mec12309-sup-0006-AppendixS2
advertisement

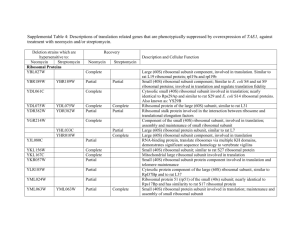
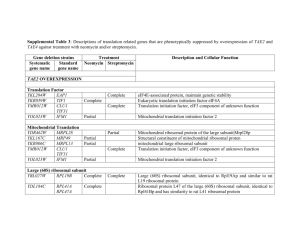
From: Primmer et al. 2013 Annotated genes and non-annotated genomes: crossspecies use of Gene Ontology in ecology and evolution research Supplementary Appendix S2- Enrichment test differences when using ALL vs. non-IEA evidence codes: Case study from a previously published dataset (Papakostas et al., 2010). Papakostas et al. (2010) used mass spectrometry to describe the proteomic profile of two early life stages, namely eyed-egg and hatching stage, of European grayling (Thymallus thymallus). They identified 213 proteins in the eyed-egg stage and 239 in the hatching stage and, among others, performed functional enrichment analyses using gene ontologies. They used the Danio rerio genome as a gene reference set for the overrepresentation tests, and hypergeometric analysis was set at the 0.05 level of significance after Benjamini-Hochberg FDR multiple-testing correction. Here we used the same gene lists and enrichment settings to investigate differences in the results when using all evidence codes or when omitted the IEA evidence from gene annotation. We used the ClueGO (Bindea et al., 2009) Cytoscape (Shannon et al., 2003) plugin to describe the functional properties of the gene lists in each case by identifying clusters of functionally related GO terms. To assess the functional similarity of the generated lists of significant GO terms we also calculated their semantic similarity using G-Sesame (Du et al., 2009). Annotations were as of 10 JUL 2012. Currently there are more than 139000 annotations assigned to Danio rerio genes out of which about 22% are non-IEA. In Fig. 1 we show the numbers of different and shared overrepresented GO terms in each case. In Suppl. Table 3 we report the five most significant GO terms for biological process, molecular function, and cellular component. Suppl. Table 4 has all the enriched GO terms in each case. Semantic similarity was found 0.714 between ALL vs. not-IEA for eyed-egg stage and 0.727 for hatch stage. Although many terms were found significant either in ALL or in non-IEA cases (Fig.1), very similar of even the same GO terms were in the list of five most significant ontologies (Suppl. Table 3). Also, the semantic similarity of the enriched GO terms was indicative of their high functional relatedness as values >0.7 are considered as high similarity (Du et al., 2009). Reference cited Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, et al. (2009) ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics, 25, 1091–1093. Du et al. (2009) gene similarity analysis and knowledge discover. Nucleic Acids Research, 37: W345-W349. Papakostas S, Vollestad LA, Primmer CR, Leder EH (2010) Proteomic profiling of early life stages of European grayling (Thymallus thymallus) Journal of Proteome Research 9, 4790-4800 Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al. (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Research 13:2498504 Fig. 1. The number of shared significant GO terms with and without IEA evidence codes in the gene lists of the eyed-egg and hatching stages. EYED-egg significant GO terms 99 42 ALL evidence codes 13 not IEA HATCH significant GO terms 104 ALL evidence codes 54 18 not IEA Suppl. Table 3: The five most significant GO terms for biological process, cellular component, and molecular function in the eyed-egg and hatching stage gene lists. In bold are terms in common in the top5 list in ALL vs. not-IEA analysis. EYED-EGG ALL EYED-EGG not-IEA Biological Process Translation Ribosomal small subunit biogenesis Translational elongation Cellular component biogenesis at cellular level Ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis Ribosomal small subunit biogenesis Ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis Cellular component biogenesis at cellular level Translation Ribosome biogenesis Cellular Component Ribosome Ribonucleoprotein complex Cytoplasm Intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle Cytoplasmic part Ribosome Small ribosomal subunit Ribosomal subunit Cytosolic ribosome Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit Molecular Function RNA binding Unfolded protein binding Translation factor activity, binding L-malate dehydrogenase activity rRNA binding nucleic acid Translation initiation factor activity Translation factor activity, nucleic binding RNA binding Actin binding Cytoskeletal protein binding HATCH ALL acid HATCH not-IEA Biological Process Translation Cellular protein metabolic process Protein metabolic process Cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process Translational elongation Ribosomal small subunit biogenesis Ribosome biogenesis Ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis Cellular component biogenesis at cellular level Regulation of cell cycle Cellular Component Ribosome Ribonucleoprotein complex Intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle Cytoplasm Cytoplasmic part Ribosome Small ribosomal subunit Ribosomal subunit Cytosolic ribosome Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit Molecular Function RNA binding rRNA binding Unfolded protein binding Translation factor activity, nucleic binding Translation elongation factor activity acid Translation initiation factor activity Translation factor activity, nucleic binding RNA binding - acid