Marine Science LEOCE Study Guide
advertisement

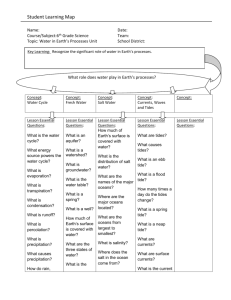
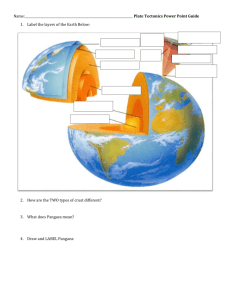
Introduction and Marine Geology Use the following resources to find your definitions and answers: Chapter 2 “History of Ocean Exploration..”, Green Timeline Chapter 13 “The Theory of Plate Tectonics” Use your notes! KEY VOCABULARY: mid-ocean ridge, continental shelf, continental slope, continental ridge, Theory of Plate Tectonics, subduction zone, trench, divergent boundary, convergent boundary, transform plate boundary, island arcs, stick charts STUDENT TASKS: 1. Explain and give evidence for the Theory of Plate Tectonics. 2. Describe ocean floor and trench formation. What is a subduction zone? 3. List the major contributors and their contributions to the field of oceanography. 4. Diagram and label the ocean floor topography. OCEANOGRAPHY Use the following resources to find your definitions and answers: Chapter 8 “The Nature of Water” Chapter 9 “Water: A Physically Unique Molecule” Chapters 10 and 11 in “The Motion of the Ocean” Unit 4 KEY VOCABULARY: Coriolis effect, high heat capacity, wavelength, wave crest, wave trough, solvent, spring tide, neap tide, pelagic, Gulf Stream Current, El Nino, cohesion, surface tension, specific heat, viscosity, water density, storm surge, photic zone, aphotic zone, disphotic zone STUDENT TASKS: 5. Explain how tides affect reproduction or nesting of different organisms. 6. Diagram and label the parts of a wind wave. 7. Describe wind wave formation and water particle movement within a wave. 8. Differentiate between surface currents and deep water currents. 9. How do surface currents affect the climate of the Earth? 10. What is the Coriolis Effect and how does it influence currents? 11. List, describe, and give examples of each of the properties of water. MARINE MICROORGANISMS Use the following resources to find your definitions and answers: Chapter 5 “A Survey of Life in the Sea Introduction…” KEY VOCABULARY: red tide, diatoms, dinoflagellates, phytoplankton, zooplankton STUDENT TASKS: 12. Differentiate between diatoms, dinoflagellates, silicoflagelates, and cocolithophores. 13. Explain what adaptations this group has which allows them to be better biological producers and producers of oxygen. MARINE PRODUCERS KEY VOCABULARY: halophyte, autotroph, nematophores, salt tolerance STUDENT TASKS: 14. Differentiate between the different types of macroalgae. 15. Differentiate between the different marine angiosperms.