Name, block, date Chapter 3 Study Guide: Review your foldable and
advertisement

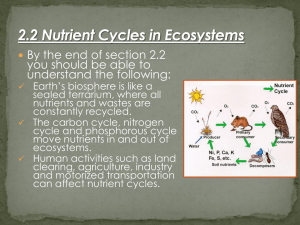
______________________________ Name, block, date Chapter 3 Study Guide: Review your foldable and know the information on spheres. 1. Geosphere – made of all the rock and above and below Earth's surface and includes the center core, and the thin outer layer the crust. 2. Asthenosphere - carries the lithosphere and tectonic plates. 3. Biosphere - life is part of this (includes humans!) 4. Hydrosphere - contains all of earth’s waters. 5. Matter that organisms require for their life processes are called nutrients. Nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous circulate endlessly throughout the environment in complex cycles called biogeochemical cycles. 6. Nitrogen is made available either by lightning strikes or bacteria called nitrogen-fixing bacteria found in legumes. Ex: soybeans 7. When too much nitrogen from fertilizer or phosphorous from detergent gets into our waterways algae blooms. What is this process called? Eutrophication. What can happen as a result? Hypoxia or reduced oxygen levels. 8. What are the 3 main parts of the water cycle and know the definitions of each as well as the term for evaporation of water from plants. Evaporation (liquid to gas from plants = transpiration) Condensation – clouds form Precipitation – rain, hail, sleet, snow 9. CO2 is an important greenhouse gas because it acts like a heat blanket making life possible on earth. Without CO2 it would be too cold. CO2 is also important because plants use it for photosynthesis. What are green plants called? producers What do green plants produce during photosynthesis? Sugar (carbohydrate) & oxygen 7. Too much CO2 in the atmosphere is causing global climate change. How have humans interfered and added CO2? By burning fossil fuels and cutting down trees. Another greenhouse gas is methane. 8. Review the 3 plate boundaries and what happens: divergent -> separate, move apart convergent -> come together (mountains & trenches) transform -> slide past (earthquakes) 9. Review positive and negative feedback loops, know which is better, and give an example of each. Negative = stability Ex: predator/prey relationship Positive = extreme Ex: erosion 10. Be able to explain eutrophication, and hypoxia. Eutrophication = Nitrogen and Phosphorus into H2O -> algae bloom Hypoxia = low oxygen