航 題目 Title:Identification of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) interferon regulatory factor 3 involved in antiviral immune response againstfish RNA virus 作者 Author(s): Youhua Huang, Xiaohong Huang, Jia Cai, Zhengliang OuYang, Shina Wei, Jingguang Wei, Qiwei Qin 期刊 Journal name: Fish & Shellfish Immunology 期頁數 Issue and page nos: 42 (2015) 345-352 摘要 Abstract: Interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) is an important transcription factor which regulates the expression of interferon (IFN) and IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) following virus recognition. In this study, a novel IRF3 gene was cloned from grouperEpinephelus coioides(EcIRF3) and its effects against Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) and red spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) was investigated. The fulllength of EcIRF3 cDNA was composed of 2513 bp and encoded a polypeptide of 458 amino acids which shared 82% identity with European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). EcIRF3 contained three conserved domains including a DNA-binding domain (DBD), an IRF associated domain (IAD) and a serinerich domain. Expression profile analysis revealed that EcIRF3 was abundant in head kidney, kidney, spleen and gill. Upon different stimuliin vitro, the transcript of EcIRF3 was significantly up-regulated after RGNNV infection or treatment with polyinosin-polycytidylic acid (poly I:C). During SGIV infection, the increase of the EcIRF3 transcription was only detected at the late stage, suggesting that EcIRF3 was differently regulated by different stimuli. Immunefluorescence assay indicated that thefluorescence signal of EcIRF3 was increased significantly after infection with RGNNV or treatment with poly I:C, but moderately at the late stage of SGIV infection. Reporter gene assay showed that EcIRF3 activated zebrafish type I IFN and type III IFN promoterin vitro. The viral gene transcription and virus production of RGNNV were significantly decreased in EcIRF3 overexpressing cells. However, the ectopic expression of EcIRF3 did not affect the gene transcription and virus production of SGIV. Moreover, the mRNA expression levels of type I IFN and IFN-inducible genes (MxI, ISG15 and ISG56) were increased in RGNNV infected EcIRF3 overexpressing cells compared to empty vector transfected cells. Together, our results demonstrated that IFN immune response mediated by grouper IRF3 was exerted crucial roles forfish RNA virus, but not for DNA virus replication. 題目 Title:Antiviral role of grouper STING against iridovirus infection 作者 Author(s): Youhua Huang, Zhengliang Ouyang, Wei Wang, Yepin Yu, Pengfei Li, Sheng Zhou, Shina Wei, Jingguang Wei, Xiaohong Huang Qiwei Qin 期刊 Journal name: Fish & Shellfish Immunology 期頁數 Issue and page nos: 47 (2015) 157-167 摘要 Abstract: Stimulator of interferon genes (STING, also known as MITA, ERIS, MPYS or TMEM173) has been identified as a central component in the innate immune response to cytosolic DNA and RNA derived from different pathogens. However, the detailed role of STING duringfish iridovirus infection still remained largely unknown. Here, the STING homolog from grouperEpinephelus coioides(EcSTING) was cloned and its effects on IFN response and antiviral activity were investigated. The full-length EcSTING cDNA was composed of 1590 bp and encoded a polypeptide of 409 amino acids with 80% identity to STING homolog from large yellow croaker. Amino acid alignment analysis indicated that EcSTING contained 4 predicated transmembrane motifs (TMs) in the N terminal, and a C-terminal domain (CTD) which consisted of a dimerization domain (DD), c-di-GMP-binding domain (CBD) and a C-terminal tail (CTT). Expression profile analysis revealed that EcSTING was abundant in gill, spleen, brain, skin, and liver. Upon different stimuliin vivo, the EcSTING transcript was dramatically up-regulated after challenging with Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and polyinosin-polycytidylic acid (poly I:C). Reporter gene assay showed that EcSTING activated ISRE, zebrafish type I IFN and type III IFN promoterin vitro. Mutant analysis showed that IFN promoter activity was mostly mediated by the phosphorylation sites at serine residue S379 and S387. Moreover, EcSTING induced type I and III IFN promoter activity could be impaired by overexpression of EcIRF3-DN or EcIRF7-DN, suggesting that EcSTING mediated IFN response in IRF3/IRF7 dependent manner. In addition, the cytopathic effect (CPE) progression of SGIV infection and viral protein synthesis was significantly inhibited by overexpression of EcSTING, and the inhibitory effect was abolished in serine residue S379 and S387 mutant transfected cells. Together, our results demonstrated that EcSTING might be an important regulator of grouper innate immune response against iridovirus infection.